Physics - Energy
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
- Created by: twilkinson
- Created on: 04-06-17 12:23
Name 5 types of energy
Kinetic, electricity, thermal (heat), light, sound, potential (elastic, gravitational), chemical/stored, nuclear
1 of 33
What is an energy system?
A group of or solitary object that uses or converts energy
2 of 33
Why does the energy store in a system change?
Because the energy currently being produced turns into another, for example electricity is turned into heat energy when boiling a kettle, and chemical energy is turned into kinetic energy whilst driving a car
3 of 33
What is energy measured in?
Joules
4 of 33
What is the equation for kinetic energy?
0.5 X mass (kg) x Velocity (m/s )
5 of 33
How do you calculate gravitational potential energy?
Mass (kg) X gravitational field strength X height (m)
6 of 33
What is the gravitational field strength on Earth?
10 to 1 significant figure
7 of 33
How do you calculate elastic potential energy?
Elastic potential = 0.5 X spring constant X extension (cm)
8 of 33
How do you calculate the amount of energy stored in or released by a system as it's temperature changes?
Change in thermal energy (J) = mass (kg) X specific heat capacity (J/kgcm ) X temp change ( C)
9 of 33
What is the specific heat capacity of a substance?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of said material by 1 C
10 of 33
What is power?
The rate at which energy is transferred or the rate at which work is done
11 of 33
What is the equation to calculate power?
Power (W) = energy transferred (J) time (S)
12 of 33
Can energy be destroyed? What can happen to it?
Energy cannot be destroyed, it can only be transferred usefully, stored or dissipated. It cannot be created either
13 of 33
Describe two energy transefrs
Light bulb - electricity in, heat and light out, fan - electricity in, kinetic and sound out, car - chemical in, light, kinetic and heat out, spring - kinetic in, elastic potential out, instrument - kinetic in, sound out
14 of 33
What is waste energy? Give examples
Waste energy is energy that is created in an energy transfer that is not wanted, such as heat energy from a light bulb, or sound energy from a car
15 of 33
How can we stop unwanted energy transfers in a home?
To keep heat energy in the home to save energy and money, we can do things such as used double glazed windows, roof insulation and wall insulation to keep heat in, and we can use anti draft strips on doors to not allow drafts of air in
16 of 33
What happens when you increase the thermal conductivity rate of a material?
rate of energy transfer by conduction increases
17 of 33
What happens when you decrease the thermal conductivity rate of a material?
rate of energy transfer by conduction decreases
18 of 33
What is rate of cooling of a building affected by?
The thickness and thermal conductivity of it's walls
19 of 33
Define energy efficiency
The percentage of energy produced that is useful
20 of 33
How do you calculate efficiency?
Efficiency (%) = useful input energy (J) total input energy (J)
21 of 33
How can you increase the efficiency of an energy transfer?
you could find ways to provide less input power for the same amount of useful output, or you could find ways to create more useful output for the same amount of input
22 of 33
What are three of the main energy resources used on Earth?
Non-renewable - Coal, oil, gas Renewable - Nuclear, biofuel, wind, hydroelectricity, geothermal, tidal, solar
23 of 33
What is a renewable energy resource?
An energy source that can be replenished once it is used - it is infinite
24 of 33
What is a non-renewable energy resource?
An energy source that cannot be replenished once it is used - it is finite
25 of 33
What are the main uses of energy resources?
Transport, electricity generation and heating
26 of 33
Name three renewable energy resources
Wind, solar, tidal, hydroelectric, geothermal, nuclear, biofuel
27 of 33
Name three non-renewable energy resources
Coal, oil, gas
28 of 33
Why are some energy resources more reliable than others?
Because most renewable ones (wind, hydroelectric, solar) will only work if there is lots of water, wind or sun at that moment in time, which is not always guaranteed, whereas if you burn a fossil fuel, you are always guaranteed to get energy from it
29 of 33
What are the impacts on the environment of fossil fuels?
They can cause air pollution, acid rain, and creating of harmful mattert
30 of 33
What are the impacts on the environment of renewable fuels?
They are often said to be ugly and ruin the landscape and cost a lot of money to build
31 of 33
What is a big problem caused by burning fossil fuels?
Contributes to global warming - trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere and warming up the planet, which melt the polar ice caps and will cause sea levels to rise
32 of 33
Why can scientists not do anything about global warming?
Because the things being affected (Earth's seas and atmosphere) are global commons (not owned by anybody), which means that they do not have the right to go and mess with them without other peoples permission
33 of 33
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What is an energy system?
Back
A group of or solitary object that uses or converts energy
Card 3
Front
Why does the energy store in a system change?
Back

Card 4
Front
What is energy measured in?
Back

Card 5
Front
What is the equation for kinetic energy?
Back
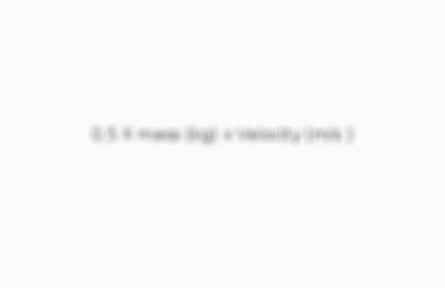
Related discussions on The Student Room
Similar Physics resources:
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
1.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
2.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
3.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5


Comments
No comments have yet been made