Section 7
0.0 / 5
- Created by: aarafa11
- Created on: 11-12-18 15:52
Define species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce a fertile offspring
1 of 51
Define population
A group of individuals, of the same species that occupy the same habitat and can potentially interbreed
2 of 51
Define gene pool
• All the alleles in all individuals •In a population • At the same time
3 of 51
Define allele frequency
• The number of times • An allele occurs • In a gene pool
4 of 51
What does Hardy-Weinberg predict
The proportion of recessive and dominant allele of any gene in a population. It should remain the same in every generation
5 of 51
Condition for Hardy-Weinberg
1) No mutation 2) Population is isolated 3) No selection 4) Population is large 5) Mating is random
6 of 51
What causes variation
• Environment factors • Genetic factors • COMBINATIONJ OF BOTH
7 of 51
Explain crossing over
•Prophase 1 •Homologous pairs of chromosomes pair up. •The chromatids twist around each other • Genetic information is exchanged • Produces a new combination of allele
8 of 51
How does asexual organism increase genetic variation
by muation
9 of 51
Define selection pressure
• The ENVIRONMENTAL factors that limit the population of species
10 of 51
What does selection pressure determine
The frequency of allele in a gene pool
11 of 51
Factors of evolution that effect natural selection
1. Over production of offspring 2. Genetic variety 3. Variety of phenotype that selection operates against
12 of 51
Why does natural selection effect over production of offspring
•High population •Increase intraspecific competition •For the limited resources •Individual will die as they can’t survive
13 of 51
How does natural selection effect over production of offspring
•Mutation help it be better adapted •Will survive better •Pass advantageous allele to offspring •Increase allele frequency
14 of 51
Define ecosystem
•Is a system made up of a community •And all the non-living factors of its environment
15 of 51
Define habitat
•Where all the organisms usually live •It is characterised by the physical condition •And the type organisms present
16 of 51
Define Ecological niche
•organisms role/position in an ecosystem •terms of its interaction •With abiotic and biotic factors
17 of 51
Where does competitive exclusion principle take place
inter specific competition
18 of 51
What is competitive exclusion principle
•Where 2 species •Are competing •For limited recourse •Will eventually eliminate the other species
19 of 51
Define Genotype
genetic constitution of an organism
20 of 51
Define phenotype
observable or biochemical characteristic of an organism
21 of 51
Define Gene
the sequence of nucleotide that codes for particular polypeptide
22 of 51
Define allele
different versions of a gene
23 of 51
Define co-dominant
2 alleles both contribute to the phenotype
24 of 51
Define multiple allele
Gene has more than 2 allelic forms
25 of 51
What is mono-hybrid inheritance
Inheritance of a single gene
26 of 51
What is pure breeding
•Breeding repeatedly an organism with the same homologous allele •For the offspring to have the same characteristic
27 of 51
What is F1 generation
TH offspring of two different pure breds
28 of 51
What is the ratio for monohybrid inheritence
3:1
29 of 51
What is the basic law of genetics
In diploid organism= characteristic are determined by allele that occur in pairs. Only 1 of each pair can be presented in single gamete
30 of 51
Define Dihybrid cross
cross involving two genes that control two different characteristics
31 of 51
Why does a characteristic only need one chromosome for it to be expressed
The other chromosome doesnt have an allele so it wont express a phenotype
32 of 51
Why is the expected ration in sex-linkage different to the observed
•Fertilisation is random •Not a large population •Fusion of gamete is random
33 of 51
What is autosomal linkage
situation where 2 or more genes are carried on the same autosome
34 of 51
What is autosome
The remaining 22 chromosome that isn't the sex chromosome
35 of 51
What is epistatis
When the allele of one gene affects or masks the expression of another in they phenotype
36 of 51
The affect of breeder only breeding a dominant allele on the frequency of heterozygous phenotype
Increase in homozygous dominant and a decrease in homozygous recessive
37 of 51
Effects the characteristic of population by stabalisng selection
PRESERVES the AVERAGE phenotype. Selection against extreme phenotype
38 of 51
When does stabilizing selection occur
• environmental condition s is constant • over long period of time
39 of 51
Effects the characteristic of population by directional selection
• changes the phonotype • favouring phenotype in one direction • selection for 1 extreme phenotype
40 of 51
Effects the characteristic of population by distruptive selection
• favours individual with extreme
41 of 51
Why is disruptive selection so important
Brings out evolutionary changes
42 of 51
When does disruptive selection take place
When abiotic factors are in more than 2 forms
43 of 51
How are new species formed
• there is a geographical isolation • mutation will occur • for better adaptations • from selection pressure • the advantageous will be passed to offspring • this will increase allele frequency
44 of 51
What is adaptive radiation
•Combination of allele produced •Subject to selection pressure •Lead to population • Adapting to environment
45 of 51
Where does genetic drift take place
In a small population
46 of 51
What are the types of speciation
Allopatric and sypatric
47 of 51
Define Speciation
is the evolution of new species from existing ones
48 of 51
What is allopatric speciation
Where 2 population become geographically separated. DIFFERENT COUNTRIES
49 of 51
What is sympatric speciation
Population in the same area leading to them becoming reproductively separated
50 of 51
Name given to the stable final stage of any succession
climax community
51 of 51
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Define population
Back
A group of individuals, of the same species that occupy the same habitat and can potentially interbreed
Card 3
Front
Define gene pool
Back

Card 4
Front
Define allele frequency
Back
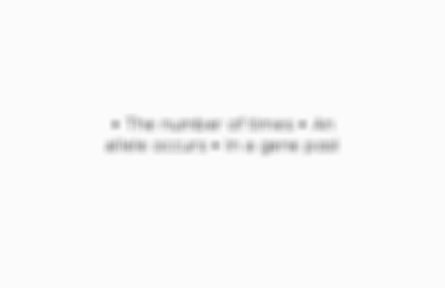
Card 5
Front
What does Hardy-Weinberg predict
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- GCSE English Language Speech Opinions »
- Biology Paper 2 AQA Triple Higher 2023 »
- biology a level electrophoresis question »
- Meiosis help alevel »
- 25 marker essay biology »
- HELPPPP!!! DNA replication & transcription »
- Biology OCR past paper question help. »
- What is DNA repair »
- AQA GCSE Biology Paper 2 Higher Tier [9th June 2023] »
- PCR A level biology »
Similar Biology resources:
0.0 / 5
1.0 / 5 based on 6 ratings
2.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
3.0 / 5 based on 4 ratings
0.0 / 5
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Comments
No comments have yet been made