Physics Paper 1 Electricity 9-1
5.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
- Created by: RendermanL
- Created on: 22-05-18 20:31
What is Current?
The flow of electrical charge.
1 of 38
What do voltage and resistance do to current?
Voltage pushes the current around the circuit, Resistance slows the flow of current.
2 of 38
What is the equation for charge with current?
Q (charge) = I (current) x t (time)
3 of 38
What is the equation that links P.d, current and resistance?
Voltage = Current x Resistance
4 of 38
At a constant tempature, the current flowing through an ohmic conductor is _____ __________ to the potential difference across it.
Directly proportional.
5 of 38
What is a LDR dependent on? How does this effect the resistance?
Light intensity. Light - resistance decreases. Dark - resistance increases
6 of 38
What is a thermistor dependent on? How does this effect the resistance?
Temperature. Hot - resistance decreases. Cool - resistance increases
7 of 38
What is a sensing circuit?
Used to turn on or off components in a room depending on the conditions.
8 of 38
In a series circuits, potential difference is ....
Shared between components
9 of 38
In a series circuit, current is .....
The same in each component
10 of 38
In a series circuit, the total resistance is ....
All the components resistance's added together
11 of 38
In a parallel circuit, potential difference is ....
the same in each component
12 of 38
In a parallel circuit, current is .....
Split between each component
13 of 38
What is AC? Give an example.
Alternating current- Mains supply
14 of 38
What is DC? Give an example.
Direct current- Battery supply
15 of 38
What is the UK Mains supply voltage? What is the frequency?
230V, 50 Hz
16 of 38
What three wires are in the plug?
Neutral Wire, Live wire and Earth wire
17 of 38
What do each of the three wires in the plug do?
Neutral wire- Completes the circuit (current flows out using). Live wire- Provides the current from the mains supply. Earth wire- Doesn't carry current and prevents the casing from becoming live.
18 of 38
What colour is each of the wires in the plug?
Neutral wire- Blue. Live wire- Brown. Earth wire - Green and Yellow.
19 of 38
What equation links Energy transferred and Power?
E (Energy transferred) = P (Power) x T (Time)
20 of 38
What equation links Energy transferred, charge and PD?
E (Energy transferred) = Q (Charge) x V (Pd)
21 of 38
What equation links Power, voltage and current?
P (Power) = V (Voltage) x I (Current)
22 of 38
What equation do you use if you dont know the PD and you are trying to calculate power?
P (Power) = I^2 (Current squared) x Resistance
23 of 38
What is the National Grid?
A system of cables and transformers that cover the UK, connecting powering stations to consumers.
24 of 38
What do electrical power stations need to assume throughout the day?
The amount of electricity usage/the demand for energy at a given time.
25 of 38
Is the current high or low in the national grid?
Low
26 of 38
Is the voltage high or low in the national grid?
High
27 of 38
Why does the National grid use certain levels for voltage and current?
Its cheaper and prevents lots of energy loss
28 of 38
What are the stages from the power station to the consumer by the national grid?
Power station - Step up transformer - Pylons - Step down transformer - Consumer
29 of 38
What two types of materials are needed to rub together to create static build up?
Two insulating materials
30 of 38
What happens when two materials are rubbed together?
Negatively charged electrons will move from one material to the other, creating two electrically charged materials. One positive, one negative.
31 of 38
What effects the direction electrons move in static build up?
The type of material used
32 of 38
What causes a spark?
Too much static - The electric charge builds up increasing the potential difference between the object and earth. Electrons then jump across causing a spark.
33 of 38
What is an electric field?
A field created around any electrically charged object
34 of 38
When you get closer to an electrically charged object, the _______ the field is
Stronger
35 of 38
How do you show electric fields around an object?
Field lines- Straight lines coming out of an object, the arrow depending on the charge. Facing away if its positive, facing towards if negative.
36 of 38
What happens when a charged object is placed in the electric field of another object?
It feels a force, attraction or repulsion.
37 of 38
How do electric fields explain sparks?
Electric fields causes electrons in air particles to be removed (ionisation) which makes the air conductive.
38 of 38
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What do voltage and resistance do to current?
Back
Voltage pushes the current around the circuit, Resistance slows the flow of current.
Card 3
Front
What is the equation for charge with current?
Back
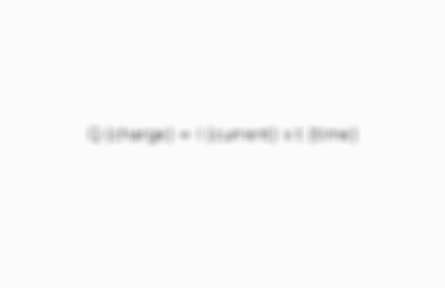
Card 4
Front
What is the equation that links P.d, current and resistance?
Back

Card 5
Front
At a constant tempature, the current flowing through an ohmic conductor is _____ __________ to the potential difference across it.
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- GCSE AQA Physics Paper 1 and 2 Revision and Study Chat »
- BTEC Applied science Unit 3 2022 Exam »
- Use a simulator to plot the frequency response of the circuit »
- Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Higher Tier 1CH0 1H - 27 May 2022 [Exam Chat] »
- content »
- A-level Physics Study Group 2022-2023 »
- higher physics revision help »
- Physics A Level »
- AQA AS Physics Paper 1 »
- Edexcel IGCSE physics (9-1) 4PH1 revison video for free »
Similar Physics resources:
1.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
4.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Comments
No comments have yet been made