1- Matter and Radiation
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
- Created by: natalie1421
- Created on: 13-10-15 12:01
What are the name and letter for the number of protons and neutrons in an atom?
Nucleon/Mass Number, A
1 of 48
What are the name and letter for the number of protons in an atom?
Proton/Atomic Number, Z
2 of 48
What is the definition of isotopes?
Atoms with the same number of protons (so same element) but a different number of neutrons
3 of 48
What is the equation and unit for specific charge?
Specific charge = charge of particle/mass of particle, unit = coulombs per kilogram
4 of 48
What is the specific charge of helium 4?
2 x (1.6 x 10^-19)/4 x 1.67 x 10^-27 = 4.79 x 10^7 Ckg^-1
5 of 48
What are the four fundamental forces of nature?
Strong nuclear, gravitational, electromagnetic, and weak nuclear
6 of 48
Which type of radiation consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons?
Alpha
7 of 48
What happens to the proton number and nucleon number after decay by alpha radiation?
Proton number (Z) decreases by 2, nucleon number (A) decreases by 2
8 of 48
Which radiation consists of a fast moving electron?
Beta
9 of 48
What happens in beta minus decay?
A neuton decays into a proton in the nucleus of an atom, an electron along with an antineutrino is emitted. The proton number increases by 1 and the nucleon number remains unchanged
10 of 48
What happens in beta plus decay?
A proton turns into a neutron and a neutrino and positron are emitted
11 of 48
Which force does the strong nuclear force overcome?
Electrostatic force (exerted by positively charged protons on each other)
12 of 48
When does the strong nuclear force provide attraction?
When nucleons have a range of about 3 femtometres (3 x 10^-15m)- holds nucleus together
13 of 48
When does the strong nuclear force provide repulsion?
At distances less than 0.5 femtometres- prevents nucleus collapsing into a point
14 of 48
Why are neutrinos/antineutrinos produced in beta minus/plus decay?
There is still kinetic energy left, so another particle must be formed (conservation of energy)
15 of 48
Why are neutrinos difficult to detect?
They have nearly zero mass and no charge. Also, they barely interact with matter.
16 of 48
What produces neutrinos?
The sun, beta-emitting isotopes, and nuclear reactors
17 of 48
Why is light a wave?
It can be deferacted
18 of 48
What is the speed of light?
3.0 x 10^8 ms^-1
19 of 48
Give a property of electromagnetic waves
They all travel at the same speed in a vacuum
20 of 48
What is a photon?
A packet or 'quantum' of electromagnetic waves. Each photon contains a set amount of energy which is proportional to the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation
21 of 48
What is the equation for photon energy?
E = hf
22 of 48
In E=hf, what is h?
The Planck constant, (6.63 x 10^-34 Js)
23 of 48
Calculate the speed of a wave with frequency 8.0x10^14Hz, a wavelength of 250nm, and energy of 530x10^-19J
2.0 x 10^8 ms^-1
24 of 48
Where are antiparticles found?
High-energy collision expreiments, interactions with cosmic rays, radioactive decay
25 of 48
Antimatter: All particles of normal matter have a corresponding particle that...
Has the same mass ad the normal particle, has the opposite charge to the normal particle (if charged), and will undergo annihilation with the normal particle if they meet
26 of 48
What happens in annihilation?
A particle and its antiparticle meet, and all their mass and kinetic energy is converted into two photons of equal frequency that move off in opposite directions
27 of 48
What is pair production?
The opposite of annihilation- the energy of one photon can be used to create a particle and its corresponding antiparticle. As all the energy is converted from the photon to the two particles, the photon ceases to exist
28 of 48
How many joules of energy is one electron volt?
1eV = 1.6 x 10^-19 J (the charge of 1 electron)
29 of 48
How many joules of energy is one mega electron volt?
1MeV = 1.6 x 10^-13 J
30 of 48
What is rest energy?
The amount of energy a stationary particle (with no kinetic energy) has
31 of 48
What is the electron volt equal to?
The kinetic energy gained by an electron when it is accelerated by a potential difference of 1 volt
32 of 48
Calculate the minimum energies of the photons produced by the annihilation of a proton and antiproton (r.e. of proton = 939.4MeV)
Each photon has an energy of 939.4MeV
33 of 48
What causes electromagnetic force?
The exchange of virtual photons
34 of 48
What is the name of the repulsive force felt between 2 like charges?
Electrostatic force
35 of 48
Why are the photons which cause electromagnetic force 'virtual'?
They can't be detected as if we intercepted them directly, e.g. by using a detector, we would stop the force acting.
36 of 48
What are Feynman diagrams?
Diagrams which represent the interaction between two particles or antiparticles or the decay of a particle or antiparticle
37 of 48
What is the mass of a photon and a W boson?
Photon = zero, W boson = non-zero
38 of 48
What is the charge of a photon?
Zero
39 of 48
What is the range of a W boson and a photon?
W boson = maximum of 0.001 femtometres, Photon = infinite
40 of 48
What type of decay is cause by the weak nuclear force?
Beta minus as a neutron converts into a proton and electron
41 of 48
Why is the weak nuclear force labelled as 'weak'?
It is only significant in unstable nuclei as unstable nuclei don't have the strong nuclear force preventing them from decaying
42 of 48
What are the exchange particles in beta decay?
W bosons
43 of 48
What is electron capture?
A proton in a proton-rich nucleus turns into a neutron due to weak interaction with an inner shell electron. A neutrino is produced also and the exchange particle is a W+ boson.
44 of 48
What is the mass of a proton (and neutron), and the mass of an electron?
Proton = 1.67 x 10^-27 kg, Electron = 9.11 x 10^-31kg
45 of 48
What is the charge of a proton, the charge of a neutron, and the charge of an electron?
Proton = +1.60 x 10^-19 C, Neutron = 0 C, Electron = -1.60 x 10^-19 C
46 of 48
What is the range, strength, and exchange particle of gravitational force?
Range = Infinite, Strength = 10^-36, Exchange particle = graviton
47 of 48
When are electromagnetic waves emitted?
When a charged particle loses energy- e.g. when a fast-moving electron is stopped or slows down or changes direction, or if an electron in a shell of an atom moves to a different shell of lower energy.
48 of 48
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What are the name and letter for the number of protons in an atom?
Back
Proton/Atomic Number, Z
Card 3
Front
What is the definition of isotopes?
Back

Card 4
Front
What is the equation and unit for specific charge?
Back

Card 5
Front
What is the specific charge of helium 4?
Back
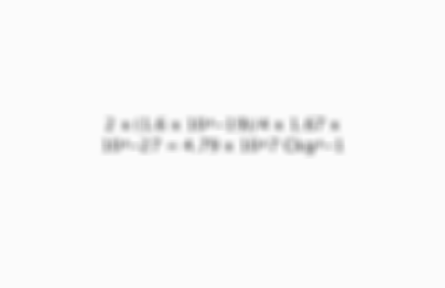
Related discussions on The Student Room
- AQA GCSE Physics Paper 1 (Higher Tier triple) 8463/1H - 25th May 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- Alevel physics »
- Specific Charge »
- Edexcel A Level Physics Paper 3: 9PH0 03 - 15th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- A Level Physics Notes »
- Physics personal statement advice »
- GCSE AQA Physics Paper 1 and 2 Revision and Study Chat »
- AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy - Physics Paper 1 (Higher) 8464/P/1H [Exam Chat] »
- 2023 entry thread for PHYSICS »
- Dr Kathy Romer answers your questions about Physics! »
Similar Physics resources:
3.5 / 5 based on 3 ratings
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made