-immobile, single-celled parasite causes malaria- one of the most
common diseases in humans worldwide
- It spends some part of its life in female mosquitoes, which inject the protist into a human’s bloodstream when it bites. The protist then continues its develop inside the human red blood cell.

Plasmodium falciparum
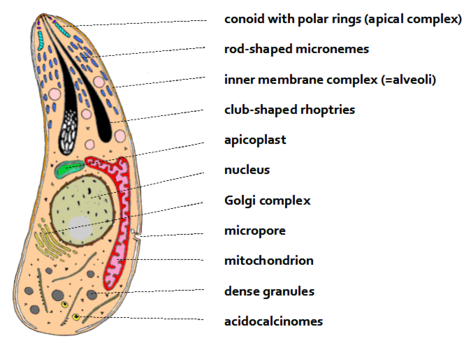
know nucleus, mitocondrion
denuse granules-secretaory organelles
micropore-function as cytostomes and the invaginations (infolding of one part in part of another organism, starts with gradulation) take in material by means of pinocytosis
apicoplast- essential to parasite survival
microenmes- smooth ER, site of detoxification of drugs and poison

Plasmodium vivrax
Comments
No comments have yet been made