Energy is conserved
Types of energy: thermal, light, electrical, sound, KE, chemical, nuclear, GPE, elastic potential energy.
Sankey diagrams show energy transfers.
total energy input=total energy output
efficiency = useful energy output / total energy input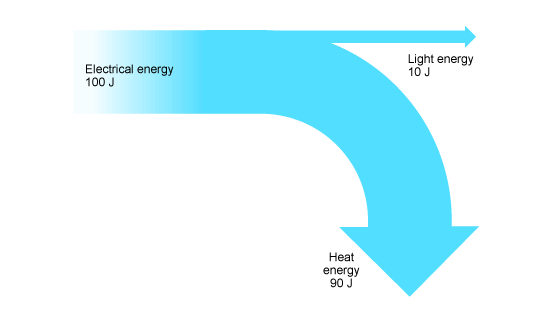
Comments
No comments have yet been made