Legal Authorities (Juries)
0.0 / 5
- Created by: lilbarc
- Created on: 22-09-15 12:58
Magna Carta (1215)
The first legal document to acknowledge a persons right to a trial by jury
1 of 30
Bushells Case (1670)
Establishes that juries are sole arbiters of fact, and couldn't be controlled or pressured by the judge in any way
2 of 30
R v McKenna (1960)
A more recent case that further demonsrates that judges cant challenge or influence jury decisions. Occurred after a judge threatmened that if a decision wasnt made in 10 minutes they would be locked up all night.
3 of 30
Juries Act 1974
Contains the majority of the present laws on juries. Particulary the power for a foreman to announce numbers both agreeing and disagreeing with the verdict (this is then ammended via R v Pigg)
4 of 30
s8 Contempt of Court Act (1981)
The act that makes discussing the case outside of the jury room a criminal offence
5 of 30
R v Pigg
Made it allowed that the foreman could read out only the number of people agreeing with the verdict, providing that number was a legal majority (11-1 or 10-12 for criminal cases with 12 jurors)
6 of 30
Administration of Justice Act 1933
Limited the right to use a jury in civil cases and they couldn't be used in breaches of contract
7 of 30
County Courts Act 1984 + Senior Courts 1981
Contains present laws for civil cases. Trial by jury is allowed in defamation, false imprisonment, malicious prosecution and fraud cases
8 of 30
Ward V James (1966)
The case that started laying down guidelines for personal injury cases. It states they shouldn't have a jury due to a difficult and complex assessment of ot only liability but of damages as well
9 of 30
Singh V London Underground (1990)
Further shows how courts have proved reluctant to allow juries in personal injury cases
10 of 30
H v Ministry of Defence (1991)
Further reinforces the Ward V James verdict
11 of 30
Coroners and Justice Act (2009)
Contains law of use of juries in the coroners court. Juries are used when their is suspicion that death was unnatural, violent, unknown, a police action/ommission or caused by notifiable accident (poison/disease)
12 of 30
Ther Criminal Justice Act (2003)
Sets out qualifications needed for jury service (what are they?), established excusals (what are they?) and allows judges, lawyers and police to be jurors
13 of 30
R v Abdroikof (2007)
Established that having a police officer on a jury doesn't neccessarily make an unfair trial. It is only unfair if they worked with anyone on the case. Is this the current UK law?
14 of 30
R v Sussex Justices ex Parte McCarthy (1924)
Case where the presence of a juror who was a crown prosecutor (an employee of the court) made for an unfair trial. The judge stated "justice must not only be done, but must also be seen to be done"
15 of 30
Hanif v UK (2012)
The European Court of Human Rights ruled that a police officer on a jury was a breach of article 6 of the echr. Is this the current UK law? Should it be? Why?
16 of 30
Article 6 of the ECHR
European Convention of Human Rights: "The right to a fair trial"
17 of 30
The Mental Health Act 1983
Describes people who are mentally disabled. Why does the Criminal Justice Act 2003 recieve criticism in relation to this?
18 of 30
Morris Commitee Report (1972)
Changed the law that in order to be on a jury you had to be an owner/tenant of a property.
19 of 30
The Criminal Justice Act 1972
Where jury qualifications were widened to include those who had the right to vote
20 of 30
s10 Juries Act 1974
lack of capacity is that someone doesnt understand english
21 of 30
s9 Juries Act 1974
lack of capacity is a disability that makes someone unable to be juror ie. deaf/blindness
22 of 30
s9(b) Juries Act 1974
Clarifies that if someone has a disability they aren't automatically disqualified, the judge decides at the court whether they can cope with juror responsibilities and give a fair trial
23 of 30
Brownlow (1980)
A case where the defendant sought to vet the jury but it was ruled as an invasion of privacy
24 of 30
R v Mason (1980)
Held that police could check juries because they need to check for disqalifications
25 of 30
s5 Juries act 1974
Holds the laws on challenging to the array
26 of 30
ABC Government Secrets Trial 1988
where deeper background checks of the jury were made to check political affiliations. (In this case two journalists and a solider were charged with collecting secret information).
27 of 30
Broderick (1970) and Ford (1989)
There are no grounds for challenging a jury panel which is imbalanced racially or not reflecting the overall racial composition of the area from which jurors are summoned
28 of 30
R v Wilson and R v Sprason (1995)
) the wife of a prison officer knew of the defendants through her husband but was not permitted to be excused so she sat on a jury who convicted two men of robbery. These convictions were later quashed because of her potential bias.
29 of 30
AG Guidlelines 1988
Make clear than a challenge to stand by should only be used rarely
30 of 30
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Establishes that juries are sole arbiters of fact, and couldn't be controlled or pressured by the judge in any way
Back
Bushells Case (1670)
Card 3
Front
A more recent case that further demonsrates that judges cant challenge or influence jury decisions. Occurred after a judge threatmened that if a decision wasnt made in 10 minutes they would be locked up all night.
Back

Card 4
Front
Contains the majority of the present laws on juries. Particulary the power for a foreman to announce numbers both agreeing and disagreeing with the verdict (this is then ammended via R v Pigg)
Back

Card 5
Front
The act that makes discussing the case outside of the jury room a criminal offence
Back
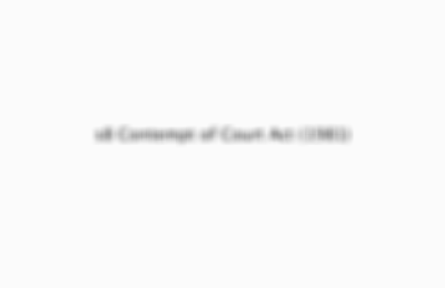
Related discussions on The Student Room
- AS Level Law paper 1 OCR »
- How important is having a duty slot as a criminal barrister »
- Court Usher Role »
- Students accused of rape at university bringing lawyers to hearings »
- Those who are convicted of Fare Evasion. »
- OCR A-level Law Paper 1 (H418/01) - 26th May 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- LNAT prep »
- Equality Act 2010 does not protect disabled students enough »
- Should you be able to call yourself a Barrister? »
- Trump ineligible to run for president in Colorado and Maine in 2024 Election »
Similar Law resources:
3.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
3.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Teacher recommended
Comments
No comments have yet been made