Year 10 mid term test
- Created by: K Kitten
- Created on: 09-02-22 20:58
Reactions of metal oxide
Keywords:
- Element - A substance made of only one type of atom.
- Compound - A substance made of two or more different atoms mixed together / chemically bonded.
metal oxides Formulas:
metal + oxygen metal + oxygen --> metal oxide
+ -2 Sodium + oxygen --> sodium oxide
Na1+ Iron + oxygen --> Iron oxide
Zn2+ Zinc + oxygen --> Zinc oxide
Finding metals:
- Metals are made from rocks called ores
- These are found in the ground and extracted by mining
- Unreactive metals like gold are found as the element
- Reactive metals like sodium are found as a compound
Metals and metal oxides
Metal oxide experiments:
Magnesium (Mg) - Outside of the flame turns bright white. The magnesium bends and then breaks, turning the flame yellow again.
Copper (Cu) - The metal glows over the flame and then turns black.
Iron (Fe) - ??
Equations:
Magnesium + oxygen --> magnesium oxide = mg + O2 --> MgO
Copper + oxygen --> copper oxide = Cu + O2 --> CuO
Iron + oxygen --> iron oxygen = Fe2O3
Reactivity Series
Potassium (K) Sodium (Na) Calcium (Ca) Magnesium (Mg) Aluminium (Al) Carbon (C) Zinc (Zn) Iron (Fe) Tin (Sn) Lead (Pb) Hydrogen (H) Copper (Cu) Silver (Ag) Gold (Au) Platinum (Pt)
Whether a metal can be extracted by reacting with Carbon or not is determined by its place in the reactive series. If the metal is higher than Carbon, it won't work. The metal has to be extracted by electrolysis. If the metal is lower than Carbon, the reaction will happen.
Redox and Smelting
'Native' Metals:
- Found as the pure metal in the ground for these, there is no need to extract the metals
- All other metals are found as ores and the metals need to be extracted (removed)
Extraction of metals:
Potassium Silver Gold Tin
Lead Sodium Iron Potassium
Copper Zinc Aluminum Magnesium
Key:
- No chemistry needed
- Extracted easily
- Need electrolysis to extract
PH Scale
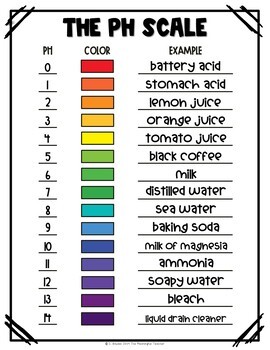
Tested with a universal indicator (UI)
- 0 to 2 is a strong acid, UI goes red
- 4 to 6 is a weak acid, UI goes yellow
- 7 is neutral, UI goes green
- 8 to 10 is a weak alkali, UI goes blue
- 12 to 14 is a strong alkali, UI goes purple
Electrolysis
If you get stressed in the exam remember to:
Positive
Anode
Negative
Is
Cathode


Comments
No comments have yet been made