Functionalism, Strain, and Subcultural explanations of Crime and Deviance
- Created by: Azazel
- Created on: 02-10-16 17:59
Fullscreen
FUNCTIONALIST/STRAIN EXPLANATIONS OF CRIME & DEVIANCE
Functionalism
- Social Structure Theory
- Consensus theory --> They believe there are shared norms and values in society.
EMILE DURKHEIM proposed key ideas of the functionalist theory on crime and deviance.
- Crime and deviance are seen as inevitable, normal, and functional parts of society – all societies – Crime is universal.
- This is because not everyone can share all the norms and values or the collective sentiments of society.
- He argued that crime and deviance sustains morality – It reaffirms/clarifies Boundaries – Boundary Maintenance.
- It promotes solidarity and he argues that it encouraged social change – Yesterday’s deviance becomes tomorrow’s Norms – e.g. Homosexuality.
- Crime and deviance only becomes dysfunctional if there is too much or too little of it.
- Anomie explains this – A sense of normlessness, loneliness or isolation – The diversity of modern societies means that the collective conscience is weakened, and this results in higher levels of C&D.
He went on to talk about the role of punishment in society.
- He said that most of the time, behaviour is kept in check by Formal Social Control.
- However, if behaviour crosses the boundaries into illegal acts then formal systems of punishment are used.
- Punishment performs essential functions for society:
- RETRIBUTION – Punishment inflicted for vengeance, heals wounds done to cultural sentiments.
- RESTITUTION – focuses on individual damage and compensation.
ALBERT K. COHEN also contributed to the functionalist view of crime, identifying two possible functions of crime.
- SAFETY VALVE – A harmless expression of discontent.
- WARNING – Crime shows when an aspect of society is malfunctioning.
TRAVIS HIRSCHI proposed a Social Control Theory.
- He wanted to know why people did not commit crime and he found it was linked to control, and to levels of social integration.
- He found that people have four controls in their life to prevent them from committing crime and deviance.
- ATTACHMENT – Family and relationships.
- COMMITMENT – People may lose a great deal.
- INVOLVEMENT – People would lose respect from communities.
- BELIEF – People have been brought up to respect rules, beliefs and others.
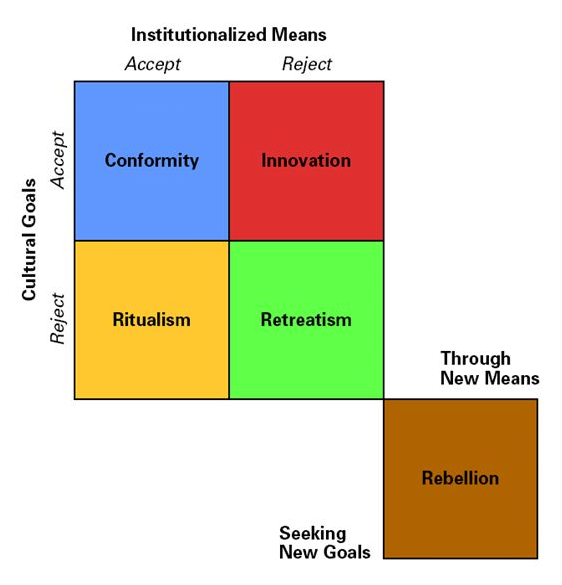
ROBERT MERTON proposed the Strain Theory –-> can be used in subcultural theory.
- He argued that there is a strain in society between the cultural Goals of a society (e.g. American Dream) and the ability to achieve those goals through legitimate means.
- He argued that there are those at the bottom of the social ladder who find it the hardest to succeed and therefore they are the ones who’re more likely to look for alternative routes to success. --> Could apply Material Deprivation and Cultural Deprivation here.
- He proposed 5 responses to strain.
SUBCULTURAL EXPLANATIONS OF CRIME & DEVIANCE
SUBCULTURALISM
- Deviance is the product of a delinquent subculture. à Have different norms/values from mainstream society.
- Subcultures provide and alternative route and status for those denied the chance to achieve legitimately.
- There are a number of subcultural theorists to explain C&D.
ALBERT K. COHEN – STATUS FRUSTRATION
Links to strain theory
- Studied the ‘Corner Boys’ – a Working Class delinquent subculture.
- Frustrated with unachievable Middle-Class norms and values. – Middle class measuring rod in education – A*-C Economy.
- Working class can’t achieve those – Material and Cultural Deprivation.
- …
Comments
No comments have yet been made