Mussolini's foreign policy 1922-40
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
- Created by: Zaid_Saleemi
- Created on: 29-04-18 14:07
Mussolini's aims
'To make Italy great, respected and feared',Dominant power in Med,Expand empire in Africa,Balkans sphere of influence,Domestic/International prestige/support,Great power status,High military spending and colonial adventure
1 of 102
Mussolini's views on foreign policy
Did not have any clear foreign policy,Rejected anti-imperialist view - supported entry into WW1 - condemned peace treaty 'mutilated'
2 of 102
Mussolini's aims in the Ethiopian war of 1935
Enhance prestige-domestic/international(Hitler),Colonies-historical,African territories provide troops,Military glory on the cheap,Restore public confidence,Revenge Adowa 1896,Divert attention from domestic failings
3 of 102
Ethiopia
A large country uncolonised by Europeans - Eritrea and Somaliland provided convenient avenues of attack
4 of 102
Pretext for Ethiopian war 1935
Italy sponsored Ethiopia's membership of LoN 1923 and signed treaty of friendship in 1928,1929 plans to annex country-began to occupy borders,Conflict between soldiers left 30 Italians killed
5 of 102
What were the consequences of the skirmish that took place between Italian and Ethiopian soldiers that left 30 Italians dead?
Mussolini demanded an apology and hefty compensation - Ethiopian gov requested LoN investigation,A huge army together with civilian support totalling half a million transported to Africa,Italy left exposed in Europe - Stresa reassured him
6 of 102
Britain and France during the growing tensions between Italy and Ethiopia?
Too preoccupied with Germany and were not prepared to involve themselves
7 of 102
The war in Ethiopia 1935
Propaganda masked brutal conflict-Italians used mustard gas and aerial bombings,Some villages were gassed and all male inhabitants killed,Women *****
8 of 102
Were the Abyssinian prepared for the Italian war?
They were ill-equipped, disorganised and armed with antiquated weapons
9 of 102
How did Mussolini describe Ethiopia on the 4th Sep 1935?
Alleged Abyssinia was a barbarous uncivilised state
10 of 102
How did Mussolini describe Ethiopia in October 1935?
Abyssinian's 'warlike, aggressive spirit' imposed war on Italy - 400,000 Fascist troops mobilised
11 of 102
How long did it take for the two Italian armies to meet their objectives?
7 months but by May 1936 Mussolini had generated great popular support
12 of 102
What were Mussolini's orders to Italian soldiers?
10 Abyssinians to be killed for every Italian casualty
13 of 102
Italian troops during the Ethiopian war
Although Italian troops were used extensively, it was the Eritreans from Italy's first colony who bore the brunt of the fighting against the Abyssinians
14 of 102
Impact of Ethiopian war on relations with Britain and France
Public opinion in Britain and France was outraged, No arms were to be sold to Italy and member nations were to ban imports of Italian goods - little more than symbolic, Hoare-Laval Pact Dec 1935
15 of 102
Hoare-Laval Pact Dec 1935
An Anglo-French attempt to find a compromise peace, giving Mussolini most of Ethiopia - handed over the greater part of Ethiopia to Italy
16 of 102
Mussolini's perspective on Britain and France after the Hoare-Laval Pact Dec 1935
Thought they were decadent, interested only in money-making and a comfortable life.His Fascism was,in contrast, dynamic and contemptuous of material efforts.Hoped it might even replace 'Bourgeois democracy' as dominant force in Europe
17 of 102
Positive effects of the Ethiopian war
Great victory-Avenged Adowa,Consolidated territory,Sanctions rallied nation,Church praise,Mussolini at peak of popularity,Italy indisputably a Great Power
18 of 102
How did Gentile and many others argue that Italy was indisputably a Great Power after the Ethiopian war?
Proven military strength and a sizeable colonial empire and demanded to be considered equal to Britain and France
19 of 102
Negative effects of the Ethiopian war
Upset GBR/FR-Sanctions,Showed weakness of LoN-Encouraged Hitler,Allowed Hitler to re-militarise,Bred complacency in Mussolini,Drain on resources,Needed 250,000 occupying troops dependent on supplies 2000m away,Italian rule corrupt/repressive
20 of 102
Economic effects of the Ethiopian war
Drain on resources - Budget deficit rose from 2.5 billion to 16 billion lire, Settlement of 130,000 Italians in Abyssinia was costly,Oct 1936 Lira devalued by 40%,1939 only 2% trade with its colonies,
21 of 102
Italy's control over Ethiopia after the war
Repressive and corrupt, Only controlled a few areas, Had to fight a guerrilla war until Abyssinia was lost to the British in 1941, Fascist Italy gained a reputation for brutality
22 of 102
What led to the confrontation with Greece?
August 1923 - Italian general and four of his staff were assassinated in Greece - they had been advising on the precise location of the new Greek-Albanian border
23 of 102
What did Mussolini demand from Greece after the events of August 1923?
Blamed the Greek gov and demanded a full apology together with 50million Lire in compensation - Greeks refused - Mussolini ordered the bombardment and occupation of Corfu
24 of 102
Consequences of the confrontation between Greece and Italy
Challenged the LoN-GBR backed by Med fleet demanded Italy's withdrawal from Corfu,Mussolini received 50m lire but never a full apology,Hailed in Italy as a great success
25 of 102
What did the confrontation between Greece and Italy in 1923 show?
Mussolini might be able to bully smaller powers but was unable to stand up to the 'Great powers', He was aware of the necessity of good relations with Britain - Austin Chamberlain was an admirer
26 of 102
Italy in 1922
Had a secure position in Europe but unable to exert much influence,Threat to northern borders removed-friendship France and dismemberment of Austro-Hungarian Empire-Italy had no powerful enemies,A resurgent Italy would have to move quickly
27 of 102
Why would a resurgent Italy would have to move quickly with regard to it's foreign policy in 1922?
GBR/FR were the dominant powers of Europe - enforcers of peace treaties, their colonies dominated Africa and fleets controlled Med,France busy consolidating influence in Europe including the Balkans
28 of 102
1924 Pact of Rome
Mussolini received Fiume - long term target, Brought him diplomatic success/prestige,Duce's success persuaded him that Yugoslavia could be pushed around + resented French influence their
29 of 102
General Ahmed Zog
Italian sponsored chieftain who took power in Albania 1924
30 of 102
How did Mussolini use diplomacy to support Ahmed Zog in Albania 1924?
Supplied Zog with money and encouraged Italian companies to invest in Albanian economy and employed Italian officers as advisers to Albanian army - Treaty of Friendship 1926 - Albania little more than a Italian satellite state
31 of 102
What did Italy's involvement in Albania mean for Yugoslavia?
Italy was clearly a potential threat to Yugoslavia - Mussolini funded ethnic minorities (Croats) who wanted to break away from Yugoslavian state, Yugoslavia refused to be intimidated into subservience - Duce maintained aggressive posture
32 of 102
League of Nations
Signed Locarno treaties - confirmed permanence of Germany's western borders, and entered into the Kellog-Brian Pact of 1928 - outlawing war - agreement between Libya and Egypt borders
33 of 102
How did Mussolini benefit from the interests of GBR and FR?
Their main interests lay in Western Europe
34 of 102
Evidence that Mussolini used positive relations with Britain and France to boost his domestic and international prestige
1925 - raced across Lake Maggiare in a flotilla of speedboats to Locarno - Italian press coverage extensive - showed Mussolini as a crucial part of Locarno - he only attended one session and did not even read the final draft of the treaties
35 of 102
Mussolini's increasing foreign policy ambitions
Increasingly determined to revise peace settlement and make Italy 'Great,Respected and Feared'
36 of 102
Friendship treaty with Hungary
1927 - another revisionist state - funded right wing groups in Hungary and Germany among others
37 of 102
Evidence of Mussolini's increasing foreign policy ambitions
Funded right-wing groups in Europe,Trained German pilots in Italy-Breach of Versailles,Told parliament in 1927 air force 'large enough to blot out sun',Immediately dismissed Kellogg-Brian Pact 1928
38 of 102
Why did Mussolini increasingly adopt a more aggressive foreign policy?
Attempt to distract public attention away from domestic problems - Aims had always been expansionist and aggressive, Fascist foreign policy became increasingly belligerent-frustrated by limited gains of diplomacy in 1920s
39 of 102
How did Mussolini try to achieve his aim 'To make Italy great, respected and feared' through peaceful diplomacy?
Locarno Treaties 1925, Kellogg-Briand Pact 1928
40 of 102
How did Mussolini try to achieve his aim 'To make Italy great, respected and feared' through aggressive diplomacy?
Corfu, Albania, Yugoslavia, Rome-Berlin Axis - Pact of Steel, Anti-French territorial claims
41 of 102
How did Mussolini try to achieve his aim 'To make Italy great, respected and feared' through war?
Ethiopia, Second World War, Spain and Albania
42 of 102
'Mussolini's foreign policy aim to create an empire and dominance in the Mediterranean and Balkans was a success'
Annexation of Fiume (1924) and Albania (1926/1939)-Took advantage of weak Yugo-Pact of Rome-General Zog,Abyssinia/Hoare-Laval Pact-manoeuvring between GBR/FR/GR-Stresa/Four Power pact-position to challenge European status quo
43 of 102
'Mussolini's foreign policy aim to create an empire and dominance in the Mediterranean and Balkans was a failure'
Abyssinia/Spain isolated Mussolini from GBR/FR,GR alliance-Italian FP aims replaced by GR-from 1936 no longer centred on his aims,Facilitating GR-Rome/Berlin Axis/Anschluss/Czecho/Pact of Steel-Non belligerence
44 of 102
'Mussolini's foreign policy aim to boost his prestige at home was a success'
Up to 1935/6 was successful-Locarno,Fiume for nationalists,Abyssinia-mutilated victory,LoN sanctions to rally support for him in Italy
45 of 102
'Mussolini's foreign policy aim to boost his prestige at home was a failure'
By 1935/6 no longer in control-Anschluss damages domestic prestige-move towards an Italian-German alliance meant that opportunities to boost his prestige at home were scarce
46 of 102
'Mussolini's foreign policy aim to compliment/facilitate his domestic policy to fascistise society was a success'
Spanish civil war exports fascism/provides momentum at home,Abyssinia boosted regimes popularity-increase in ONB and Dopolavaro membership,Preparing for war-Strengthening gov control over heavy industries
47 of 102
'Mussolini's foreign policy aim to compliment/facilitate his domestic policy to fascistise society was a failure'
Expensive campaigns-Spanish civil war 8b lire and LoN sanctions,Living standards decline and poorer women had to work,Anti-Semitic laws-ruin relationship with church and question what it means to be Italian and general reluctance to accept laws
48 of 102
Hitler's impact on the success of Mussolini's foreign policy
Italy temp disposed towards GR and whatever Mussolini's territorial demands were impossible to concede,Hitler preferred Italy as an ally but did not take it seriously,Insensitivity towards Italian interests-Anshluss/Czecho,Ill prepared for WWII
49 of 102
Italy's entry into the Second World War?
June 1940-Mussolini declared war on Britain and France - Still favoured Germany, but was jealous of Nazi success and considered being a mediator at negotiating table,Appeared to Mussolini and world that Western allies on brink of defeat
50 of 102
If Germany won the war, what were the consequences to Italy if Mussolini remained neutral in the war?
Would be faced with a Europe dominated by Germany - Italy would have gained nothing, would lack Great Power status and would be under physical threat from its Nazi neighbour
51 of 102
If Germany won the war, what were the consequences if Mussolini committed Italy to the Axis?
Germany would be a friend and not a potential enemy - Italy would share Europe with Germany and Italians possibly having a free hand in the Mediterranean and Africa
52 of 102
When was the Corfu incident used by Mussolini to promote Italian power and prestige?
1923
53 of 102
When did Yugoslavia give up Fiume to Italy in the Pact of Rome?
1924
54 of 102
When did Mussolini pose as a major European statesman in the Locarno treaties?
1925
55 of 102
When did Italy increase it's influence over Albania through the Treaty of Friendship?
1926
56 of 102
When did Hitler come to power in Germany?
1933
57 of 102
When were Italy involved in the conflict over Austria?
1933-4
58 of 102
When did Italy invade Ethiopia?
1935
59 of 102
When were Italian troops sent to Spain to aid 'Fascists' in civil war?
September 1936
60 of 102
When was Mussolini drawn closer to Nazi Germany as a result of the Rome-Berlin Axis?
November 1936
61 of 102
When was the Italian invasion of Albania?
April 1939
62 of 102
When did the Pact of Steel commit Italy to Nazi Germany if there would be a future European conflict?
May 1939
63 of 102
When did Germany invade Poland and ultimately start the Second World War?
September 1939
64 of 102
When did Germany invade France?
May 1940
65 of 102
When did Italy join the Second World War on the Nazi side?
June 1940
66 of 102
How did the Stresa Front in 1935 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Improved, German: Worsened drastically
67 of 102
How did the war in Ethiopia in 1935 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Worsened drastically, German: Improved
68 of 102
How did the Rome-Berlin Axis in 1936 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Worsened drastically, German: Significantly improved
69 of 102
How did the Spanish Civil war in 1936 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Worsened, German: Improved
70 of 102
How did the Stresa Front in 1935 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Improved, German: Worsened
71 of 102
How did the Anschluss in 1938 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Improved slightly, German: Worsened significantly
72 of 102
How did the Munich conference in 1938 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Improved significantly, German: Improved slightly
73 of 102
How did the Invasion of Albania in 1939 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Worsened, German: Improved
74 of 102
How did the German seizure of Czechoslovakia in 1939 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: Remained bad, German: Worsened
75 of 102
How did the Pact of Steel in 1939 affect International relations?
Anglo-French: At the lowest point-very bad, German: At the highest point-very good
76 of 102
How did Mussolini take advantage of Germany?
Used a resurgent Germany to frighten GBR/FR into submitting to their demands,Funded right wing groups in Germany 1920s-Nazis
77 of 102
What did the rise of right-wing extremism in Germany show Mussolini?
That Fascism was spreading through Europe - however did not want to be overshadowed
78 of 102
Why was Mussolini worried about Nazi Germany?
Could overshadow him as dominant extreme right in Europe, Possibility of Germany taking over Austria-lose security of Northern borders - Italy might be pressures to hand back German-speaking areas gained in 1919
79 of 102
Anschluss
Annexation of Austria by Germany which had been prohibited by Versailles
80 of 102
Dollfuss
Austrian chancellor-looked for support-Visited Rome 3 times on 1933-Told to suppress Nazis in Austria and Italy would protect from Germany
81 of 102
What did Mussolini encourage Dollfuss to do in Feb 1934?
To set up a right-wing authoritarian regime modelled on Italian Fascism but anti-Nazi
82 of 102
When was Dollfuss assassinated by Nazis and what were the effects?
July 1934 - Mussolini sent troops to Austrian border to deter Anschluss - Mussolini called Hitler a 'horrible sexual degenerate'
83 of 102
How did Hitler breach Versailles in March 1935?
Luftwaffe + introduced military conscription to make an army 5 times the permitted size
84 of 102
Stresa Front 1935
Mussolini met with GBR/FR to prevent any further breaches of Versailles by German threat, Gave him protection against Anschluss
85 of 102
Why were GBR/FR eager to meet Mussolini's demands in the Stresa Front of 1935?
Western powers were anxious to avoid Germany allying with Italy - Mussolini saw this as an ideal opportunity to expand his colonial empire at minimal risk
86 of 102
Rome-Berlin Axis 1936
Hitler agreed not to carry out Anschluss,Mussolini dropped objection of Nazi interference in Austria,Public declaration of friendship,Italy rearming-did not commit to European war-was prepared to risk in pursuit of his FP goals
87 of 102
How was the Rome-Berlin Axis of 1936 a public declaration of friendship?
Italy would direct its expansionist policies to the Med while Germany looked towards eastern Europe and the Baltic
88 of 102
Spanish Civil War 1936
German/Italian forces on same side,Supported Spanish conservatives to overthrow elected Republican gov,No quick victory and no public enthusiasm-only withdrew in 1939
89 of 102
What motivated Italy's involvement in the Spanish Civil War of 1936?
Angry at French reaction and fearful French gov would supply weapons to anti-Fascist forces in Spain
90 of 102
How many Italian troops were involved in the Spanish Civil War of 1936?
40,000
91 of 102
Costs of the Spanish Civil War 1936
No quick victory and no public enthusiasm,Anti-Republican Spanish took brunt of fighting, 4000 Italian lives, Over 8 billion lire in expenditure, Worsened relations with GBR/FR
92 of 102
Anti-Comintern Pact
Nov 1937 - Italy joined Germany and Japan to work against soviet Russia
93 of 102
When did Hitler carry out Anschluss without consulting with Mussolini?
March 1938
94 of 102
Evidence that the Duce's admiration for German dynamism only increase
Signed agreement guaranteeing status quo in Med,Sep 1938 Hitler's demands over Sudetenland likely to lead to Eu war,In Munich Mussolini secretly colluded with Hitler-Sudetenland handed over to Germany
95 of 102
Mussolini's territorial demands in 1938-9
Instructed parliament to annex Nice,Corsica and Tunis from France - made it clear he was prepared for confrontation with GBR/FR - Confirmed their weaknesses
96 of 102
When did German troops march into Czechoslovakia and how did the effect Mussolini?
March 1939 - Real fear of Germany was now added to grudging admiration for its successes
97 of 102
Invasion of Albania April 1939
Put the Duce back in the limelight,Albania had been a satellite for over 10 years,Victory won without any major fighting,A propaganda victory against the inferior state
98 of 102
Italian Non-Belligerence
Mussolini realised Italy not ready for war and that it would be unpopular and would not be fought for Italian interests,Duce declared his ally had been 'treacherous' and had thereby made the Pact defunct - Italy would not join the war
99 of 102
What motivated Mussolini to sign the Pact of Steel in 1939?
Mussolini angry that Albania caused GBR/FR to give military assistance to Greece/Turkey
100 of 102
Pact of Steel
Signed in May 1939-committed GR/IT to join the other in war even if the other caused it
101 of 102
What were Mussolini's demands in the Pact of Steel in 1939?
Although there was no doubt about Italy's willingness to go to war, any war should be postponed for at least three years to allow it to rearm fully - Hitler ignored this appeal and did not even bother to reply
102 of 102
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Did not have any clear foreign policy,Rejected anti-imperialist view - supported entry into WW1 - condemned peace treaty 'mutilated'
Back
Mussolini's views on foreign policy
Card 3
Front
Enhance prestige-domestic/international(Hitler),Colonies-historical,African territories provide troops,Military glory on the cheap,Restore public confidence,Revenge Adowa 1896,Divert attention from domestic failings
Back

Card 4
Front
A large country uncolonised by Europeans - Eritrea and Somaliland provided convenient avenues of attack
Back

Card 5
Front
Italy sponsored Ethiopia's membership of LoN 1923 and signed treaty of friendship in 1928,1929 plans to annex country-began to occupy borders,Conflict between soldiers left 30 Italians killed
Back
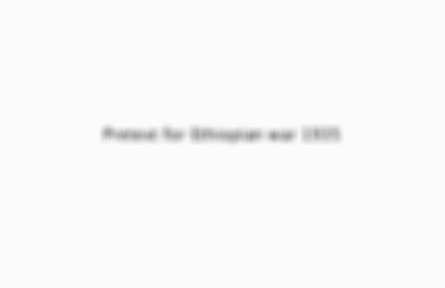
Similar History resources:
2.0 / 5 based on 5 ratings
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Teacher recommended


Comments
No comments have yet been made