Processes of Financial Management
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
- Created by: Alice
- Created on: 04-04-13 16:28
What's the planning process?
the setting of goals and objectives, determining strategies to achieve those, identifying and evaluating alternative courses of action and choosing the best one
1 of 70
What are the five stages in the planning and implementing cycle?
determining financial needs, developing budgets, maintaining record systems, identifying financial risks, estabslihing financial controls and addressing present financial position
2 of 70
short term is..
1-2 yrs and more specific goals
3 of 70
long term is..
2-10 yrs
4 of 70
planning and implementing determines?
how a business's goals will be achieved
5 of 70
examples of financial information
balance sheets, sales and price forecasts, budgets, bank statements, break even analysis, reports from financial ration analysis and intepretation
6 of 70
financial needs determined by?
size of the business, current phase of the business cycle, future plans for growth and development, capacity to source finance and management skills for assessing financial needs and planning
7 of 70
why is a business plan important?
sets out the finance required, proposed sources of finance, range of financial statements and guarantees a strong financial commitment to investing instituions
8 of 70
what is a budget?
information in facts and figures about the requirements to achieve a particular purpose
9 of 70
what do budgets show?
cash requires for planned outlays, cost of capital expenditure and asscioated expenses, estimated use and cost of raw materials, no. and cost of labour hours required for production
10 of 70
what are the three different types of budgets?
operating budgets, project budgets, financial budgets
11 of 70
features of budgets
reflects strategic planning decisions, provides financial info for business goals and enables constant monitoring of objectives
12 of 70
what are operating budgets?
the main activities of the business and used in preparing budgeted financial statements e.g. sales production
13 of 70
what are project budgets?
project budgets relate to capital expenditure and research and development
14 of 70
what are financial budgets?
the predictions of budgets which specifically relate to the financial data of a business
15 of 70
example of a financial budget
income balance sheet and cash flow statement
16 of 70
what are record systems?
Mechanisms employed by a business to ensure that data are recorded and info provided is accurate, reliable, effecient and accessible
17 of 70
advantages of a record system
minimising errors in recording process, producing accurate and reliable financial statements
18 of 70
what type of information are collected for record systems?
collection of revenue, payment of employees, accounts payable, taxes
19 of 70
what is a control measure?
recording entries twice
20 of 70
what is a financial risk?
risk to a business of being unable to cover its financial obligations
21 of 70
example of a financial risk
debts, theft, interest rate increases, non-payment of accounts recievable
22 of 70
what are financial controls?
policies and procedures that ensure that the plans of a business will be achieved in the most effective way
23 of 70
financial problems stop businesses from acheving goals. What are the common causes of finance problems?
theft, fraud, damage/loss of assets, errors in record systems
24 of 70
examples of policies which promote control within a business
seperation of duties, clear authorisation and responsibility for tasks in the business, rotation of duties, control of cash, protection of assets control of credit procedures
25 of 70
what is gearing?
measurement of the relationship between debt and equity. The proportion of debt and equity used to finance the activities of a business
26 of 70
advantages of debt finance
funds are readily available, increased funds should lead to increased earnings and profits, tax deductions for interest payments
27 of 70
disadvantages of debt finance
increased risk if debt comes from financial institutions (interest and charges need to be repaid), security required, lenders have first claim on any money of the business if it becomes bankrupt, regular repayments
28 of 70
What is equity finance?
funds which remain within the business and does not need to be repaid
29 of 70
advantages of equity finance
safer then debt, lenders more willing to lend, does not need to be repaid unless owner leaves the business,cheaper than other sources of finance, low gearing, less risk, owners retain control over how finance is used
30 of 70
disadvantages of equity finance
lower profits and lower return, no tax deductions, proportion of profits go to new owners, expectation that the owner will have a return on investment, safety net not for business problems
31 of 70
what is the matching principle?
the appriopriate finance for purchasing an asset.
32 of 70
how should current assets be bought?
with short term finance
33 of 70
how should non-current assets be bought?
long term finance
34 of 70
Name the 7 influences on the matching principle
Terms of finance, cost of each source of funding, structure of the business, costs, flexibility, availability of finance, level of control
35 of 70
what is the terms of finance?
the suitable of funds for the structure of the business and its purpose
36 of 70
what is the cost of each source of funding?
the required rate of return taken into consideration and balanced again costs of each source e.g. interest payments
37 of 70
why are costs measured?
to check the fluctuation of each source of funds
38 of 70
why are monitoring and controlling important in financial management?
it shows the inconsistant and the consistant methods which impact the viability of a business
39 of 70
why is accounting information important?
used to monitor and control business's functions
40 of 70
what is the purpose of financial reports?
to communicate information about the business to make decisions
41 of 70
what are the main financial controls for monitoring?
cash flow statement, income statement, balance sheet
42 of 70
what is a cash flow statement?
an indication of the movement of cash receipts and payments resulting from transactions over a period of time (identifies trends in predicting change)
43 of 70
who use cash flow statement?
creditors/lenders of finance, owners and shareholders (to assess ability of business to manage cash)
44 of 70
cash flows show whether a firm can
generate a favourable cash flow, pay its financial commitments, have sufficient funds for future expansion, obtain finance from external sources and pay drawings to owners and dividends
45 of 70
what are the three acitivities a cash flow statement is divided into?
operating activities, investing activities, financing activities
46 of 70
what are operating activities?
inflows and outflows relating to the activity of business provision of goods/services
47 of 70
what are investing activities?
the inflows/outflows relating to purchase/sale of non-current assets and investments
48 of 70
what are financing activities?
inflows/outflows relating to borrowing activities of business. either equity or debt
49 of 70
what is an income statement/profit or loss statement
The income earned and expenses incurred over the accounting period with the resultant profit or loss (operating effeciency)
50 of 70
what are the two things that an income statement/profit or loss statement show?
operating income earned from main function of business, operating expenses
51 of 70
equation for cogs
operating stock + purchases - closing stock
52 of 70
equation for gross profit
sales - COGS
53 of 70
equation for net profit
GP - expenses
54 of 70
what's a balance sheet?
a representation of a business's assets and liabilities at a particular point in time and represents the net worth (equity) of the business. It shows the financial stability of the business
55 of 70
what does a balance sheet indicate?
if a business has a enough to cover debts, interest and money borrowed can be paid, assets are being used to maximise profits, owners are making a good return on investment
56 of 70
what is a current asset?
a quick conversion to cash
57 of 70
what is a non-current asset?
takes longer to convert to cash (furniture, car)
58 of 70
what is a current liability?
quick to pay off
59 of 70
what is a non-current liability?
takes longer to pay off
60 of 70
what's owner's equity?
represents owners financial interest in the business and is repaid by the business to owners
61 of 70
what does the accounting equation show?
the relationship between assets, liabilities and owners equity
62 of 70
equations for current assets
liabilities +OE
63 of 70
equation for OE
assets - liabilities
64 of 70
equation for liabilities
assets - OE
65 of 70
What are the roles of financial ratios?
It summarises the activities of business over a period of time
66 of 70
what does a verticle analysis show?
A comparison of figures within one year
67 of 70
what does a horizontal analysis show?
a comparison of figures from different financial years
68 of 70
what does a trend analysis show?
a comparison of figures from 3-5yrs
69 of 70
what is the definition of liquidity and an example of a sound financial position
2:1 the ability of a business to pay its debts in the short term
70 of 70
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What are the five stages in the planning and implementing cycle?
Back
determining financial needs, developing budgets, maintaining record systems, identifying financial risks, estabslihing financial controls and addressing present financial position
Card 3
Front
short term is..
Back
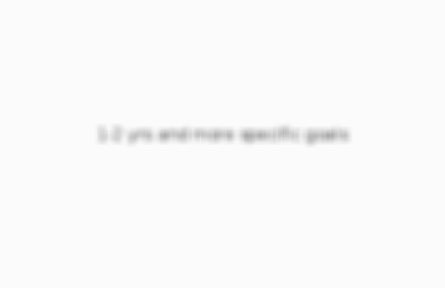
Card 4
Front
long term is..
Back

Card 5
Front
planning and implementing determines?
Back

Similar Business Studies resources:
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5


Comments
No comments have yet been made