Investment Appraisal
- Created by: Leary103
- Created on: 15-01-21 11:22
Investment Decisions
Investment decisions: The process of deciding whether or not to undertake capital investment (the purchase of non-current assets) or major business projects
Investment appraisal: a scientific approach to investment decision making, which investigate the expected financial consequences of an investment, in order to assist the company in its choices
Methods of investment appraisal:
- payback period
- Average Rate of Return (ARR)
- Net Present Value (NPV)
Payback Period
Payback period: the length of time that it takes for an investment to pay for itself from the net returns provided by that particular investment
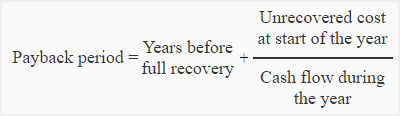
Payback Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- the payback period is easy to calculate
- the concept of payback is easy to understand
- the payback method emphasises cash flow by focusing only on the time taken to return the money - relevant approach for businesses that have some cash-flow difficulties
- by emphasising the speed of return, the payback period is popular with firms operating in markets that are experiencing rapid change because estimates for years in the distant future are going to be less reliable than those for the near future
Disadvantages:
- the calculation of payback ignores any revenues or costs that occur after the point at which payback has been reached - does not consider the overall net return from a project
- It is very difficult to establish a target payback time. Some major investments will take many years to pay for themselves
- Payback values future costs and revenues at the same value as current costs and revenues - does not consider the time value of money in the way that net present value does
- By focusing on payback, the business may be encouraged towards short-termism. A firm using the payback method would fail to look at the long-term consequences of an investment
Average Rate of Return
Average Rate of Return % (ARR%): total net returns by the expected lifetime of the investment (usually a number of years), expressed as a percentage of the initial cost of the investment

ARR Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- The result (a percentage calculation) can easily be compared with the next best alternative (the opportunity cost), such as the percentage interest earned from a savings account
- The ARR shows the true profitability of the investment. It is the only method that takes into consideration every item of revenue and expenditure at its face value
- Percentage returns, such as the ARR, are usually understood by non-accountants
Disadvantages:
- The ARR is harder and more time consuming to calculate than the payback method, so it may rise valuable company time in compiling shortlists of potential investments
- It considers all income and expenditure as equal in value. Thus, projections a long time into the future are given the same importance as predictions of present costs and incomes
Net Present Value
Net Present Value (NPV): the net return on investment when all revenues and costs have been converted to their current worth
NPV Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- NPV is the only method that considers the time value of money. By discounting future figures, NPV recognises that people and organisations place a higher value on money paid/received not than in the future
- As sums of money far into the future are discounted more heavily, this approach reduces the importance of long-term estimates. As long=term estimates are probably the least reliable predictions, NPV helps to make the conclusions more accurate
- NPV is the only method that gives a precise answer. A positive NPV means that, on financial grounds, the investment should be undertaken. A negative NPV means that project should be rejected
Disadvantages:
- NPV is time-consuming and more difficult to calculate than the other methods
- It is more difficult to understand than the other approaches - may mean that decision-makers distrust any conclusions drawn from using this method
- The calculation of NPV is based on an arbitrary choice of percentage discount rate. Although the method is calculated scientifically, the final conclusion often relies on the discount rate used
Factors influencing investment decisions
- Investment criteria: the ways in which a business will judge whether an investment should be undertaken
- Non-financial (qualitative) factors - aims of the organisation, reliability of the data, personnel, the economy, legal requirements, subjective criteria
- Risk and uncertainty: the probability of unforeseen circumstances that may harm the success of a business decision
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis: a technique used to examine the impact of possible changes in certain variables on the outcome of a project or investment
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Digital Marketing Student needing some advice! »
- gcse aqa drama devising log »
- Could someone please help with some feedback »
- a little over a month til a levels - exam practice strategy? »
- Could you give me feedback on this please »
- Which degree course is better for analyst jobs? »
- Unveiling the Realm of Investment Banking »
- Can I get into investment banking with an Accounting and Finance degree? »
- BTEC Business Unit 6 Exam Discussion January 16th 2023 »
- HR Executive »
Comments
No comments have yet been made