Protein structure diagram 1
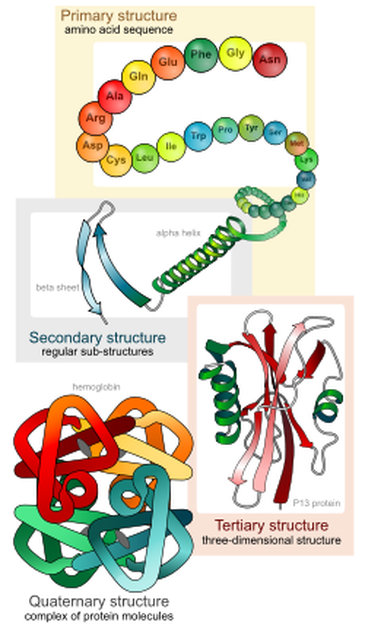
Primary structure: Amino acids join together in condensation reactions in a specific sequence. The peptide bonds form between amino acids resulting in a polypeptide.
Secondary structure: Amino acids which are 'close' to one another bond through weak hydrogen bonds, forming some common alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
Tertiary structure: Amino acids which are 'distant' bond together through hydrogen bonds, sulphur bonds and ionic bonds. This forms a unique 3D shape.
Quaternary structure: Here many polypeptide chains join together and some prosthetic groups may also add on. Prosthetic group are non-protein, and include the iron containing haem group in haemoglobin.
- Created by: Former Member
- Created on: 22-01-13 08:32
Similar Biology resources:
Teacher recommended


Comments
No comments have yet been made