Biopsychology
0.0 / 5
- Created by: Niamh Crawford-Thomson
- Created on: 09-02-19 12:35
KEY ASSUMPTIONS OF BIOPSYCHOLOGY
- Behaviour and experiences are caused by activity in the nervous system
- The nervous system transmits signals for communication via billions of nerve cells
- Nerve cells communicate with each other through electrical and chemical impulses
1 of 14
NEURONS
- Cells that conducts nerve impulses
- The things that people thinks, say, do and feel are controlled by electrochemical events occuring between neurons
2 of 14
TYPES OF NEURONS
- Sensory neurons carry messages from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system, they have long dendrites and short axons
- Relay neurons connect the sensory neurons to the motor neurons or other relay neurons, they have short dendrites and axons
- Motor neurons connect the central nervous system to the effectors e.g muscles or glands, they have short dendrites and long axons
3 of 14
ELECTRIC TRANSMISSION
- In resting neurons the inside of the cell is negatively charged and the outside positively charged
- When activated by a stimulus the inside becomes positively charged for a split seconed creating an action potential
- This creates an electrical impulse that travels down the axon toward the end of the neuron
4 of 14
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
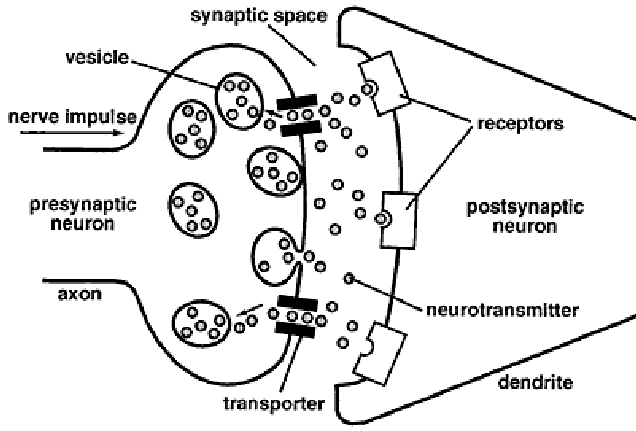
- Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles at the end of the neuron (pre-synaptic terminal)
- When the electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron these neurotransmitters are released into the synapse
- These neurotransmitters move along the synapse and attach to the receptors on the dendrite of the cell (post-synaptic terminal)
- Enzymes are then released into the synapse and any left over neurons are either destroyed by the enzymes or taken back up in a process called reuptake
5 of 14
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM

6 of 14
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Made up of the brain and the spinal cord
- The brain is the centre of all consciousness and the spine is responsible for reflex actions
- The central nervous system connects nerves to the peripheral nervous system
7 of 14
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Transmits messages via millions of neurons to and from the central nervous system
- It is subdivided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system
8 of 14
THE SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Part of the peripheral nervous system that is responsible for carrying sensory and motor information to and from the spinal cord
9 of 14
THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Governs vital functions in the body e.g breathing, heart rate and digestion
- Subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
10 of 14
PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Increases digestion, decreases heart rate, contracts bladder e.t.c
- Your parasympathetic nervous system kicks in to return you body to normal after a response to fear
11 of 14
SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
- The sympathetic nervous system acts opposingly to that of the parasympathetic nervous system
- E.g it slows digestion, increases heart rate, dilates pupils e.t.c
- It kicks in as a response to fear of the environment, it forms part of the fight or flight response
12 of 14
FIGHT OR FLIGHT RESPONSE
- The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for this
- It creates bodily changes when we are faced with a situation in which we may need to defend ourselves or escape
- Anxiety and fear are important for survival becuase they are mechanisms to protect are body from stress and anger
- In order to return to normal the parasympathetic nervous kicks in
13 of 14
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- Responsible for bodily functions such as cell growth
- Various glands in the body are responsible for secreting hormones in the bloodstream that can effect any cell that have hormone receptors on them
- The nervous system and endocrine system work together to allow the body to function properly
14 of 14
Similar Psychology resources:
2.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
5.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
4.5 / 5 based on 3 ratings
2.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
2.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5


Comments
No comments have yet been made