Charges and Current - What is Electricity?
- Created by: pastelcloud
- Created on: 05-01-23 14:26
What is an Atom?
An Atom is a particle that makes up everything that you see. They are small - think of the smallest thing ever.
What does an atom look like? Structure?
They have smaller particles, protons and nucleus which make up a nucleus.
Protons are positive while Neutons have no charge.
They have electrons which fly about the nucleus. Electrons are negative charged.
Electrons can move to places. Where?
Electrons can move between atoms or between items.
Rubbing a comb with a cloth
When rubbing a comb with a cloth, electrons pass from the cloth to the comb. The comb is negative charged with more electrons while the cloth is positively charged with less electrons.
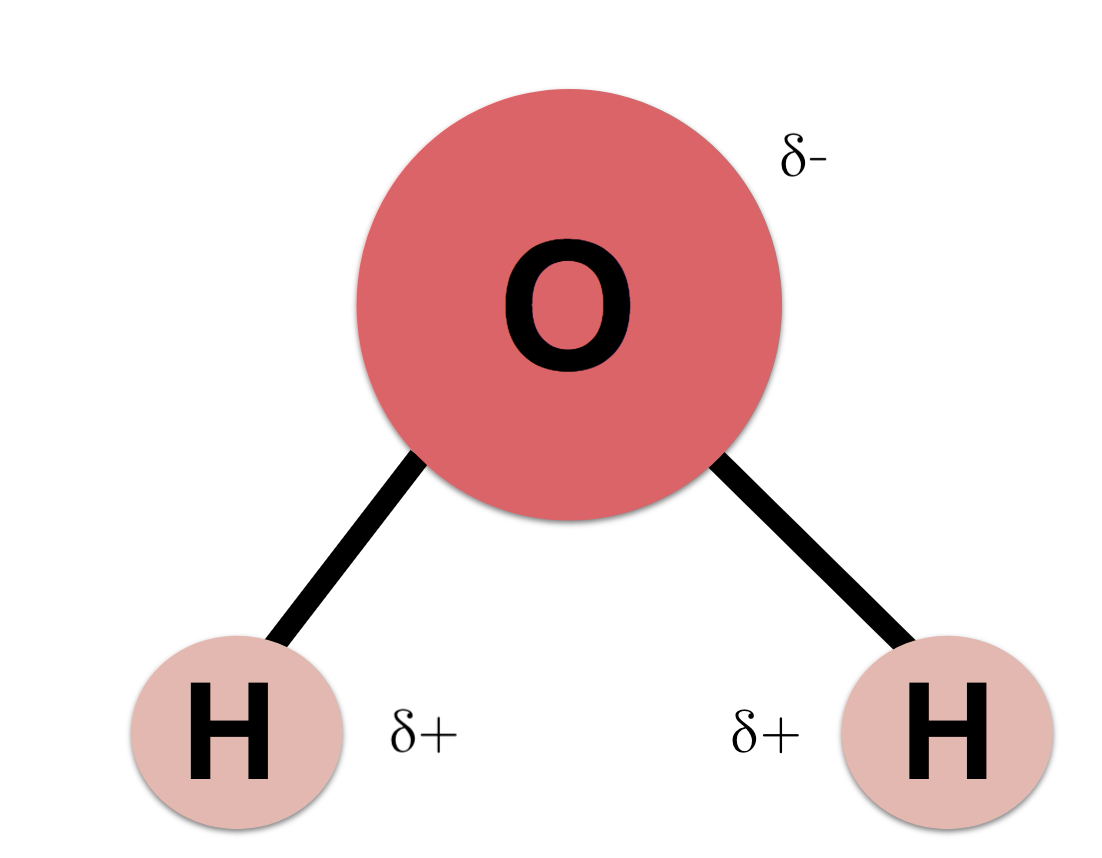
Now the comb is negatively charged and NEW FACT water is polar (meaning that it has negative and positive side to its molecules). When placing the negative charged comb near water, the positve side of the water will draw near or be attracted by the comb. That's why you see water coming closer to the comb. Try it at home.
What is Electricity?
Now is time for the BIG QUESTION and BIG ANSWER of the day.
What is Electricity?
Well electricity, just as we looked previously, is a movement of electrons as we also call current.
What causes the movement or flow of electrons?
A battery and the way it does is that a collection of electrons are formed at one side of the battery leaving the opposite side completely positive charged with no electrons present. Now the electrons want to go at the opposite side and need a passage way to do it. So if you connect a wire or something to act as a path between the opposite sides, there will be a flow of electrons. You just formed a circuit.
What are coulombs?
The total batch of electrons that are moving about.
Cell
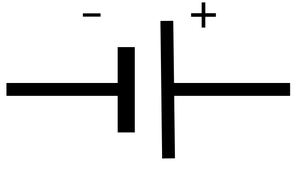
Ammeter

Voltmeter

Open Switch

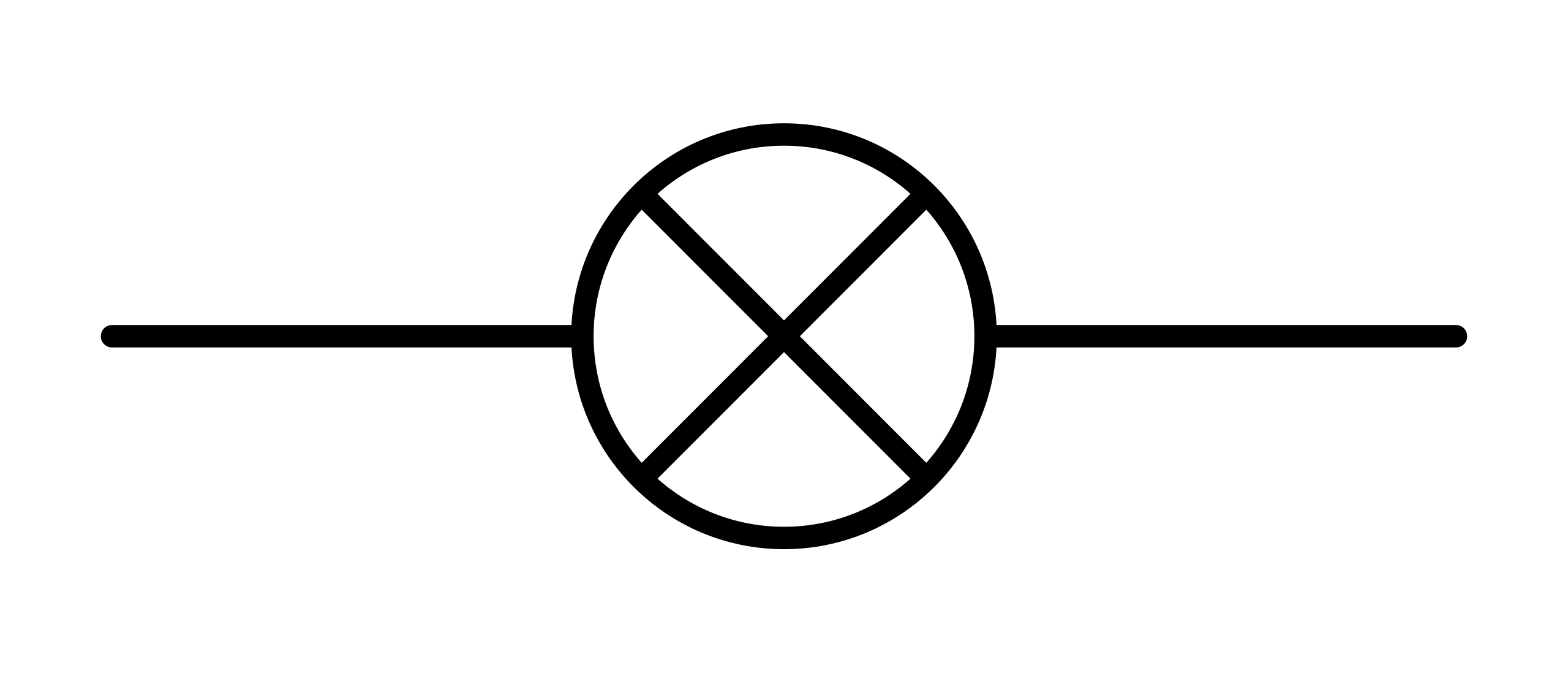
lamp
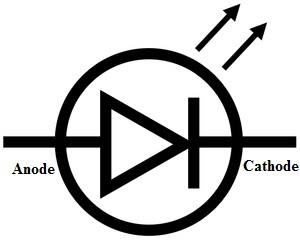
Diode
LED
Resistor

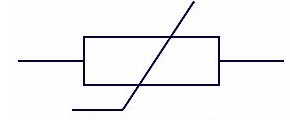
Variable Resistor

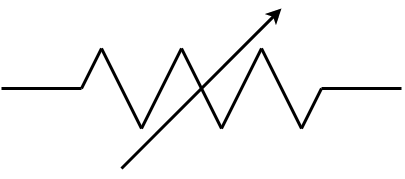
Fuse

Thermistor
LDR
![What is LDR? (Photoresistor) - Types, Working, Application, Diagram & Symbol [Complete Details] - Engineering Learn](https://engineeringlearn.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/LDR-Symbol.jpg)
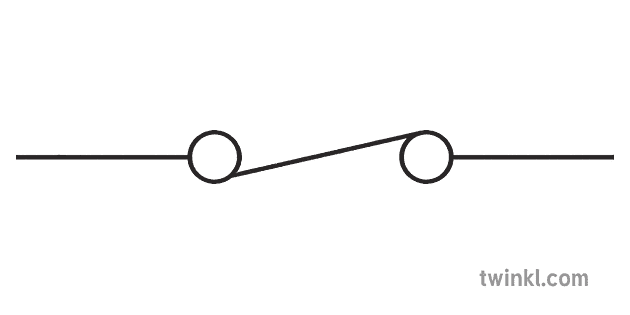
Closed Switch
What is Charge?
Charge is the energy given from a charged object like an electron.
What is the equation that links Charge, current an
Charge = Current x Time
How to work out Potential Difference? or What equa
Potential Difference (Volts) = Current x Resistance
Current in Series Circuit
The current in a series circuit is the same.
Current in a Parallel Circuit
The current in a parallel circuit splits between the branches/ladders.
Potential Difference in a Series Circuit
The potential difference in a series circuit is split up across the devices.
Potential Difference in a Parallel Circuit
The Potential Difference in a Parallel Circuit is the same.


Comments
No comments have yet been made