Memory
- Created by: ZLomas
- Created on: 30-11-18 13:26
Fullscreen
Long Term & Short Term Memory Pg 44
- Key Terms & Definitions
- Capacity - This is the measure of how much can be held in memory. (7 ± 2)
- Coding - The way information is changed so that it can be stored in memory.
- Duration - How long a memory lasts before it is no longer available.
- Long-term Memory (LTM) - Your memory for events which hav hapeened in the past
- Short-term Memory(STM) - Your memory for immediate events.
- Experiments
- Capacity of STM (Jacobs, 1887)
- Procedure: The particepents were given lists of random numbers to remember each with one more digit than the last. They were given a breif time to remember their lists and then asked to write them down. On average, people remembered 9.3 digits & 7.3 words.
- Evaluation:
- Not Replicated
- Size of chunk affects memory
- STM is not the same for everyone (AO3)
- Study built on by Miller (1956) - Came up with the magic number. (7 ± 2)
- Duration of STM (Peterson, 1959)
- Procedure: Asked 24 particapents to recall a number over a 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 or 18 second period. During the interval they were asked to count backwards from 100. On average the results were 90% after 3 seconds, 20% after 9 and 2% after 18 without rehersal.
- Evaluation:
- Artificial
- Measured displacement not decay
- Duration of LTM (Bahrick et al, 1975)
- Procedure: Asked 400 participents between the ages of 17-74 to try and remember their class mates based on photos of them from their yearbook. 15 years after graduation recognition was at 90%, 48 years was 60%. And at free recall, People were 60% accurate after 15 years and 30% after 48.
- Acoustic & Semantic Coding (Baddeley, 1966)
- Procedure: Participents asked to remember acoustically similar words (sound the same) and semantically similar words (mean the same). It was found that people who remembered acoustically similar words remembered it in STM but not LTM at all & semantically similar words were in STM but got muddled in LTM.
- Evaluation:
- Some experiments show visual codes are in STM (Brandimote et al,1992)
- LTM is not always semantic (but usually is) (Frost, 1972)
- Baddeley may not have teasted LTM as the memory may not have got to the LTM in 20 minutes.
The Multi-Store Model of Memory Pg 46
- Key Terms
- Multi-store Model - An expalnation of memory based on three separate memory stores, and how information is transfered between these stores.
- Sensory Register - Where information collected from the senses (eyes, ears, mouth, nose, touch) is stored.
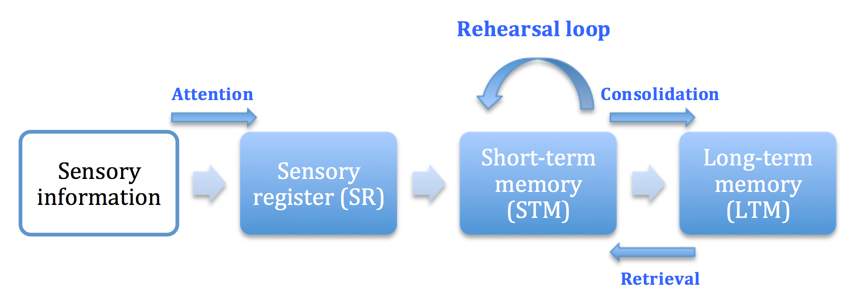
- Evaluation:
- Supporting evidence - Beardsley & Squire et al. 1997
- Different parts of the brain are involved in STM & LTM from study into brain damage - Scoville & Milner 1957
- STM & LTM are different kinds of stores therefore they are not comparible.
Working Memory Model Pg 49
- Key Terms
- Centeral Executive - Monitors & coordinates all other mental functions in working memory.
- Episodic Buffer - Receives input from many sources, temporarily stores this information…


Comments
No comments have yet been made