Physics 30th January -7 th March
- Created by: Katie19942002
- Created on: 27-04-17 16:41
Momentum
momentum kg m/s (p) = mass kg (m) x velocity m/s (v)
Conservation of momentum > a closed circuit system in which the total momentum before an event is the same as the total momentum after the vent
change of momentum = impact force x impact time
Impact Force
When vehicles collide force depnds on:
- mass
- change of velocity
- length of impact time
Longer impact time = reduced impact force
When 2 vehicles collide:
- they exert equal & opposite forces on eachother
- their total momentum ios unchanged
If the result is negative the force decelerates the object
Centre of Mass
To find irregular shapes centre:
- Using a pin pierce anywhere around the outside of the shape
- Put the pin in a cork and suspend it using a clamp
- Hang a weight on to the pin using a plumb line
- Draw a line where the string comes to rest
- Complete with at least one other point
- Draw a dot where the two lines cross > centre of mass
Centre of mass > the point at which the weight can be thought of as being cocncentrated
Moment
> A measure of the turning effect of a force
Moment (Nm) = force (N) x distance (m)
Gears
- Gears change the moment of a turning effect
- To increase the moment of a turning effect > small wheel needs to drive larger wheel
- Low gear = low speed
Why does a child sitting on a swing come to rest directly below the top of the swing?
If you suspend an object and then release it, it will come to rest with it's centre of mass directly below the poinbt of suspension.
Pressure & Hydraulics
- Hydraulics- the use of pressure in liquids
- Pressure (pascals) = force / area
- The bottom hole's water goes furthest as it has the most pressure on it (due to greter volume & hence weight) > open system
Hydraulics (continued)
- Liquids are virtually incompresible
- Pressure in liquids are transmitted equally in all directions
The force in a hydraulic system depends on:
- The force exerted by the system
- The area of the cylinder which the force acts on
- The area of the cylinder that exerts the force
Pressure in liquid = height x density x gravity
Upthrust
Weight = upthrust
- If the upthrust is smaller > boat will sink
Upthrust depends on:
- amount of water displaced
- density of liquid
Amount of water displaced = volume of object
Atmospheric pressure
Crushing can demo:
- Air vapour gets cooled in water (takes up less room)
- leaves vaccum in can
- air pressure pushes in from outside casuing can to crush
pressure = hight x density x gravity
- Atmospheric pressure decreses with a higher altitude
- Less air above pushing down
- Less oxygen the higher you go as less particles
Energy
- Most > magnetic
- Kids > kinetic
- Hate > heat
- Learning > light
- G > gravitational
- C > chemical
- S > sound
- E > electrical
- Energy > elastic
- Names > nuclear
energy (continued)
Energy transfer diagram: (TV)
Electricity > light + heat + sound
starting energy > energy used
useful energy > enrgy we want
wasteful energy > energy we don't use
Energy can only be transferred & transformed
Gravitational potential energy
work done = force x distance
weight = mass x gravity
Gravity > the force between 2 objects that have a mass
> further away = further to fall = greater GPE
Gravitational potential energy = mass x gravity x height
(measured in joules)
Kinetic energy
Moving objects always have kinetic energy.
Affected by:
- velocity
- mass
Velocity > speed in a given direction
KE = 0.5 x mass x velocity^2
GPE lost = KE gained
power of appliances
Power > energy transferred in a certain amount of time
Watts > amount of joules transferred in 1 second
Energy = power / time
How a lightbulb works:
- simple circuit with filament in middle
- electrons travel along circuit & continiously bump in to the tungstuns atoms which vibrate
Power of appliances (continued)
Energy efficient light bulbs:
- electricity excites mix of gases inside bulb
- emites ultra violet light which is absorbed by fluorecent coating which transforms into light
No. of units (kWh) = power rating (Kw) x time appliance on (in hours)
Conservation of energy
- Always waste energy in energy change
- Wasted energy goes in to surroundings

Conservation of energy for a pendulum
The higher the initial hight the more enrgy is wasted through heat & soundmeaning there is less GPE.
Efficiency
more efficient = less wasted energy
efficiency = useful output / total input > number between 0 & 1 (can be converted to percentage x100)
(dosen't have units > dividing joules by joules so cancel out)
Fossil fuels
Fuel > anything that can be burnt to produce light & heat
Chemical > (combustion) heat + light
Non-renewable:
- nuclear
- natural gas
- oil
- coal
Renewable:
- solar
- wave
- hydroelectric
- wind
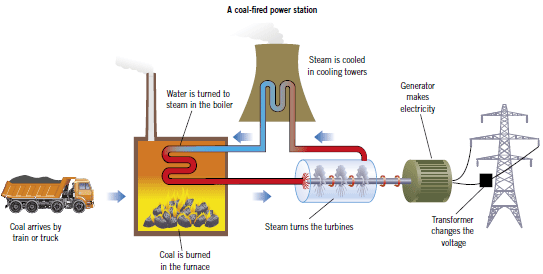
Power stations
Momentum
momentum (kg m/s) = mass x velocity
When a vehicle collides it depends on:
- mass
- change of velocity
- direction of impact
Longer impact = reduced force
When two vehicles collide:
- exert equal & opposite forces
- total momentum = unchanged
Momentum (continued)
- All moving objets have momentum
- Measur of how hard something is to stop
Mass x 2 = speed / 2
- Scalar > size
- Vector > size & direction
Conservation of momentum = sum of momentum before a collsion or explosion is the same as the sum of monetum of tensions
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Go ahead in time as far as possible »
- When's your birthday »
- Mphil criminological research »
- Haven’t received a decision from University of Southampton 2024 »
- Cambridge CISL 2024 »
- Southampton Replacement Student Tenant Needed Jan 1st-May 30th 2024 »
- offers for Leeds Uni »
- When is the deadline for international students applying to UK? »
- How long until I hear back from Swansea University »
- Quiz of the Week: The Master Thread! »


Comments
No comments have yet been made