Ozone Summary Notes
- Created by: BethRB1312
- Created on: 14-03-17 17:38
Dipoles
Dipole: Two opposite charges separated by a (short) distance.
The bonds are types of intermolecular bonds (bonds between molecules. Ex: H -- Cl)
Types:
- Instantaneous dipole-induced dipole (1)
- Permanent dipole - induced dipole (2)
- Permanent dipole - permanent dipole (3)
1.When two neighboring molecules do not have a permanent dipole, they are attracted. These constantly break and reform - constant change in electron distribution.
2. The charge of the permanent dipole causes a temporary change in the neighboring molecule
3. If both molecules have a permanent dipole, there is an electrostatic attraction between the charges of the dipoles.
hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
How these bonds arise:
- Electrons in a molecule are in continuous random motion, and may be distributed unevenly (creating an instantaneous dipole)
- Dipole can induce another dipole (permanent-induced or instantaneous-induced)
- Electrostatic attraction between both dipoles
Factors:
- Electrons in the molecule. the higher the no. of e-, the more chance of instantaneous dipole
- Less distance between molecule = greater electrostatic attraction
jjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
Hydrogen Bonding:
- The strongest type of intermolecular bond
- H atoms are represented as multiple lines between molecules (see O-H bond)
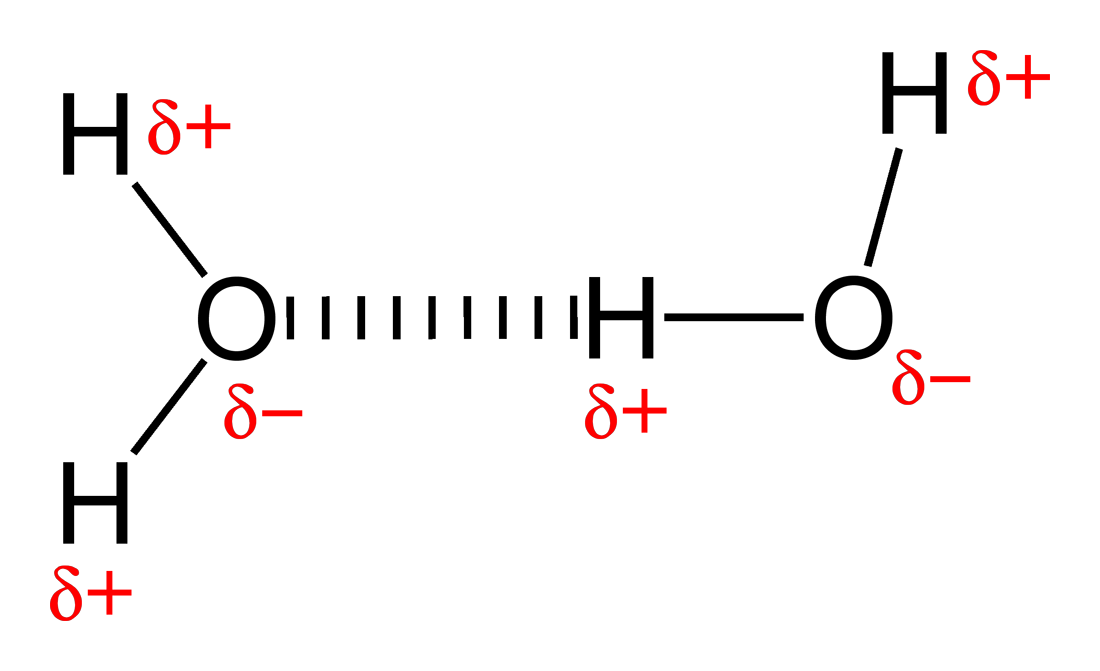
- A d+ H atom in one molecule and a small electronegative atom (O,N or F). There is a lone pair on the electronegative atom
- The lone pair points directly at the d+ H atom.
- There is a linear structure so the bond angle = 180 degrees.
- Liquid Water:
- Contain O atom with 2 lone pairs and 2 d+ H atoms attached.
- Has a higher boiling point than other molecules of similar Mr values.
- Ice (as 2 H2O molecules are shown above):
- H bonds are formed when water freezes.
- Tetrahedral shape
- Arrangement around the O atom gives ice an open structure
- Low density, hence it floats on water
hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
Haloalkanes
- Boiling…


Comments
No comments have yet been made