Chemistry GCSE
0.0 / 5
- Created by: Jamie Hall
- Created on: 26-02-20 17:43
What is the atomic number?
Number of protons
1 of 39
What is the mass number?
Number of protons and neutrons
2 of 39
What is an isotope?
Same number of protons but different number of neutrons
3 of 39
Explain paper chromatography:
• Pencil line • Dot • In water – ink not touching • Mark solvent front • Calculate Rf Value
4 of 39
What are the different forms of separation?
• Crystallisation • Evaporation • Filtering • Chromatography • Distillation
5 of 39
Describe group 1 elements?
Low boiling and melting points Less dense More reactive
6 of 39
Describe halogens?
High boiling and melting points More dense Bleaches / Coloured gases Diatomic
7 of 39
Describe noble gases?
Unreactive Dense Full outer shell
8 of 39
Ionic Bonding?
• Positive metal + negative non-metal • Electrostatic force • High boiling point • Conducts when aqueous or liquid
9 of 39
Covalent Bonding?
• Sharing of electrons • Non-metals • Simple molecule • Intermolecular forces • Low boiling point • Does not conduct
10 of 39
Metallic Bonding?
• Positive metals • Delocalised electrons allow it to conduct electricity • High boiling points
11 of 39
Test for chlorine?
Bleach damp litmus paper (white)
12 of 39
Test for oxygen?
Relights glowing splint
13 of 39
Test for carbon dioxide?
Limewater cloudy
14 of 39
Test for hydrogen?
Squeaky Pop
15 of 39
Test for metals?
Conduct electricity
16 of 39
How does increasing the temperature affect the rate of reaction?
The particles move faster, therefore they collide more frequently and have more energy so more of the collisions will have enough energy to react.
17 of 39
How does increasing the concentration and pressure affect the rate of reaction?
There are more particles knocking about in the same volume of water. Likewise, with pressure. This makes collisions more frequent.
18 of 39
How does increasing the surface area affect the rate of reaction?
Breaking it up into smaller pieces will increase its surface area. Collisions more frequent.
19 of 39
How does using a catalyst affect the rate of reaction?
They decrease the activation energy.
20 of 39
Formula for rate of reaction:
Amount of reactant used or amount of product formed/Time
21 of 39
Three ways to measure the rate of reaction?
1. Precipitation and colour change (Cloudy) 2. Change in mass (usually gas given off) 3. The volume of gas given off
22 of 39
What is a closed system?
None of the reactants or products can escape and nothing else can get in.
23 of 39
What is le chatelier’s principle?
You can change the conditions of a reversible reaction at equilibrium and the system will try to counteract those changes.
24 of 39
How do properties of hydrocarbons change when the chain gets longer?
• Shorter = More runny • Shorter = More flammable • Shorter = More volatile
25 of 39
What is the general formula for an alkane?
CnH2n+2
26 of 39
What is the test of alkenes?
Add bromine water, it should turn from orange to colourless
27 of 39
What are alkenes used for?
Polymers (plastics)
28 of 39
What is phase 1 of the evolution of the atmosphere?
Volcanoes give out gases. Atmosphere made up of carbon dioxide and virtually no oxygen. Volcanoes released nitrogen, water vapour and methane.
29 of 39
What is phase 2 of the evolution of the atmosphere?
Oceans, algae and plants absorbed the carbon dioxide.
30 of 39
What is phase 3 of the evolution of the atmosphere?
Plants etc released oxygen by photosynthesis and levels of oxygen built up over time.
31 of 39
Composition of earth’s atmosphere today?
• 78% Nitrogen • 21% Oxygen • 1% Small proportions of other gases including carbon dioxide
32 of 39
How to reduce carbon footprint?
• Renewable energy sources • More efficient processes • Governments taxing companies • Technology that captures CO2
33 of 39
How are metals recycled?
By melting them and then casting them into the shape of the new product.
34 of 39
How is glass recycled?
Glass is separated by colour and chemical composition. It is then crushed and melted to be reshaped for use in glass products.
35 of 39
Describe the effect of each pollutant - carbon dioxide?
Burning fuels = Causes climate change
36 of 39
Describe the effect of each pollutant - sulphur dioxide?
Burning fuels = acid rain that kills plants
37 of 39
Describe the effect of each pollutant - nitrogen oxide?
Nitrogen and oxygen reacting in the air = Acid rain
38 of 39
Describe the effect of each pollutant - particulates?
Unburnt hydrocarbons = global dimming
39 of 39
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What is the mass number?
Back
Number of protons and neutrons
Card 3
Front
What is an isotope?
Back
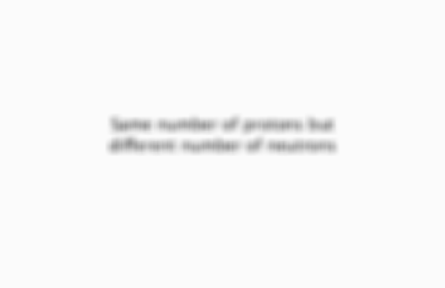
Card 4
Front
Explain paper chromatography:
Back

Card 5
Front
What are the different forms of separation?
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- GCSE Chemistry Study Group 2023/2024 »
- I don't know if i can make it to medicine or pharmacology lol »
- Is chemistry a level hard? »
- Urgent Help!! MEDICINE AND GCSEs »
- A level choice dilema!!! »
- Get into medicine with no chemistry? »
- GCSE Subjects to go to medical school »
- How many GCSEs are you getting? »
- Getting into med school without alevel chem »
- GCSE subject choice »
Similar All resources:
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made