Structures and functions in living organisms
- Created by: Twoodl31
- Created on: 21-12-17 12:00
2a) Levels of Organisation
Organelles - Nucleus
Cells - Red Blood Cell
Tissues - Xylem Tissue
Organs - Lungs
Systems - Digestive System
2b) Cell Structure
Nucleus - Contains genetic material and control's the cell's activities.
Cytoplasm - Where most of the cells reactions happen. Contains enzymes that control these reactions.
Cell Membrane - The outer surfcae of the cell and controls the substances that go in and out.
Cell Wall - A rigid structure made of cellulose. It supports and strengthens the cell.
Chloroplasts - Photosynthesis. Chlorroplasts contain a green pigment which is used in photosynthesis.
Vacouole - A large organelle that contains cell sap. It helps to support the cell.
2c) Biological Molecules
Carbs are made of simple Sugars - Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
Proteins are made up of Amino Acids - Carbon, Nitrogen, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
Lipids are made of Fatty Acids and Glycerol - Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen.
Glucose - Benedicts
Starch - Iodine
Enzymes are biological catalysts and break up big molecules into smaller ones.
pH and Temp affect. Bile neutralises the stomach acid so the enzymes in the small intestine work. If the temp is too high then the active site is changed so the enzyme no longer works. Describe Experiment
2d) Movement of Substances
Diffusion - Net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis - Net movement of Water molecules across partially permeable membrane from a region of high conc to a region of low conc.
Active Transport - Movement of particles against a concentration gradient using energy released during respiration.
Plants need water so that they can be turgid cells.
Factors that affect movement - Surface Area to Volume ratio, Temperature, Concentration Gradient.
2e) Nutrition Part 1
Photosynthesis produces Glucose using Sunlight.
Carbon Dioxide + Water --------> Glucose + Oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O --------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
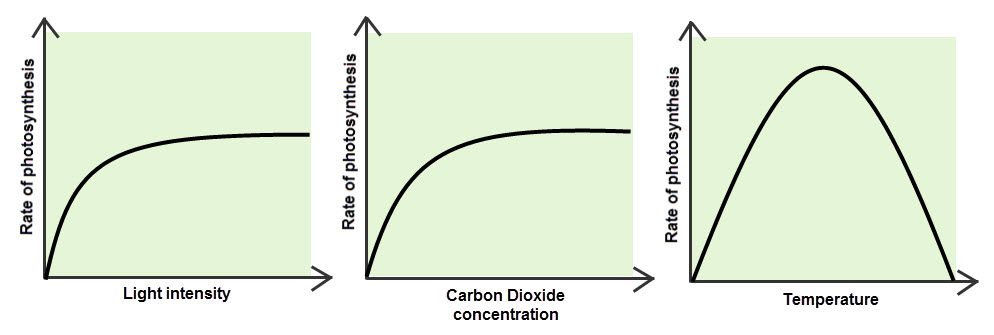
2e) Nutrition Part 2
2e) Nutrition Part 3
Nitrates for Amino Acids and Proteins. Without them, plants will be stunted with yellow leaves.
Phosphates for making DNA and Cell Membranes. Without them, they have poor root growth and purple leaves.
Potassium to help enzymes for photosynthesis and respiration. Without them, they have poor flower and fruit growth and discoloured leaves.
Magnesium for making chlorophyll. Without them, they will have yellow leaves.
Photosynthesis Tests
- Test a Leaf for starch
- Lime to take in the CO2 to prove it is needed.
- Test Oxygen Production
2e) Nutrition Part 4
Carbs in Pasta or Rice to provide energy.
Protein in Meat or Fish needed for growth and repair.
Lipids in Butter or oily fish to provide energy and act as an energy store.
Vitamins A in Liver for hair skin and eyes, B in oranges, D in eggs for calcium.
Minerals Calcium in milk for bones and teeth, Iron in Red Meat for haemoglobin.
Water found in food and drink for everything.
Dietary Fibre in Wholemeal bread aids movement through the gut.
Energy Requirements depend on AGE, ACTIVITY LEVEL and PREGNANCY.
2e) Nutrition Part 5

2e) Nutrition Part 6
Ingestion - Eating.
Digestion - Break down of molecules can be mechanical or chemical.
Absorption - Moving the molecules through the walls into the gut.
Assimilation - Moved into body cells.
Egestion - Getting rid of waste products as Faeces
Peristalsis is the squeezing of food through the gut through muscular contractions.
Bile Neutralises the Stomach Acid and Emulsifies Fats.
- Produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine.
- Bile is alkaline so neutralises the acid so that the enzymes can work.
2e) Nutrition Part 7
Amylase converts Starch into Maltose.
Maltase converts Maltose into Glucose.
Proteases converts Proteins into amino acids.
Lipases convert Lipids into Glycerol and Fatty Acids.
Burn the food and measure change in temperature of water.
Energy = Mass of Water x Temp change of water x 4.2
Then work out energy per gram.
Villus have Large Surface Area, Small Distance
2f) Respiration
Respiration is the process of Releasing Energy from glucose.
Aerobic Respiration needs plenty of Respiration
Glucose + Oxygen --------> Carbon Dioxide + Water (+ Energy)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --------> 6CO2 + 6H2O
Anaerobic Respiration doesn't use Oxygen
Glucose --------> Lactic Acid
(or in Plants.....)
Glucose --------> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
2g) Gas Exchange Part 1
Plants exchange gases by diffusion.
When the plant is photosynthesising it uses up lots of CO2 which makes more CO2 move into the leaf by diffusion due to concentration...
O2 is being made as a waste product, some of which is used in respiration the rest diffuses out the stomata.
Photosynthesis is only in the daytime. Respiration happens all the time so net exchange changes depending on light level.
- Large Surface Area for diffusion (Inside a weel, lots of air spaces)
- Leaves are thin so gases only have to travel a short distance.
- Stomata to let gases in and out (And let water out) Close at night or when there isn't much water. Controlled by guard cells.
Hydrogen-carbonate indicator shows changes in CO2 conc so it can be used to show the difference in net gas exchange in plants.
2g) Gas Exchange Part 2
2g) Gas Exchange Part 3
Breathing IN...
- Intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract.
- Thorax Volume increases.
- This decreases the pressure drawing air in.
Breathing OUT...
- Intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax.
- Thorax volume decreases.
- Air is forced out.
Alveoli carry out gas exchange in the body. Adaptions...
- A huge number so enormous surface area.
- There's a moist lining for gases to dissolve in.
- The alveoli have very thin walls so short distance for diffusion.
- Great blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient.
- The walls are permeable so gases can easily diffuse across.
2g) Gas Exchange Part 4
An experiment involving running and counting breaths.
Smoking Tobacco causes problems...
- Damages walls inside the alveoli, reducing surface area.
- Tar damages the cilia. These hairs are supposed to catch dust and bacteria before they reach the lung. However, they do not work when clogged up.
- Tar also irritates the bronchi and bronchioles, encouraging mucus the be produced which can't be cleared because the cilia are damages.
- The carbon monoxide reduces the amount of oxygen blood can carry, so heart rate increases.
- Tobacco smoke also contains carcinogens which lead to cancer.
2h) Transport Part 1
Unicellular organisms can rely on diffusion because diffusion because stuff only needs to travel a short distance. Multicellular organisms are much larger so need a transport system.
Phloem transports SUGARS like sucrose and amino acids all around the plant.
Xylem carries water and mineral salts from the roots up the shoot to the leaves in the transpiration stream.
Root hair cells take in water. They have long hairs which means there's a large surface area. Higher conc in the soil than in the cell so water is drawn in by osmosis.
2h) Transport Part 2
Transpiration is the loss of Water from the plants. Caused by evaporation and diffusion. It is a side-effect of the way leaves are adapted. Water is drawn out because there is less water in the air than in the leaves.
LIGHT INTENSITY - The brighter the light the greater the transpiration rate.
TEMPERATURE - the warmer it is, the faster transpiration happens.
WIND SPEED - the higher the wind speed the faster the rate of transpiration.
HUMIDITY - the drier the air around a leaf the faster transpiration happens.
Ideal conditions for a plant - Low wind speed, Very Humid.

2h) Transport Part 3
Blood has four main components - Plasma, Platelets, Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells
Plasma is the liquid bit of the blood it helps to transport everything.
Platelets are small fragments of Cells that help Blood Clot when you damage a blood vessel. They clump together to 'plug' the damaged area. This is known as blood clotting.
Red blood cells carry oxygen and are adapted...
- Small and biconcave shape to give a large surface area.
- They contain haemoglobin. In the lungs, it reacts with oxygen to form Oxyhaemoglobin.
- No nucleus - frees up space for more haemoglobin.
2h) Transport Part 4
Phagocytes Ingest Pathogens - They are non-specific.
Lymphocytes Produce Antibodies. Antibodies are produced until the correct one is found and then these are produced in large volumes. Some of these stay around in the blood as memory cells. So they can be reproduced very fast if there is another infection. So you don't get the same infection twice.
Vaccination protects from Future Infections.
You are injected with a dead or inactive pathogen. These carry antigens, so even though they are harmless they trigger an immune response so antibodies are produced and some stay as memory cells.
2h) Transport Part 5
2h) Transport Part 6
How the heart functions.
- Right Atrium DeOxy (through vena cava)
- Right Ventricle DeOxy (via the tricuspid valve)
- Lungs (via the pulmonary artery)
- Left Atrium Oxy (from the pulmonary vein)
- Left Ventricle pumps to the rest of the body
Exercise and adrenaline increase heart rate as muscles need more energy so you can respire more.
Arteries carry blood under pressure so there are thick walls of muscle.
Capillaries are really small with thin walls only one cell thick.
Veins have big lumens to help blood flow despite lower pressure. They also have valves.
2h) Transport Part 6
2i) Excretion Part 1
Lungs, Kidneys and skin are organs of excretion.
Ultrafiltration - Water, Urea, Salts and Glucose is forced into the Bowman's capsule by high pressure. Proteins stay in the blood.
Reabsorption - All Glucose is reabsorbed. Proximal Convoluted Tube. Sufficient salt is reabsorbed. Sufficient water is reabsorbed from the collecting duct.
Waste products are released.
ADH works on a negative feedback loop to control water content.
More ADH = More Water. Less ADH = Less Water.
Urine contains water, urea and salts.
2i) Excretion Part 2
2i) Excretion Part 3
2j) Coordination and Response Part 1
Responding to their environment helps organisms survive. MRS GRENC
Homeostasis is the maintenance of constant internal environment
Body water content and body temperature are both examples of homeostasis.
Receptors detect stimuli. Effectors bring about a response to the stimuli.
Receptors communicate with receptors via the nervous system and/or hormonal system. Plants also respond to stimuli with Auxins - Growth hormones.
Shoots are positively phototropic (grow towards light)
Shoots are negatively geotropic ( grow away from gravity)
Roots are positively geotropic (grow towards gravity)
2j) Coordination and Response Part 2
CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and is linked to sense organs by nerves.
2j) Coordination and Response Part 3
2j) Coordination and Response Part 4

Ciliary Muscles
2j) Coordination and Response Part 5
Too Hot - Sweat is produced. Blood vessels close to surface widen. Hairs lie flat.
Too Cold - Very little sweat. Blood vessels near surface constrict. You shiver.Hairs stand on end.
ADH - Pituitary Gland - Water Control - Changes permeability of kidney tubules.
Adrenaline - Adrenal Glad - Fight or Flight - Increases heart rate and blood flow.
Insulin - pancreas - Blood Sugar Level - Makes liver to turn glucose into glycogen.
Testosterone - Testes - Male Sex hormone - Secondary sexual characteristics.
Progesterone - Ovaries - Supports pregnancy - Maintains the lining of the uterus.
Oestrogen - Ovaries - Female Sex hormone - Menstrual cycle. Sexual Charac.
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Is a myofibril an organelle »
- 25 mark essay question »
- AQA A-level biology essay topics »
- groningen biology selection test »
- Paper 3 AQA a Level biology »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 3 [21st June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Alevel bio synoptic essay »
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology | PAPER 2 »
- mark scheme biology 2022 gcse combined science higher paper 1 »
- What is DNA repair »
Comments
No comments have yet been made