Crop production systems - Potatoes I
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
- Created by: Joe Cluley
- Created on: 19-05-15 16:08
When was the potato introduced into england?
16th century.
1 of 56
What did potatoes provide high yields of?
Protein, carbohydrates and energy.
2 of 56
What is the average yield per hectare? Is it increasing?
45 T/Ha. Yes.
3 of 56
How many producers supply to the UK market?
fewer than 3000.
4 of 56
How many million tonnes of potatoes are produced each year?
5-6 million tonnes anually.
5 of 56
What is the annual consumption of potatoes per head per year?
110kg/head/year.
6 of 56
What is the consumption of fresh potatoes vs processed potatoes?
45% fresh/55% processed.
7 of 56
Who dominates the supply of potatoes?
Supermarkets.
8 of 56
Of all the potatoes grown annually, how many go for human consumption?
80%
9 of 56
How many potatoes annually go for seed?
10%
10 of 56
What is the remaining 10% used for?
Stockfeed.
11 of 56
Give examples of processed potatoes?
Frozen chips, crisps, ready meals.
12 of 56
How much does it cost to grow 1 Ha Of potatoes?
£5000
13 of 56
What is a price for potatoes?
Volatile, £50-400 per tonne. often weather dependant.
14 of 56
Can anyone grow potatoes?
Requires specific soil types and specialist machinery.
15 of 56
Are potatoes easy to grow?
No, require good crop husbandry and attention to detail.
16 of 56
What does variety choice depend upon?
The intended market. Chipping, crisping, fresh.
17 of 56
Can varieties be pest and disease resistant?
Yes.
18 of 56
What is one feature of a potato intended for the chipping and crisping market?
High DM.
19 of 56
What qualty does a potato intended for the fresh market enhibit?
Uniform shape with good cooking and peeling qualtiies.
20 of 56
1 variety of a fresh produce potato?
Maris piper.
21 of 56
1 variety of a chipping potato?
Shepody
22 of 56
1 example of a crisping potato?
Lady rosetta.
23 of 56
can potatos be grown on contract?
Yes, often with volumes and prices set.
24 of 56
what are non contract potatoes known as?
Free buy potatos, and are subject to price fluctuations.
25 of 56
What are first early potatoes?
Planted for harvest in may - aug for immediate sale.
26 of 56
What are second earlies?
early planted for immediate sale or long term storage.
27 of 56
What are main crop potatoes?
Harvested in the autumn for long term storage.
28 of 56
why can potatoes not be grown in close rotation?
because PCN builds up in the soil.
29 of 56
How many years should you leave between potato crops?
Traditionally 1/4 but now 1/6 or however long you can!
30 of 56
What characteristic of soil do potatoes require?
Fertile soils and high fert inputs. good sturcture. irrigation and fert has improved potato production on sandy soils.
31 of 56
Climate requirements for potatoes.
Ideally a dry spring for seedbed prep. Protection from late frosts. Low levels of rainfall at harvest.
32 of 56
Seedbed prep for potatoes.
Tillth free from stones and clods. SUbsoiled. ploughed. ridged. destoned. planting.
33 of 56
What crop do potatoes usually follow?
Wheat
34 of 56
What can happen to the residual fertiliser in the soils?
They can be of benefit to the following cash crop.
35 of 56
With leftover fertiliser in the soils, what are potatoes known as because of this?
A nutrient builder.
36 of 56
WHat does subsoiling acheive?
Creates fissures at depth. Breaks compaction pans. essential on some soil types. Improves drainage.
37 of 56
Wat does ploughing acheive?
Buries trash. Loosens top soil. Creates depth of tilth. begins weed control. Lets air in. Can dry out soils in dry years.
38 of 56
What are the benefits of bed forming?
Less web agitation on the harvester and so less chance of damage. Ensures wheelings and crop are kept seperate. Moves all cultivated soil into a bed. No clods at lifting.
39 of 56
What is bed rotivating?
When a special rotivator used to rotivate in situ beds. Only needed in heavier soil types. Slow and expensive operation.
40 of 56
Why is destoning carried out?
This is to prevent harvest inequality and remove the chance of clods damaging the tubers at lifting.
41 of 56
What does a destoner acheive?
A fine tilth throughout the seedbed. Weed control.Improved tuber soil contact. Easier lifting.
42 of 56
What plant family do potatoes belong to?
Solanacea family.
43 of 56
What does PCN cause?
Growth retaradtion, and at high populations, damage to the roots and early senescene of plants. Cause of massive yield loss.
44 of 56
What proportion of the UK's arable land is infected with PCN?
60%
45 of 56
Does broadcast nematicide show an increase in potato yield compared to untreated?
Yes, significantly using different products.
46 of 56
How can nematicides be applied to potatoes?
Incorporated into soil cultivations or broadcast across the crop. Additionally, it can be applied in furrow on the planter.
47 of 56
What is the purpose of nematicides?
Control soil bourne pests such as PCN and FLN. Highly toxic.
48 of 56
WHat are seed potatoes?
Potatoes used for seed, not seeds off a potato plants but tubers which sprout and re grow.
49 of 56
How can seed tubers be kept?
in cold storage and planted from there or they can be chitted.
50 of 56
What does chitting usually ensure?
More uniform emergence. Earlier tuber initiation. Earlier sensescence (dieback). Potentially earlier harvesting with added advantages for earlier drill date and less compaction issues on wet ground.
51 of 56
How is seed chitted?
Seed is ages by using temperature and light to encourage the seed tuber to produce a strong and healthy chit (sprout).
52 of 56
How deep are potatoes planted?
15cm.
53 of 56
How far apart are potatoes planted?
Between 20-40cm depending on market and variety.
54 of 56
can fertilizers be applied during planting?
Yep, N P K can all be applied during planting.
55 of 56
Can potato seeds be treated?
Yep, can be treated to control soil and seed diseases.
56 of 56
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What did potatoes provide high yields of?
Back
Protein, carbohydrates and energy.
Card 3
Front
What is the average yield per hectare? Is it increasing?
Back

Card 4
Front
How many producers supply to the UK market?
Back

Card 5
Front
How many million tonnes of potatoes are produced each year?
Back
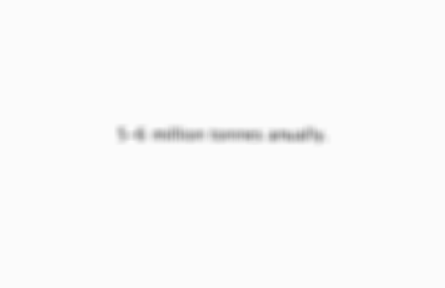
Related discussions on The Student Room
- How to introduce new foods to diet? »
- Why am I prone to infection »
- How to reset my body clock? »
- Meal ideas? »
- University - recipe suggestions for students »
- Triple biology paper 1 2024 aqa unofficial mark scheme »
- Masters Dissertation Guidance »
- Helpful little memory tricks I use for AQA GCSE Biology »
- How to budget £50 a week living at Kingston University »
- 2 day water fast - on antibiotics for acne »
Similar Agriculture resources:
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
4.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5


Comments
No comments have yet been made