Superpowers
5.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
- Created by: helentaylor
- Created on: 23-04-18 13:51
Why is USA seen as a 'Superpower'?
- USA's GDP per capita = $53,000 whereas China's is only $6,000- shows high gini-coefficient and shows that the USA potentially has far higher levels of social development
- 80% of global financial transactions are done in US dollars as well as 87% of foreign market currency transactions are in dollars
- USA's military spending is 4-5x that of China, accounting for 37% of global military spending
- USA is the most favoured destination of migration- 45 million people who live in the USA were born in a foreign country - 4x that of the next highest country
- USA hands out the most financial aid in the world
- 16/20 of the top world universities are in the USA
1 of 28
The importance of culture for global significance
UK
- 'Cultural Hegemony' as a form of soft-power
- HISTORY
- Families send their children to be educated in Britain, especially in areas such as London, Oxford and Cambridge
- Cultural relationships formed through the old empire
- Many legal systems based on Britain's system
- Financial influence of the London Financial District
- CULTURE
- BBC, musical legacy, literature
- English is the 2nd most spoken language
- 2012 Olympics
- Invented internet- intellectual additions to society
- Knowledge management exporter e.g. finance- international consultancy firms- PriceWaterHouseCoopers
- DIPLOMACY
- One of the largest networks of embassies
- UK diplomats highly respected
2 of 28
America's Hard Power
- MILITARY
- Confronted the Taliban and brought about the death of Osama Bin Laden
- Responded to Kuwait's request for military help in the Gulf War following the invasion by Iraq and subsequently removed Saddam Hussein from power in 2003
- The Afghanistan War was propmted by the 2001 terrorist attack on the World Trade Centre by Al-Qaeda
- ECONOMIC
- Although USA and Chinese GDP totals are similar, 2015 GDP per capita was 4x that of China
- USA remains the largest trading partner for many countries, exporting high value goods e.g. military aircraft and global brands such as Apple
- The USA has dominance in innovation and intellectual property such as patents, the WTO, WB and IMF are vital tools for spreading Western influence
- Although hard power is neccessary for establishing dominance, the consequences of US and British operations in the Middle East have damaged the reputations of both countries, and both have become increasingly reliant on soft power to maintain dominance
3 of 28
Link
GetRevising notes for the topic that are good
https://getrevising.co.uk/resources/superpowers-complete-notes-edexcel-a2
4 of 28
MacKinder's Geographical Pivot Theory (Heartland T
- Believed that the world was divided into 3 sections
- The World Island- Europe, Asia and Africa- the largest and most wealthy combination of continents
- Offshore islands- British Isles and Japan
- Outlying islands- North and South America as well as Australia
- At the centre of the heartland is the heartland - MacKinder described this as the Pivot Area becuase it contained 50% of the world's resources
- Controlling this area means controlling the rest of the World Island, and consequently, the rest of the world
- When MacKinder was writing his work, the heartland was Russia but could be invaded by Germany or Japan and an alliance
- Previous invasions had not succeeded as land transport technology was not good enough and therefore conflict inland could not be sustained e.g. Napoleon's ill-fated invasion of Russia in 1812 which failed due to a lack of resources and reinforcements as well as the Russian winter
- Britain's naval forces could control the coastal waters but MacKinder wanted to ensure that technology would allow for inland conflict
5 of 28
Colonial Control
Britain:
- At its height, the British empire extended over about 1/4 of the world's land area and ruled 1/5 of the population
- Early colonial actions included settlements in Ireland, the Carribean and North America
- Unlike other European countries, Britain established trading companies to finance voyages to search for valuable commodities such as spices from the East Indies and India
- These raw materials were brought back to British cities such as Liverpool, Bristol, Hull and London which drove the Industrial Revolution
- 1875- Britain bought the laegest sharehold in the Suez Canal and subsequently occupied Egypt- the empire grew to Australia, India, large expanses of Africa and Britain became, largely, an unchallenged superpower
- British cultures spread round the qorld- e.g. cricket in India is still popular today
- The Empire worked by direct colonial control + they controlled the 'All-Red-Line' which was a connection cable under the Atlantic Ocean to America
- WW1 showed a challenge to Britain's power
- WW2 meant that Britain emerged nearly bankrupt and was facing anti-colonialism
- One consequence of dismantling European Empires was that the colonial boundaries did not consider cultural frictions and these boundaries became the new borders of new countries e.g. Palestine was split into Israel and Palestine and India was separated from Pakistan and Bangladesh
6 of 28
Post-War Indirect Control
- Militarily:
- Independence was not an easy process for some countries and in some cases, the independence was followed by civil unrest and war
- e.g. Mau Mau uprising in Kenya
- e.g. IRA
- e.g. Guerilla war in Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe)
- Britain and the USA for examples will exercise influence in many countries such as Sierra Leone, the Falkland Islands etc
- Politically:
- During the Cold War, the USA tried to stop the spread of communism through the Marshall Plan which provided aid to countries who were at risk of becoming communist
- Economically:
- IMF and WB set up to provide aid to developing countries in the form of 'structual adjustment programmes' to ensure that governments reformed their countries into pro-Western democracies
- Culturally:
- British sports have spread, western music, arts- there are many TNC's acting globally
7 of 28
Geopolitical Stability and Risk
- The global pattern has changed from unipolar to bipolar - the 21st century is predicted to become unipolar
- Somalia and Somaliland
- Somaliland - British
- Somalia- Italy
- Somaliland declared independence in 1960+ united with Somalia to form the Somali Republic
- 1969- army leader Barre- civil war with Somaliland (Barre supported by Russia)
- US troops deployed in the area +Russia constructed runway
- Resistance to Barre= civil war in 1991 and collapse of the government
- Somaliland declared independence in 1991
- Somalia= failed state while Somaliland = relatively stable autonomous region in Somalia
- Many Somali's fled to Europe - France and Britain- Somalia relied on money from those escaping through the hawala islamic finance system
- Anger has been created through neo-colonialism and the borders which ignore ethnic boundaries 'scramble for Africa'
- 2009 S.Arabia lifted livestock ban on Somaliland- imports
- Tensions between the rich diaspora returning aswell as terror groups e.g. Al Shabaab
8 of 28
The Influence of the Emerging Powers- BRICs +G20
- July 2014- BRICs announced they would create two new financial institutions in order to increase their influence around the world
- The New Development Bank will compete with the IMF to finance infrastructure and other development projects with a budget of $50 billion
- As a rival to the WB, $100 billion will be made available through the 'Contingent Reverse Arrangement
9 of 28
Modernisation Theory Evidence
- Developed by Walter Rostow in the 1960s -'take off'
- CHINA
- 1. Traditional Society- pre-industrial revolution- society was based on subsistence farming, fishing and mining etc.. relied on traditional ideas of collecting and making your own food
- 2.Conditions for pre-take off- implementation of rail/ roads etc.. China later to do this than Europe - geog location? Potential of China realised 35 years ago which led to FDI, implementation of industry - Apple in China - increased their infrastructure- TURKEY- large population + politically important (strategically)
- 3.Take off- SEZ's and industrial cities e.g. Chongqing increased industry and capita, Yangtze River Canal for transport ease, Three Gorges Dam- HEP and transport, FDI in form of energy companies
- Culture changes in China as it developed- change of economy to mixed economy away from communism - but not fully e.g. the Great Firewall of China
- 4. Drive to maturity- spread of economic growth - China currently profits from manufacturing - in 12th year plan there is an idea to move towards biotechnology and environmental maintenence, new cities to be created to spread the wealth- Xiongan- will create further urbanisation
10 of 28
Modernisation Cont
- 5. High Mass Consumption- starting to establish this - large consumer markets, westernised society, China is beginning to invest FDI in other countries such as Africa 'scramble for Africa'
- China has invested $4.2 billion in Kenyan railway- is creating new markets to allow the continued growth of its own economy
11 of 28
Dependency Theory
- Andre Frank 1971
- Believed that TNC investment in developing countries led to the exploitation of skilled workers, cheap raw resources and created international debt
- 'Development of underdevelopment'
- USA's influence over WTO and IMF may have allowed this to ocur- new creation of BRIC's development bank may stop this
- E.g the African states and China
- Replaces colonialism with neo-colonialism
- China is Africa's biggest trading partner as Chinese Direct Investment in Africa has risen from 0.6% per annum in 1990s to 2.8% in 2000s- rapid
- 200 Chinese companies invested in 49/54 of the African countries
- $4.2 billion rail line from Dibjouti to Addis Ababa - employs 20,000 and can be seen as increase in social development e.g. training of women to drive trains
- Is the debt too much though? Debt of Kenya = 50% of Kenya's output - sustainable?
- China plans to reach the line further - also notable that China invested on the East side first- close to China for trade
- Capitalist motives
12 of 28
World Systems Theory Evidence
- Immanuel Wallerstein 1974- looks at change from a wider spacial and temporal perspective
- More social approach
- Examines the core exploiting the periphery on a global scale
- Looks at link between geographical locations and development
- World economy moves in Kondratiev waves e.g. technology
- Turkey
- Traditional view of development would say it is in prime location for development - MINT country, could be open to exploitation due to semi-peripheral location and rich quantities of resources, large popualtion- could be helped or hindered by the migrant crisis
- Used as a political buffer to the migrant crisis and issues with terrorism in the Middle East- European countries give aid- is it selfish aid?
- Mexico
- Semi-periphery to America - trading partner
- At risk due to protectionism under Trump - vulnrable as the USA is their biggest trading partner
13 of 28
Impacts of superpowers on the global economy, poli
- Cote d'Ivoire, West Africa
- IMF didn't allow the Ivory Coast to recieve aid until 2013 when its government agreed to set up commercial courts and allow free presidential elections
- After economic reforms, US$4.4 billion of debt was cancelled but a further $10 billion of debt depended on reform of the country's electricity sector to allow companies to react to changes in world energy prices
- Investment in education and training has depended on the government creating more competitive banking sector
- UN still bans diamond exports from country after the country used them to finance civil war in 2005
- After minimum wages agreements and investment in road infrastructure was achieved in 2011, the country was allowed to export cocoa again
JUBILEE DEBT RELIEF
- Programmes established between 2000 and 2010 which require countries to stay on track to continue with debt cancellation
14 of 28
The cultural impact of Apple
- Development of Apple products has transformed how people work, listen to music and socialise
- In 2015, Apple was largest company in USA worth $274 billion which was 2x the second largest company
- It has invested into similar industries such as digital music which has created an industry worth $6.85 billion
- By 2015, Apple had sold more then 1 billion IOS devices
- The culture has been extremely popular in China
- Apple has become a status symbol
15 of 28
International Decision Making
- NATO -North American Treaty Organisation
- ANZUS -Australia and New Zealand
- EU
- UN
- NAFTA
- ASEAN- many ASEAN countries have experienced huge growth on their own and with their young populations their political will to work together hasnt been particularly strong
- IPCC
- These organisations aid international decision making while prioritising certain countries or standpoints e.g. IPCC with climate change and the environment
16 of 28
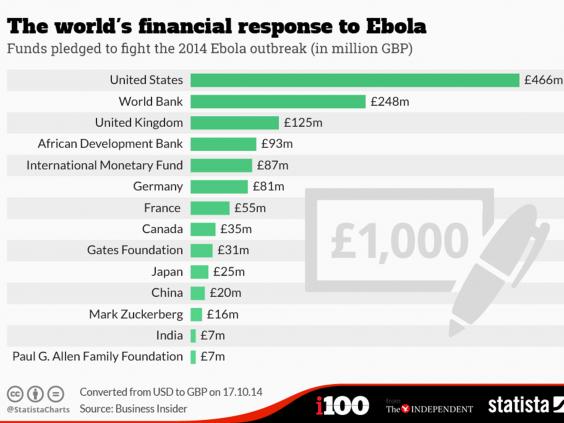
Crisis Response
- Britain donated $1.5 billion to the 2015/16 humanitarian crisis in Syria by improving the aid in source countries to stop the migrants moving further into the EU
- EBOLA
17 of 28
The role of NATO
- Successful geostrategy requires countries to work together both militarilty and economically
- France, UK + USA were the founding members in 1949- committed to aiding member countries from any threats
- It expanded with many Eastern European countries joining after the fall of the USSR
- In 2016 NATO was operating in Turkey to install Patriot Missile Systems to defend against factions in Syria
- In Afghanistan NATO trained Afghan security forces to combat terrorists
- I n 2014, after Russia's invasion of Ukraine, NATO became a world player again as some Western Asian countries requested membership
18 of 28
Environmental Concerns/Degredation
- 2010 -BP's Deepwater Horizon drilling rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico
- 450 million litres escaped polluting the sea and nearby coastline
- Chemicals in the spraying dispersant used to reduce the oil slick damaged other marine life and wildlife along the coast near the Mississippi Delta
- Removal of forests- Brazil
- Brazil's food production increased 26% between 2002 and 2012 turning it from the largest importer to largest exporter
- Forest has been cleared to be converted to cropland and pasture e.g. soya and cattle feed
- Beef exports have been increased 10x and is the second largest exporter
- But beef production needs extensive resources + agriculture causes 8-18% of global greenhouse emissions especially when forests are removed for the cause
- In the 1990's, Brazil deforested an area of forest the size of Belgium but rates have fallen 70% in recent years
19 of 28
Willingness to act
- The USA and China agreed in 2014 to reduce CO2 emissions
- Superpowers and emerging countries are often reluctant to change their technologies through fear of their economy being weakened
- CHINA- post 2008 has shown the environmental degredation of China- heavy investment in solar pannels and some of the biggest clean energy firms are now Chinese
- EU- subsidies to allow more environmentally friednly farming
- RUSSIA- reducing greenhouse emissions through nanotechnology, energy efficiency laws + mandatory changes
- USA- politics have affected greenhouse emission controls with the right vs left wing parties - TRMP influence
20 of 28
Food supply
- Green Revolution in India caused soil degredation and chemical runoff due to excess fertlisers which resulted in euthrophication
- Rice consumption has increased by 50% in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Rising middle class in China and meat consmuption- unsustainable due to the environmental implications of the changing desire of luxury lifestyles in emerging countries and superpowers
- China eats around 28% of the world's meat – including half its pork – according to the OECD and FAO. In total in 2014, the Chinese served up over 86,000 tonnes of meat. The new guidelines hope to see the level of per capita consumption reduced from the nearly 50kg consumed in 2014
21 of 28
Territorial Disputes-Artic Oil
- Receeding polar ice is allowing more possiblity to access the oil reserves in the Artic Ocean but it has started to question the sovereignity of the area
- Currenly it would cost $37 to extract a barrel of oil in the Artic vs $2 in Saudi Arabia but as oil reserves reduce it may make it economically feesable
- UNCLOS - UN law of the sea says that you can economically exploit an area in the sea up to 200 miles beyond your coastline
- Russia has claimed nearly half of the Artic but Canada, USA and Norway don't see their claim as legitimate - this has raised geopolitical tensions
- Threatens natural environment
- OPEC decided to keep its prices low which threatened the development of countries e.g. Nigeria who were trying to become front runners in theoil industry
22 of 28
South China Sea Disputes
- Japan and China in dispute over 8 islands which are currently administered by Japan
- Sovereignity is critical to each countries as the surrounding seas are rich fishing grounds and the extensive gas and oil reserves under the seabed
- Islands transferred to US in 1972 but evidence since 1600s justifies Chinese ownership
- Chinese fishing trawler rammed by Japan in 2010 and arrested them- Japanese activists staged protest- angry reaction from Bejing
- China has established small military presence on Spratly Islands but are disputed territory
- One of world's busiest shipping routes (30% of world trade passes through)
- China has dredged area to create reefs and an airstrip
- 2016, China launched batteries for surface to air missiles -possible response to US navy actions in the area
- USA committed to protecting Japan and Phillippines
23 of 28
Tensions- Western Russia and Eastern Europe
- Tensions between Russia and other former communist states have been growing since the Accession 8 countries joined the EU in 2004
- Putin wants Russia to reassert its former glory and power
- Has control of Gazprom - they raised prices and cut Ukraine off during the winter
- When Georgia wanted to join NATO in 2010 but Russia argued ethnicity to stop it
- Meant that Russia could control more territory
24 of 28
Mozambique's resource boom
- Coal, oil and gas are abundnt - its reserves could make it the world's 4th largest gas producer
- 17 year civil war ended in 1993, but country only uses small amount of gas as it cannot afford the enormous capial investment required to extract and distribute the gas
- Has growth rate of 6.9% (similar to China and India's) with the IMF predicting that the GDP will rise to $59.2 billion in 2020
- Prospect of resource boom has led to rising tension between gov and opposition groups over who is allocated the contracts
- It was dropped from being a list of electoral democracies in 2010
- International concerns have focused on land grabs, forced relocations, poor working conditions, bribery and the unwillingness of mining companies to stick to promises to build infrastructures for the workers
- The WB is putting pressure on the investors to help social development but TNC's are frustrated over the complicated tax + concession arrangements with many waiting 3 years to start drilling
- Neo-colonialism?- Portugal- its ex-colony has started to return + Brazil and Australia, UAE + China has built a SEZ in Beira and is developing rail line on one of the main trading routes - this has brought other economic activity e.g. tourism, airports
25 of 28
The changing centre of gravity - India + its growi
- 3rd largest national market
- 7.5% growth rate which is higher than China's
- Population of 1.2 billion- democratic country- makes it easier to hold political leaders responsible for crimes such as corruption
- Many parts of the economy have been privatised by Prime Minister Singh
- High economic growth has meant that it has been able to invest in road infrastructure (Golden Quadrilateral project links 4 major cities), rural health care, national security + education
- These reforms have continued under Prime Minister Modi
- 'Digital India' and 'Smart Villages' schemes
- Diplomatic relations have improved significantly and USA has supported their development of nuclear reactors
- Relations have improved with Afghanistan with India being its largest aid donor + Israel who now looks to India over Russia for advice
- BRIC's + Commonwealth member
- Seeking to be permament member of UN
- Ethnic issues e.g. Caste System
- Home to many tech start-up
26 of 28
India 2
- Cultural diaspora prominent- sold 3.6 billion Bollywood tickets in 2014 vs 2.6 billion in Hollywood
- Indian Ocean= key trade route as India has naturally deep harbours
- Tourism contributes to 6% of GDP
- Solar energy has potential
- Some geographers believe that India's democratic nature may allow it to counterbalance China's authoritarian approach
- India has invested in space industry- first Asian nation to put satellite into orbit around Mars shows its ambition
- It is a form of hard power with its nuclear power + armed forces
27 of 28
Tensions in the Middle East
- Involvement of superpowers in the Middle East dates back to early 20th century
- Sykes-Picot Agreement of 1916 divided former Ottoman Empire into zones of influence for Britain and France, eventually supported by Roosevelt and Churchill post 1945
- West's post colonial establishement of new sovereign states of Iraq, Jordan and Israel (controversial)
- Tensions between Palenstine territories represented by terrorist groups Hamas and Hezbollah as it is hard to resolve due to the religious implications of the tensions
- There is also disputes between countries over Muslim branches e.g. Sunni Muslims in S.Arabia and Shia Muslims in Iran which creates a political threat
- Many of the Middle East countries are huge exporters of resources e.g. oil and therefore political relations are integral to the interdependece created by globalisation
- US politcal scientist Samuel Huntington has suggested that contrasting cultures may be the next source of major conflict e.g. US military action against Al Qaeda in 2001 by attacks in Afghanisatan and Iraq
28 of 28
Similar Geography resources:
2.5 / 5 based on 3 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating



Comments
No comments have yet been made