Global Systems and Governance
0.0 / 5
- Created by: Noah Richardson
- Created on: 12-12-22 11:45
what is meant by Globalisation?
countries are getting more inter-connective. enabled by technology and transport developments, boosts interconnectivity. encompasses trade, politics and cultural exchanges.
1 of 39
what is economic globalisation?
intensification of economic interrelations around the globe. encompasses emergence of a new global economic order, internationalisation of trade and finance, changing of power of TNCs, and the enhanced roles of international economic institutions.
2 of 39
what is political globalisation?
intensification and expansion of political interrelations around the globe. includes the modern-nation state system and its changing place in todays world, role of global governance, direction of our global political systems.
3 of 39
what is cultural globalisation?
intensification and expansion of cultural flows across the globe. topics under this include discussion about the development of a global culture, or lack of thereof, the role of the media in shaping our identities and desires, globalisation of languages.
4 of 39
what is ecological globalisation?
includes population growth, access to food, worldwide reduction in biodiversity, the gap between rich and poor as well as between the global North and South. human induced climate change and global environmental degradation.
5 of 39
what is meant by a shrinking world?
refers to how quick we can get across the world due to transport improvements.
6 of 39
what are periphery areas?
areas are poorer and may experience exploitation, economic leakage and out migration. LICs in Africa, Central Asia and parts of Latin America are in these peripheries.
7 of 39
what are loans?
money that is borrowed from someone.
8 of 39
what is meant by capital?
can take many forms but for the purpose of this it will refer to capital as money.
9 of 39
what are core areas?
economically important and attract investment, capital and people. these include HICs like the US, Canada, western Europe and Japan to be core areas.
10 of 39
what is meant by aid?
provide support or help. can take many different forms ranging from giving money and loans to providing technology and expertise to providing food and rescue teams.
11 of 39
what is meant by debt repayment?
paying back of money that you have borrowed.
12 of 39
what is meant by Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
investment made by overseas governments, businesses or individuals in foreign enterprises.
13 of 39
what is meant by remmittances?
money sent home to friend and family by migrants living in a different location (often abroad).
14 of 39
what is meant by repatriation of profits?
TNCs operating in foreign countries will normally send any profits made back to the TNCs HQ. this is also known as economic leakage.
15 of 39
what is meant by trade?
movement of goods and services from producers to consumers.
16 of 39
what is comparative advantage?
countries should specialise in producing goods and services they excel in producing. should import what they aren't good at producing. make trade easier as there less barriers in accessing the market. rationalises trade and increase production.
17 of 39
what is protectionism?
government policy restricting international trade help domestic industries. Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) of the EU. EU imposes tariffs rates on a range of agricultural markets, protects European farmers from imported agricultural goods.
18 of 39
what is meant by free trade?
policy in which a government doesn't discriminate against imports or interfere with export by applying tariffs (to imports) or subsidies (to exports). trade agreements provides state with free access to one another's markets and break down "protectionism"
19 of 39
what is meant by outsourcing?
obtaining key products from alternative, cheaper locations, often abroad, than original home-sources. recently TNCs are using suppliers closer to home due to risks of supply chain disruption due to natural hazards and conflict in Middle East, North Africa
20 of 39
what is meant by acquisition?
TNCs launch a takeover of a company in another country. seen by Tata group buying Tetley a British company for $450 million in 2000- made Tata go on the global arena. 3/5 of their revenue comes from outside India.
21 of 39
what is meant by mergers?
two firms in different countries join forces, usually voluntarily, to create a single corporate entity.
22 of 39
what are trading blocs?
associations between different governments that promote and manage trade. they remove trade barriers between their members, while keeping common barriers to countries who aren't part of the bloc. they are typically regional like the EU.
23 of 39
what is a Special Economic zones?
areas that have different trade and investment rules to the rest of the country. they increase trade while keeping barriers in the rest of the country. increase volume of trade in emerging economies and less developed countries.
24 of 39
what are SDT agreements?
WTO's special differential treatment (SDT) agreements allow least developed bypass developed countries' tariffs. EU's Everything But Arms (EBA) Agreement allow least developed export products to EU without paying tariffs. diversify industry.
25 of 39
what is meant by trade liberalisation?
process of trade becoming free from trade restrictions.
26 of 39
what is a TNC?
where a company has their production of goods and services, foreign investment and income and asset management in more than one country. they are footloose industries- not geographically tied to a country.
27 of 39
what is meant by global supply chain?
many activities for a product to go through many factories and the organisation required to produce goods or services and then to eventually bring them to consumers after they are done.
28 of 39
what is vertical integration?
company takes over other parts of its supply chain. do it through mergers, acquisitions and FDI.
29 of 39
what is Horizontal integration?
company merges with or take over another company at the same stage of production (retail chain might take over another retail chain). e.g., Disney in 2006 took over PIXAR studios- both firm production companies.
30 of 39
what is meant by Economies of scale?
cost advantage reaped companies when production becomes efficient. due to this TNCs can profit, they ensure a higher share price and can absorb, put out of business small businesses by capturing majority of market and offering product at low price.
31 of 39
what is offshoring?
moving part of a company's production process to another country. builds new factories in China, where wage rates are lower. reduces cost TNC's pay. tax rates lower. closer raw materials reduces transport cost, environmental regulations. some produce own.
32 of 39
what is outsourcing?
process where a firm contracts with another company to obtain goods and services from it. this is more flexible than offshoring, TNCs can switch suppliers if there is a cheaper source out there. however, will lead to less control over the production.
33 of 39
what is McDonaldisation?
states that society adopts the characteristics of a fast-food restaurant. fast-food restaurants come to dominate more and more. this is called western globalisation.
34 of 39
what is Glocalisation?
a product or service will be adjusted to accommodate the user or consumer in a local market such as taste, culture and laws. e.g., McDonalds only has vegetarian outlets in some parts of India due to the local Hindu belief.
35 of 39
what is a Global Common?
area lack of one nation ownership. responsibility to protect them. they are at the heart of global research. all important environmentally. any slight action on them could have global ramifications. we are reliant on them. extreme environment.
36 of 39
what are hyperglobalists?
globalisation as irrelevancy of nation state due to new transactional networks of production, trade and finance. see as victory for capitalism over socialism. consumerism is forefront. spreading liberal democracy. see more homogeneity of cultures.
37 of 39
what are sceptics?
globalisation not new and suggests was happening in 19th century. disagree with hyperglobalists and say labour is relatively immobile and protectionist policies limit amount free trade. nation states = most important. homogeneity exists.
38 of 39
what are transformationalists?
less extreme and between hyperglobalists, sceptics. see the change as extension of colonial society. see nation governments as changing, not becoming redundant. see states actively engaged in its own economic, cultural issues, increases unevenness.
39 of 39
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
intensification of economic interrelations around the globe. encompasses emergence of a new global economic order, internationalisation of trade and finance, changing of power of TNCs, and the enhanced roles of international economic institutions.
Back
what is economic globalisation?
Card 3
Front
intensification and expansion of political interrelations around the globe. includes the modern-nation state system and its changing place in todays world, role of global governance, direction of our global political systems.
Back

Card 4
Front
intensification and expansion of cultural flows across the globe. topics under this include discussion about the development of a global culture, or lack of thereof, the role of the media in shaping our identities and desires, globalisation of languages.
Back

Card 5
Front
includes population growth, access to food, worldwide reduction in biodiversity, the gap between rich and poor as well as between the global North and South. human induced climate change and global environmental degradation.
Back
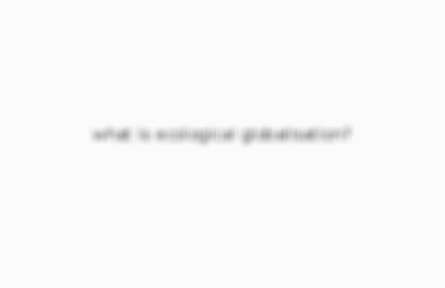
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Eduqas A Level Geography Exams »
- GCSE Citizenship Revision »
- A level Geography revision »
- Rida's experience studying MA Peace, Resilience & Social Justice »
- Edexcel A Level Politics Paper 3B: 9PL0 3B - 17 June 2022 [Exam Chat] »
- AQA geography a level 2023 past paper help »
- AQA A Level Geography Paper 2 (7037/2) - 6th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- A-level Geography Study Group 2023-2024 »
- Help one out »
- AQA A Level Geography Paper 2 7037/2 - 8 Jun 2022 [Exam Chat] »
Similar Geography resources:
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
4.5 / 5 based on 3 ratings
4.0 / 5 based on 4 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made