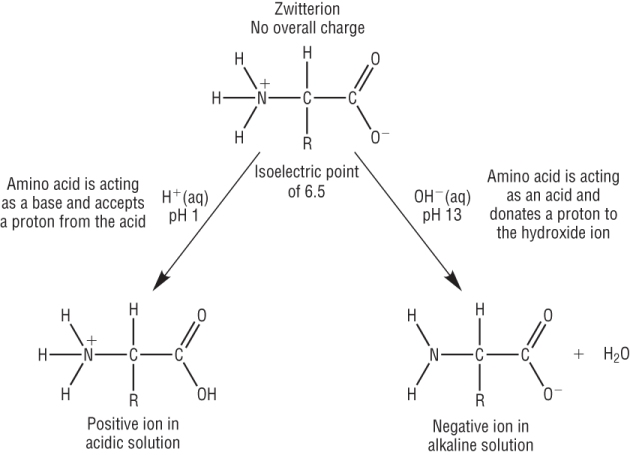
The isoelectric point of an amino acid is the pH at which there is no net electrical charge.
At a pH which is more acidic than the isoelectric point, the amino acid behaves as a base and accepts a proton from the acid, becoming postively charged.
At a pH which is more alkaline than the isoelectric point, the amino acid behaves as an acid and donates a proton to the base, becoming negatively charged.
Comments
No comments have yet been made