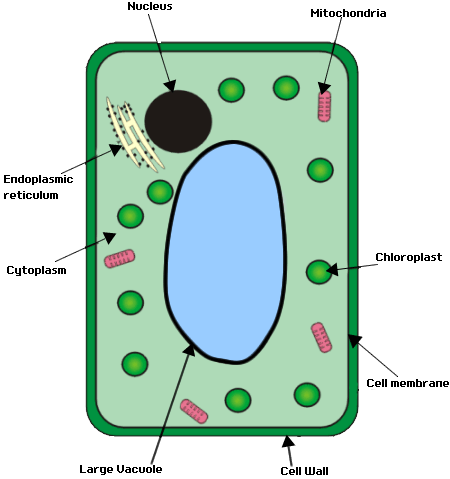
 Also has: ribosomes, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria
Also has: ribosomes, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria
Chloroplast - is filled with chlorophyll and moves around the cell to absorb the maximum amount of sunlight for photosynthesis
Cell Wall - made rigid around the cell to support the plants structure (made of cellulose)
Vacuole - a permenant large bag filled with cell sap surrounded by a membrane which exerts pressure on the cell wall
Comments
No comments have yet been made