Chemistry Core (Unit 1)
4.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
- Science
- AtomsChemical reactionsCalcium carbonateMetalsAlloysCrude oil and fuelAcids and alkalisPolymersPlants and vegetable oilsThe EarthHydrocarbons
- GCSE
- AQA
- Created by: yumna15
- Created on: 22-12-16 15:27
What electrical charge does a proton have?
Protons have a positive Charge - +1
1 of 43
What electrical charge does a electron have?
Electrons have a negative charge - -1
2 of 43
What electrical charge does a neutron have?
Neutrons have a neutral charge - 0
3 of 43
Where is the Mass number and Atomic number found?
The Mass number is the top number and the Atomic number is the bottom number.
4 of 43
What do you get from Ionic Bonding?
Metal atoms lose electrons to form positively charged ions, Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged ions.
5 of 43
What is Thermal Decomposition?
Calcium carbonate breaks down when heated strongly. This reaction is called thermal decomposition.
6 of 43
What is the equation for Thermal Decomposition?
Calcium Carbonate --- Calcium Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
7 of 43
How is Limestone broken down?
Limestone is broken down by the use of Thermal Decomposition.
8 of 43
What are Limestones Uses?
Building Blocks - Quarried and cut to shape. Cement - Heat limestone with clay. Mortar - Mix cement with sand and water Concrete - Mix mortar with small stones (aggregate).
9 of 43
What are Limestones advantages?
Limestone Buildings are good to look at. They are cheap. Easily shaped. Increase of jobs.
10 of 43
What are Limestones disadvantages?
Ugly looking. Loss of wildlife habitat due to quarrying. Lorries are dirty. Blasting is noisy. Produce masses of pollution,
11 of 43
How is Cement made?
Powdered limestone is HEATED in a kiln with POWDERED CLAY to make CEMENT.
12 of 43
How is Mortar made?
Cement can be mixed with SAND and WATER to make mortar.
13 of 43
How is metal extracted by the use of Bioleaching?
Bioleaching, bacteria is used to separate copper from copper sulfide. The bacteria gets energy from the bond between copper ad sulphur, separating out the COPPER from the ore in the process.
14 of 43
How is metal extracted by the use of Phytomining?
Phytomining, Some plants absorb copper compounds through their roots. They concentrate these compounds as a result of this. The plants can be burned to produce an ash that contains the copper compounds.
15 of 43
How is Copper extracted?
Copper can be extracted from these ores by heating them in a furnace, a process called smelting. The copper is then purified using a process called electrolysis. Electricity is passed through solutions containing copper compounds, such as copper sulf
16 of 43
What are Alloys?
Different sizes of metals are mixed together to make Alloys. They are transfixed metals, good conductors of electricity.
17 of 43
What is Crude Oil?
Crude oil is a mixture of compounds called hydrocarbons. It can be separated into different fractions using fractional distillation, and some of these can be used as fuels.
18 of 43
How is Crude Oil seperated?
Crude Oil is separated by the use of Fractional Distillation.
19 of 43
What is the sequence of Fractional Distillation?
A tall condenser is fitted above the mixture, coming off at different heights, the column is hot at the bottom and cool and the top. Substances with high boiling points condense at the bottom and with low boiling points condense at the top.
20 of 43
What is Complete Combustion?
Complete Combustion needs a lot of Oxygen to be able to react.
21 of 43
What is Incomplete Conbustion?
Incomplete Combustion is when the supply of air is poor. Carbon Monoxide is then produced.
22 of 43
What are the harmful Emissions from Burning Fuels?
Sulphur Dioxide cases ACID RAIN - Carbon Dioxide causes GLOBAL WARMING - Solid Particles cause GLOBAL DIMMING.
23 of 43
What is Cracking?
Cracking, allows the large molecules to break down into smaller more useful carbons.
24 of 43
How is Cracking taken place?
The large hydrocarbons are heated to be VAPORISED, then are passed over a hot Catalyst to break the chemical bonds in the moelcule, this is called Thermal Decomposition.
25 of 43
What are Alkenes?
CnH2n, the number of hydrogen atoms in an alkene is double the number of carbon atoms.
26 of 43
What are Alkanes?
They have a single bond. Methane CH4, Ethane C2H6, Propane C3H8, Butane C4H10
27 of 43
What are Polymers?
Polymers are very large molecules made when many smaller molecules join together, end-to-end.
28 of 43
What are Monomers?
The smaller molecules are called monomers.
29 of 43
What are the uses of Polymer?
Polythene is used for plastic bags and bottles, Polypropene uses for crates and ropes, Polychloroethene is used for water pipes and insulation on electricity cables.
30 of 43
What is Ethanol?
Ethanol is used for alcohol and useful fuels, it is a cleaner fuel to use because it burns to produce water and Carbon Dioxide only. No particulates or sulphur dioxide is produced.
31 of 43
What is Fermentation?
Ethanol is also produced by Fermentation with yeast. This is used by a renewable plant material.
32 of 43
What are Saturated Fatty Acids?
Saturated Fatty Acids have a single bond.
33 of 43
What are Unsaturated Fatty Acids?
Unsaturated Fatty Acids have a double bond.
34 of 43
What is a Emulsion?
A Emulsion is special mixture of oil and water that are thicker than oil and water like mayonnaise. Emulsions provide better texture, coating ability and appearance.
35 of 43
What are Emulsifiers?
Emulsifiers stop the oil and water mixture from separating. In mayonnaise the egg yolk is the Emulsifier. The egg yolk makes the emulsions, oil and water, stick together.
36 of 43
How does a Emulsifier work?
An Emulsifier molecule contains a hydrophilic 'head' and a hydrophobic 'tail'. The head is attracted to the water, whereas the tail is attracted to the oil and repels against water.
37 of 43
What are carbon-carbon double bonds?
A carbon-carbon double bond is in unsaturated vegetable oil. This is detected by Bromine Water, the water becomes colourless with an unsaturated oil, but it stays in a orange-brown colour if saturated.
38 of 43
What is hydrogenation?
The hydrogenation oils have higher melting points so they are solids at room temperatures, making them useful. They are part of the double carbon bond.
39 of 43
What is the Crust, Mantle and Core?
CRUST - Thin and Rocky (1st layer) - Mantle - Properties of a solid, can flow very slow( layer 2) - Core - Liquid Nickel and Iron ( outer and inner core )
40 of 43
What are Plate Tectonics?
The Earths crust and the upper layer of the mantle are broken into large pieces this is called Tectonic Plates.
41 of 43
Why do the Tectonic Plates move?
They move due to the convection currents in the Earths Mantle. These are driven by the heat produced by the natural decay of radioactive elements in the Earth.
42 of 43
What is the Cause of Earth Quakes?
Where tectonic plates meet, the Earth's crust becomes unstable as the plates push against each other,Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen at the boundaries between plates, and the crust may ‘crumple’ to form mountain ranges.
43 of 43
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What electrical charge does a electron have?
Back
Electrons have a negative charge - -1
Card 3
Front
What electrical charge does a neutron have?
Back
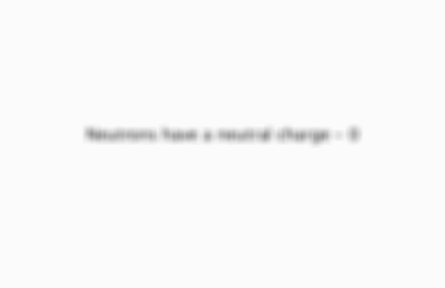
Card 4
Front
Where is the Mass number and Atomic number found?
Back

Card 5
Front
What do you get from Ionic Bonding?
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- AQA Chem Unit 1 May 22nd 2015 *OFFICIAL THREAD* »
- PAG 1.2 chemistry A-Level OCR A »
- AS/A Level Chemistry Study Group 2023/2024 »
- Moles in A-Level Chemistry »
- Physics homework help »
- GYG - GCSEs in a month »
- Specific Charge »
- A Level Chemistry Moles (OCR) »
- Atoms, molecules etc a level chem »
- A level chemistry question help. »
Similar Science resources:
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
2.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made