Radioactivity
0.0 / 5
- Created by: errolshine
- Created on: 24-02-15 16:56
What is the mass and charge of a proton?
Mass = 1 Charge = +1
1 of 26
What is the mass and charge of a neutron?
Mass = 1 Charge = 0
2 of 26
What is the mass and charge of an electron?
Mass = 1/2000 Charge = -1
3 of 26
What is alpha?
It is a helium nucleus that is slow and heavy. Alpha is strongly ionising and weakly penetrative
4 of 26
What is beta?
It is an electron that is light and fast. It is moderately ionising and moderately penetrative.
5 of 26
What is gamma?
Electromagnetic radiation that has no mass and is very fast. It is weakly ionising and strongly penetrative.
6 of 26
What is a positron?
This is an antiparticle of an electron. They have a mass of 1/2000 but their charge is +1 instead of -1. They're light and fast moving and are moderately ionising/penetrating.
7 of 26
Positron radiation is...
positively charged beta radiation.
8 of 26
What is neutron radiation?
Neutrons are more penetrative than alpha or beta and sometimes more than gamma. Neutrons however aren't directly ionising but they can be absorbed by a nucleus. Absorbing a neutron can make a nucleus radioactive.
9 of 26
What happens to these radioactive nuclei?
They emit ionising radiation, so neutrons are called 'indirectly ionising'
10 of 26
What materials are used to shield from neutron radiation and why?
Neutrons are absorbed best by light nuclei and a hydrogen nucleus is lightest of all, so materials like water, concrete and polythene are used to make shielding.
11 of 26
Why can thick lead also be used?
Because neutron absorption often makes nuclei emit gamma radiation so lead is used to stop gamma rays too.
12 of 26
What can make a nucleus unstable?
If it has... too many neutrons/too few neutrons, too many protons and neutrons, or too much energy.
13 of 26
What does an NZ graph show?
N represents the number of neutrons and Z the number of protons. An NZ graph shows a curve of stability for stable isotopes.
14 of 26
What if an isotope is not on the curve?
This means that it is unstable.
15 of 26
What does it mean when an isotope is above the curve?
This means it has too many neutrons to be stable.
16 of 26
What does it mean when an isotope is below the curve?
This means it has too few neutrons to be stable.
17 of 26
What is B- decay?
It is the emission of an electron from a nucleus.
18 of 26
When does B- decay happen?
It happens in isotopes that are neutron rich (so have more neutrons than protons)
19 of 26
What happens in B- decay when a nucleus emits an electron?
One of the neutrons in the nucleus turns into a proton, changing the atomic number by 1. The mass number stays the same.
20 of 26
What is B+ decay?
This is the emission of a positron from a nucleus.
21 of 26
What happens when a positron is emitted from a nucleus?
A proton gets changed into a neutron when a positron is emitted. The atomic number decreases by 1 and the mass number stays the same.
22 of 26
What is alpha decay?
It only happens in very heavy atoms that have lots of protons when the nuclei of these atoms are too massive to be stable
23 of 26
What happens when an alpha particle is emitted?
The atomic number increases by 2 and the mass number decreases by 4
24 of 26
What happens in gamma radiation?
When alpha and beta decay, the nucleus often has excess energy which it loses by emitting gamma rays.
25 of 26
When does gamma radiation occur?
It only ever occurs with beta or alpha decay, it never happens on its own.
26 of 26
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What is the mass and charge of a neutron?
Back
Mass = 1 Charge = 0
Card 3
Front
What is the mass and charge of an electron?
Back
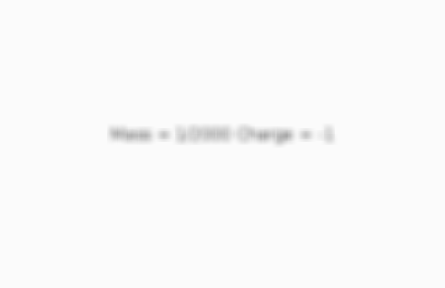
Card 4
Front
What is alpha?
Back

Card 5
Front
What is beta?
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Please help »
- Fun top secret info, Spread to your friends/try the first three »
- Should I do computer science or physics at uni? »
- Question 3 a and b on topic 26.5 of the Jim breithaupt AQA physics book »
- Relative atomic mass »
- Why are my reflexes insane »
- GCSE revision journey »
- A level nuclear question (2) »
- Could Cobalt 60 be used to generate heat energy? »
- Hard Biology question »
Similar Physics resources:
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
4.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
2.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made