Organic: Carboxylic acid and esters
- Created by: Nabeela_Jabeen
- Created on: 22-10-17 17:55
c=0 =carbonyl group
Suffix= -oic R= Alkyl group OH- hydroxyl group Suffix-oate
Reactivity of COOH- depends on its polarisation.
Cδ+ = easily attacked by a nucleophile in a nucleophilic susbitution reaction. Oδ− atrrached to a proton/ +vly charged species and Hδ+ loses a proton, and compound act likes a (lewis) acid.
---> produces an weak acid that can still liberate c02 from carbonates. Weak acid- as they are partially ionised in solutions.
--> Dissociates into a strong acid.
Uses of COOH:
- Polymers -Food
- Addictives -Cosmetics
 Naturally occuring amino aicd has COOH
Naturally occuring amino aicd has COOH
Reactivity of COOH:
- Lose H+--> Act as an lewis acid- proton donor.
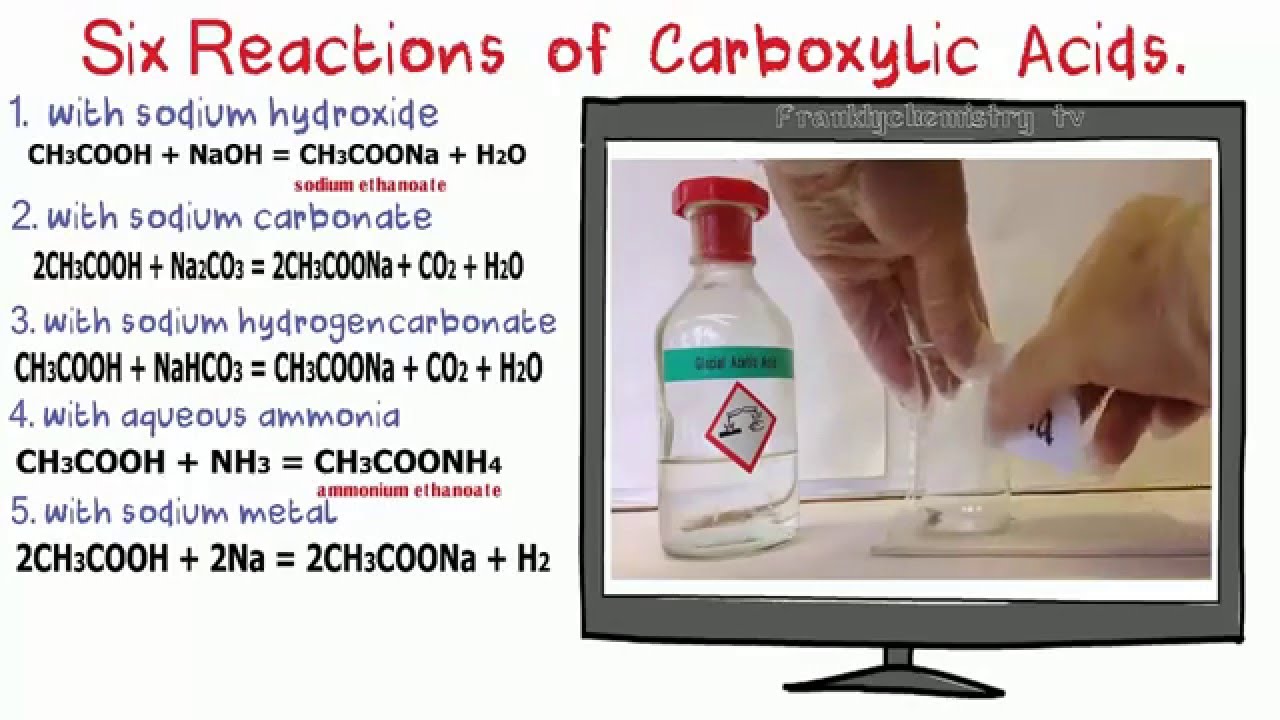
-Can React in a neutralisation reaction with reactive metals e.g metal oxides, metal carbonates and alkalis to form ionic salts --.> salts are known as carboxylates.
e.g ethanoic acid + (NaOH)/ (Na2C03) -- sodium carbonates --> produces sodium ethanoate +H20
Equation:
(CH3COONa= sodium ethanoate)
COOH- can react to form an ester and an amide
COOH + ALCOHOL--> ESTER | COOH + ACID CHLORIDE --> AMIDE.
- Those COOH with less than 6 carbon atoms are water soluble--> as the H20 molecules can Hydrogen bond, and have a higher mp than alkanes.

COOH- weak acid as it can partially ionise in solutions, but because there is an sufficent amount of hydrogen ions in COOH it can react with aqueous solution sodium carbonate to produce co2
Ethanoic acid- smells like vinegar
Butanoic acid- smells like rancid butter.
Loss of proton: - 1. hydrogen of OH- is lost and forms a carboxylate salt with a -ve charge.

Delocalisation of the Proton forms a more stable ion (stable) than that of the COOH- as it's a weak acid. However, it is stong enough to react with sodium hydrogencarbonate to give c02
Ester:
Suffix- oate
Nonmenclature;
1. Identify alkyl group attached to oxygen in in single bond (goes first)
2. Then identify chian that contains the carbonyl group
COOH + OH --> ESTER (use H+ (acid) catalyst)
Short chain ester- fairly volatile - fruit smelly in flavouring and perfumes, used in solvents and plasticiser.

Preparation of ester: esterification
- are acid derivatives
COOH+ OH ----> ester (use acid catalyst and heat) - reversible reaction- produces low yeild of ester- equilibrium shifts towards product side, when mixture is destilled with water, or excess OH used.
( concentrated strong H+ Catalyst either HCL , h2s04) n H20 eliminated

c-o bonds break in COOH rather…


Comments
No comments have yet been made