Hair and Beauty
- Created by: klaudia_1107
- Created on: 18-03-18 15:15
Hair Structure
Hair Follicle = anchors each hair into the skin (without it our hair would fall straight out).
Inner & Outer Root Sheath = surrounds and protects the growing hair (without these our hair could be damaged in the growing phrase).
Hair Shaft = the part of the hair we can see. Made up of 3 structures:
- Cuticle = the outer layer of the hair shaft (protects the cortex).
- Cortex = provides the hair's strength and determines hair colour and texture.
- Medulla = the inner layer, but not always present in our hair.

Nail Structure
- Nail Plate = protects the nail bed.
- Nail Bed = provides the blood supply.
- Nail Cuticle = protects the matrix from bacteria.
- Matrix = responsible for producing cells.
- Lunula = visible part of the nail.
- Hyponychium = a seal to protect the nail bed.
- Free Edge = protects fingertips.
- Nerve Endings = provides sensation.
.
Skin Structure - Epidermis
Epidermis:
- Basal Cell Layer = bottom layer of cells in the epidermis, attached to dermis where cells reproduce by mitosis.
- Prickle Cell Layer = layer above the basal cell layer, where keratin is produced and injected into cells.
- Granular Layer = layer above the prickle cell layer, where keratinisation takes place.
- Clear Layer = layer above the granular layer forming a waterproof layer.
- Horny Layer = outer layer of the epidermis made of dead, flat keratinised cells, which are shed and help to prevent dehydration.
Skin Structure - Dermis
- Collagen = structural protein fibres that add strength and support to the dermis.
- Subcutaneous Layer = made up of fat cells for protection.
- Elastin = elastic protein fibres allow the skin to stretch and recoll, providing the skin's elasticity.
- Sweat Glands = excretes watery substances onto the skin's surface.
- Sensory Nerve Endings = end organs for pain, touch, heat, cold and pressure sensations.
- Sebaceous Gland = attached to hair follicles creating sebum.
- Arrector Pili Muscle = reacts to cold and heat, traps warm air in the body keeping in heat.
- Blood Vessels = provide nutrients to the skin and help regulate body temperature.
- Dermal Papilia = contains nerve endings and blood capilaries to help nourish the hair.
Skin Structure - Hypodermis
- Fat Cells = provide protection and heat to the body.
- Loose Connective Tissue = body tissue supporting internal structures.
Epidermis = regulates what is allowed to pass in and out of the skin
Dermis = provides the structural support and nutrients for the surrounding layers.
Hypodermis = protective, helps to regulate body temperature by providing insulation.
The Functions of the Hair, Skin and Nails
S - Sensation = reacts to touch and feelings.
H - Heat regulation = helps to keep you warm/cool.
A - Absorption = sucks in the moisture you need.
P - Protection = from UV rays, bacteria etc.
E - Elimination of waste products - sweating.
S - Secretion of oil and water.
Pathogens - Internal Defence
Pathogen = a microorganism that causes infections and diseases.
Internal Defence:
- White Blood Cells surround the pathogen to fight against disease. They can injest pathogens and destroy them, produce antibodies to destroy pathogens.
- Histamine is a natural immune response - it serves as a red flag in immune system, notifying the body of any potential attackers. It causes blood vessels to swell or diliate, so that your white blood bells can quickly find and attack the infection or problem.
- Bacteria and viruses (pathogens) have antigens on their outer cell surface; this makes it recognisable to our body that they are invaders and that they don't belong. Pathogens are recognised by the body due to their antigens and also by the fact that the body cells under attack release chemicals, such as histamine.
Pathogens - External Defence
External Defence:
- Skin's acid mantle creates a natural, slightly acidic, protective layer on the surface of human skin acting as a barrier against bacteria, viruses and potential contaminants that might penetrate the skin. It is secreted by sebaceouse glands. The pH of the skin is between 4.5 and 6.2 - slightly acidic. It prevents bacteria from entering or growing on the skin.
- Unhealthy acid mantle will let moisture escape and cause skin conditions.
- Condom
- Washing hands frequently
Contagious Diseases - Bacterial Infections
Bacterial Infections:
Bacteria = tiny, single-celled organisms of varied shapes. Large numbers inhabit the surface of the skin and can cause skin diseases.
- Impetigo = an inflammatory disease of surface on the skin.
- Carbuncles = red, swollen and painful cluster of boils that are connected to each other under the skin. A boil (or furuncle) is an infection of a hair follicle that has a small collection of pus (ansceses) under the skin.
- Folliculitis = an infection in the hair follicle. Common on the beard area.
All can be contagious.
Contagious Diseases - Fungal Infections
Fungal Infections:
Fungi = microscopis plants. They depend on their host for their existence. Fungi diseases on the skin feed off the waste products of the skin. Some fungi are found on the skin's surface and others attack the deeper tissues.
- Ringworm (tinea capitis) = a fungal infection on the head.
- Ringworm (tinea pedis) = a fungal infection (aka Athletes foot) found on the feet.
- Ringworm (tinea unguium) = a ringworm infection of the fingernails.
All are contagious.
Contagious Diseases - Viral Infections
Viral Infections:
Virus = miniscule entities, too small to see even under an ordinary microscope. Invade halthy body cells and multiply within the cell. The cell walls break down, allowing the virus to escape and attack further cells.
- Herpes Simplex = a reocurring skin condition, appearing at times when skin's resistance is lowered through ill health or stress.
- Warts = small, epidermal skin growths. Warts can be raised or flat, depending on their position.
All are contagious.
Contagious Diseases - Infestations
Infestations:
Infestations = the presence of an unusually large number of insects or animals in a place, typically cause damage or disease.
- Pediculosis Captitis (Head Lice) = small parasites infest the scalp hair.
- Pediculosis Humanus (Body Lice) = small parasites live and feed on the body skin.
- Sarcoptes Scabei (Scabies) - itchy mite, an animal parasite burrows beneath the skin and invades the ahir follicles.
All are contagious.
Types of Tests - Skin Test
Skin test:
To test for an allregy to colour products.
- Negative reaction = no reaction.
- Positive reaction = red, inflammed, itchy skin.
Test should be carried out in the following cirucmstances:
- for a client new to the salon.
- for a client new to colour.
- for a client who has not had a colour treatment in previous 12 weeks.
- if a client changes to a different colour product or shade.
Potential for client to take legal action if hair or scalp is damaged.
Types of Tests - Elasticity Test
To determine the condition of the cortex.
Hair should stretch and return to its normal length without breaking.
This test should be done before any chemical process.
It is potential for the client to take legal action if damage to hair or scalp occurs.
Types of Tests - Porosity Test
To determine the condition of the cuticle.
Hair should feel smooth.
This test should be carried out before any chemical process.
Types of Tests - Strand Test
To check the development of colour or bleach applications.
Remove colour or bleach from strands of hair. The colour result should be as required or it will need further development time.
This test should be carried out during the colour or bleach development process and after manufacturer's recommended development time.
The risk is that the result may not meet requirements.
Types of Tests - Incompability Test
To determine the presence of metallic salts.
If metallic compound are present, hair may change colour, the mixture may bubble or frizz and heat may be created.
This test should be carried out before any chemical process.
The consequence may be disinterigation of hair colour or damage to the hair.
Types of Tests - Hair Pull Test
To determine the amount of hair loss.
Gently lift up clients hair from the bottom and drag your hair upwards. Then hold up a hand up and see how much hair has been pulled out.
This test should be carried out before any chemical treatment.
Skin and Hair
- Hair and skin has a pH value of 5.5 when healthy, which means that hair and skin are slightly acidic.
- Acids and alkalines are present in the human body and are essential for continued life, because they help out bodies to function properly.
- If we know the correct balance of chemicals that our body needs, we will be able to find out which products are suitable.
- If chemicals are not the same combination of pH as skin and hair, manufacturers will be able to advise on how to use them safely.
- Strong acids (skin) - cause skin burns and limit its protective function.
- Weak acids (skin) - soothing to the skin
- Weak acids (hair) - close the cuticle scales and help protect and smooth the hair.
- Strong alkalines (skin) - break down the skin cells and have exfoliating properties.
- Strong alkalines (hair) - swell the hair and have a depilatory action.
Hair
Healthy hair:
The hair is protected by the intact cuticle, which seals in the moisture and natural oils. This helps to maintain strong hair.
Damaged hair:
The loss of moisture and natural oils, makes hair fibres more susceptible to damage.
As well as the skin, it is important that pur hair stays healthy, because we want it to look good and grow well, even after heat and chemical treatments.
Rinsing hair in water or mildly acidic solution reverses any actions and returns the hair to its normal state. In cleaning out hair, most shampoos are alkaline, because they are able to dissolve grease present in the hair. However, alkalines can also damage hair. Rinsing the hair with hair conditioners (contain weak natural acids) will neutralise any excess alkali left in the hair after shampooing and restore the pH of hair to its normal value.
Testing for pH
We can test the pH of chemicals and product by the use of:
- Universal indicator
- Litmus paper
- pH meter
Products within Hair and Beauty sector - Sun Scree
There are many tpes of products used withing hair and beauty sector and it is important that we are aware of their purpose and the effects that they will have on the are we use it for. This is because if we use them for a wrong purpose then they may: cause irritability to the skin, cause spots, cause an allergic reaction. It is important that they are used for their purpose, to make sure that the client remains safe.
Sun Screen
- Reflects and absorbs UV rays.
- Each grade of sun screen protects the skin at different levels.
- Zinc oxide is the best sun screen ingredient.
- There are 3 types of UV rays (C- Cancerous, B- Burning (stronger in summer) and A- ageing).
- UV A is all year round, this is why we should wear SPF all year to protect our skin from ageing.
- Some sun screens filter the UV rays.
Products within Hair and Beauty Sector - Skin Clea
Skin Cleansers:
- Cleanse the skin while remowing foreign materials, such as basteria, dirt, sweat, makeup, etc.
- Helps to remove excess dead skin.
- Helps to prepare for other products.
- Breaks down oils.
Exfoliators:
- The process of exfoliating can be done in different ways (creams, gels with beads, acids, etc.)
- Exfoliation gives a radiant look, could decrease wrinkles (takes off layers of skin (chemical peel)), removes dead skin cells and makes skin smooth.
- Our skin constantly renews.
Products within Hair and Beauty Sector
Mousse/lotion:
- used to control the hair,
- should be stored away from heat, as it could cause explosion/fire.
Serum/Oil/Wax/Gel:
- used to moisturise the hair and tame down the frizz,
- used to style the hair,
- heat should not be used on top of these products - could burn the hair,
- only small amount should be used to avoid losing volume,
- stored away from heat and preferably in a cool, dry place.
Hair Spray:
- hold hairstyle in place
- add volume and texture
- stored away from hear - very flammable.
Products within Hair and Beauty Sector
Heat Protector:
- protects the hair from heat damage
- activate when heat is applied
- heat protector needs to be appriopriate for the temperature you are using on your hair.
Brush:
- used on dry hair
- used to style the hair into a desired hairstyle
Comb:
- different types
- wide-tooth combs are used to detangle wet hair
- can be used to part the hair
Ingredients within Hair and Beauty Sector
Parabens = preservative, anti-fungal/fungicidal and bactericidal (shampoo, anti-ageing cream, shaving foam, shaving gel, moistuiser).
Oxidising Agents = add oxygen to products during a chemical reaction (hair colour/bleach, foundation, sunscreen, perm neutraliser, whitening tooth paste).
Mineral Oils = occlusive to increase moisture levels by providing a physical barrier to skin and hair moisture loss. (conditioner, bath oils, moisturiser, anti-frizz serum, conditioning treatments).
Stabilisers = stop from oils and water from seperating, so that the product is usable for longer. They keep produts stable (cleansers, toners, hair conditioners, moistuisers).
Emollients = provides some occlusivity and improve the appearance of skin by smoothing flaky skin cells (lipstick, moisturisers, body lotion, lip balm).
Antiseptic = used to prevent infections on the skin that are caused by bacteria (deodrant, soap, cleansers, mouth wash).
Ingredients within Hair and Beauty Sector
Humectants = keep the moisture content of the roduct and adds it to skin and hair (lipsticks, anti-ageing creams, eye creams, hair conditioner).
Emulsifiers = keep the ingredients in a product mixed together (moistuisers, sun block, night creams, body lotions).
UV Filters = protect hair and skin from damage from the sun and bright light. Protects hair from colour fading in the sunlight (anti-wrinkle cream, hair clour, hand cream, sun screen, colour protection shampoo & conditioner, nail strenghtener).
Exfoliators = removes dead skin cells. Can be abrasive (scratchy) or chemical, (sugar, salt, tiny plastic beads, pumice stone, fruit acids).
Pigments = intestify strong colour (eye shadow, eye liner, lipstick & mascara).
Atringents = have a drying effect on the skin, remove oil and help to close the pores (skin toners, facial washes, spot treatments).
Allergies
Allergic rections can be mild or very serious.
A mild allergic reaction is when something causes itching, redness of skin, flaky skin, dermatitis or a rash.
A serious allergic reaction can cause intense itching, swelling or anaphylactic shock.
Anaphylatic shock:
- felling dizzy
- losing conciousness,
- unable to breathe properly,
- tongue may swell up and block breathing tubes,
- low blood pressure,
- heart failure,
- DEATH.
People may be allergic to many things, such as bee stings, chemicals found in hair and beauty products. This is why it is important to carry out tests before treatments.
Ingredients that can cause allergies
Paradyes - found in dark coloured permanent hair dyes. Usually man made from coal tar.
Detergents - can cause contact dermatitis (flaky, itchy, red skin). Can appear as small blisters that ooze. Appear shortly after touching the product.
Oils - products can contain oils made from peanuts, coconut, pine nuts or lanolin (from sheeps wool). All of these are known for causing allergic reactions. They usually result in contact dermatitis.
Methylisthiazoline - found in 'rinse off' priducts (shampoo, conditioner, facial wash, bubble bath, shower gel). It is a toxic ingredient and can cause nerve damage. It is a chemical used to kill microorganisms which allows the product to be usable for longer.
Common Words
Hydrating = something adds moisture.
Hypoallergic = tested to reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Non-comedogenic = reduced the risk of clogging the pores/acne.
Soothing = calming, reduces the redness of the skin.
Regenerating = encourages cells to renew themselves.
Anti-oxidant = stops the oxidation process and helps to prevent ageing.
Stimulating = encourages growth & repair.
Depilatory = removes unwanted hair.
Dihydroxyacetone (DHA) = a pigment used in a fake tan.
Paraphenylenediamiie = a pigment used in permanenet hair colour.
Ethical Considerations for Testing Cosmetics - Reg
Cosmetic products = any substance or mixture intended to be placed in contact with the various external parts of the human body.
Why cosmetic products are tested prior to being made available? - For safety (Cosmetic Products (Safety) Regulations) and to fit its description, be fit for purpose and satisfactory quality.
The Trade Description Act 1986 makes it an offence for a trader to make false or misleading statements about goods or services.
It carries criminal penalties and is enforced by trading standards officers, making it an offence for a trader to:
- apply a false trade description to any goods,
- supply or offer to supply any goods to which a false trade description has been applied,
- make certain kinds of false statements about the provision of any services, facilities or accommondation.
Sale of Goods Act: The product must be satisfactory quality, the product must perform as expected.
Ethical Considerations for Testing Cosmetics - Eff
Potential effects could be:
- Eyes: ulceration, haemorrhaging, cloudinessin vision and blindness.
- Internal organ poisoning (toxicity): lungs, liver, heart or nervous system could lead t convulsions, seizures, paralysis and death.
- Skin corrosion and irritation: ulcers, scaling or inflammation.
- Carcinogenicity: carcinogens are substances that cause or increase the risk of cancerous cells growing.
- Reproductive & developmental toxicity: the reproductive system and foetuses could be affected.
Ethical Considerations for Testing Cosmetics
Animal testing and ingredients tested on animals are illegal in UK and EU countries, but it is still legal in China and USA.
A complete ban on the sale of cosmetics developed through animal testing has taken effect in the EU and alternative methods of skin testing are now commonly carried out on hair and beauty product including: use of humans, scientific research.
Scientific research uses reconstructed tissue (eg.: episkin). These are sophisticated tests using human cells and tissues (aka invitro methods), advanced computer (modeling techniques, aka sillico models).
Invitro methods are cheaper, quicker and more effective than animal testing.
Affecting Treatments - Keloids & Split Ends
Keloids (lumpy scar tissue):
- carefully work around the area,
- avoid the area if it is sensitive,
- conceal the patch if possible,
- reduce pressure.
Split Ends (weak hair broken at tips):
- recommend cutting the ends of the hair,
- recommend a conditioning treatment,
- recommend moisturising and nourishing products,
- reduce the use of styling equipment,
- reduce the use of chemical treatments.
Affecting Treatments - Alopecia areata & Eczema
Alopecia Areata (areas of baldness, often circular):
- conceal the area where possible,
- adapt the style/treatment requested,
- recommend the client to see a trichologist,
- concetrate massage in the area to stimulate blood supply.
Eczema (dry, rough, inflammed skin):
- reduce pressure,
- avoid irritating the sensitive area with products,
- adjust the service/treatment where required,
- avoid the area if it is inflammed.
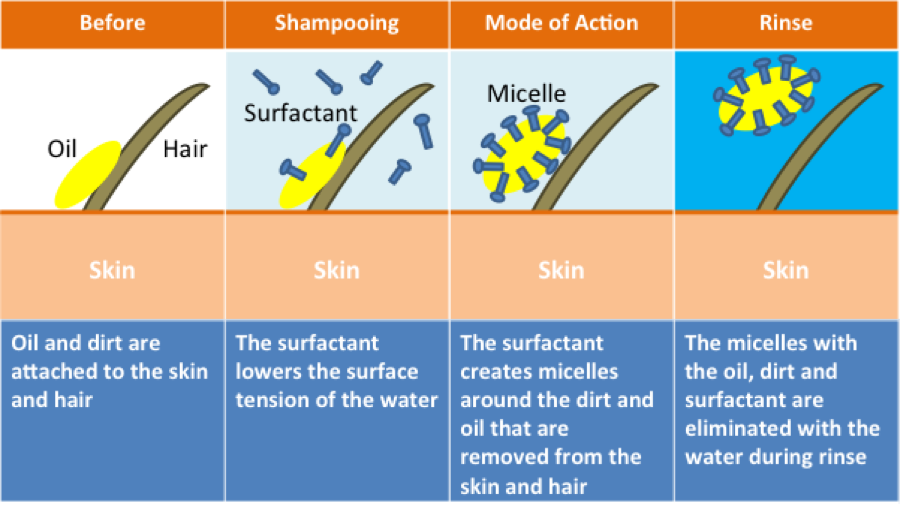
How Detergents Work in a Shampoo?
- Detergent molecule has a water repellent (hydrophobic) tail.
- The head breaks the surface tension of water allowing the hair to be fully wet.
- The tail embeds into the dirt/grease.
- Dirt/grease is rolled up when the hair/scalp is agitated.
- The dirt/grease is suspended in the water forming on emulsion.
- The dirt/grease is suspended long enough to be rinsed before being re-deposited on the hair.
The Importance of using Design
Things that need designing:
- website
- logo
- bags
- leaflets
- product displays
- television
- business cards
- packaging
- price list
- uniforms
- newspaper/magazine
- posters
- salon interiors
- signage
- window displays
- social media
The Importance of using Design - Laws
Equality Act 2010 = protects people from discrimination in the workplace and in wider society.
Trades Description Act = makes it an offence for any trader to make false or misleading statements about goods or services.
Health and Safety at Work Act = ensures that salonds are providing treatments in a safe and clean enviroment.
Target Audience
Types of target audience:
- mature
- younger clients
- professional clients
- eldery
- children
- teenagers
- adults
- men
- women
Resources:
- timescales
- ICT
- budget
- location
- people
- specialist products
The Importance of using Design - Consider
Consider:
- The purpose of the design (as a marketing tool to launch or strenghten a new or existing business brand, to aid sales and illustrate examples of services or products provided within the business and to use during the design and development phase of brigning new products to market).
- Target audiencest/customers requirements and expectations (gender appeal, age, pricing, etc).
- Relevant legal requirements (The Equality Act 2010, Health and Safety at Work Act, Trades Description Act).
- Resources required to create the design (people, specialist products/equipment, budget, location, timescale, ICT).
The Importance of using Design - Collecting Inform
Primary research provides new data for a specific purpose.
Primary research (field research) involves gathering new data that has not been collected before (eg.: surveys, questionnaires, interviews with groups of people in a focus group).
Secondary research (desk research) involves gathering existing data that has already been produces (eg.: searching on the internet, newspapers, company reports).
Factual information is called quantitive data. Information collected about opinions and views is called qualitative data.
Accurate market research helps to reduce the risk of launching new or improved products.
Some businesses opt out of field research and rely instead on the know-how and instincts of the entrepreneur to 'guess' customer requirements. They do this becase market research costs time and money. Existing businesses can make use of direct customer contact to help them identify changing fashion and market trends.
Hair and Beauty Job Roles
Hairdresser = cutting, styling, shaving, colouring, perming, relaxing, extensions.
Beauty Therapist = manicure, pedicure, facials, lash and brow treatments, make up, massage, hair removal.
Spa Therapist = massage, body wrap, body scrub, hot stone, facial, thermal services, holistic treatments.
Media Makeup Artist = wig-making, fashion/photographic makeup, special effects, prosthetics, body art, hair styling.
Nail Technician = manicure, pedicure, nail art, extensions.
Barber = male grooming services, cutting, finishing, facial skin care, massage, shaving.
Cosmetic Consultant = gives advice and sells specialist brands.
Trichologist = treat a range of hair and scalp conditions
Educator / Teacher
Receptionist
Other Trades and Businesses
Trichologist = treating a range of hair and scalp disorders, supporting the sector by dealing with a range of diseases and disorders of the hair and scalp.
Media = suporting the sector by working with modelling agencies, TV/film, fashion, theatre, advertising etc).
Leisure Industries = reliant upon the spa, beauty and hair industries with businesses running simultaneously (eg.: entertainment, recreation, sports, tourism (linked by communication, customer facing skills and anatomy, physiology)).
Customer Research and Development and Para-medical services = such as laser treatments, cosmetic injections (linked by extensive knowledge of anatomy and physiology and disordes/diseases).
Health and Well-being Industries = complementary therapies, dietician, health and lifestyle (linked by knowledge of disorders of the body and consultation services).
Journalism = in the subject area of specialism - hair/beauty (eg.: writer, broadcaster, web reviewer, editor, designer, marketing, PR, photographer).
The Supply Chain
Manufacturer = making and producing products and equipment, developing and manufacturing new as well as existing products and equipment.
Wholesaler = sells products and equipment at a discounted rate to hair and beauty businesses, selling to salons and practicioners.
Retailer/Salon = selling hair and beauty products and equipment to the public, selling associated products and equipment for use within the sector.
Consumer/Client = member of the public who buys the products and equipment.
Ancient Egypt
- Makeup using copper and lead ore
- Use of wigs for males and females
- Use of henna
- Scented oils and ointments
Ancient Greece
- Natural, pale facial skin
- Hair styling techniques - braiding, curling etc.
- Typical male facial hair
- Hair lightening by the use of bleach and properties of the sun
- Face masks made from ***'s milk
Ancient Japan
- Use of rice powder to make facial skin white
- Eyebrows were shaved off
- Teeth were painted gold or black
- Henna was used to stain hair and skin
- Bright red rose bud lips were drawn over
20s and 30s
- Smudgy, smoky eyes
- Cupids bow was usually in matte red
- Thin eyebrows
- Natural nails
- Womens hair was short and bobbed with flat finger-waves.
- Men's hair was typically short at the back and sides and slicked back at the top.
40s and 50s
- Men wore small, fine moustaches
- Men had slicked back hair
- Woman favoured red lips and set rolled hair
- 'Movie star glamour' was typified by Marilyn Monroe
- The war had an inpact on product availability
- Media and celebrity played a big role in post-war fashion
- Hair colouring rose in popularity
60s and 70s
- Wigs and hair pieces were used to give weight and volume for bee-hives
- Precision cutting by Vidal Sassoon contrasted the heavily lacquered bouffant styles
- The natural look of 'Afro' was mimicked by Europeans who permed their hair
- Pale eye shadow and black eyeliner was popularised by Twiggy
- The Beatles influenced men to have longer hair.
80s and 90s
- The 'Mullet' was warn by males and females
- Bright neon makeup was popular
- 'Big hair' - achieved by perming
- Many people had 'white-blonde' highlights
- Flat-tops returned
- Lady Diana introduced a more subtle, feminine look
Social Factors
Social diversity, culture and celebrity have affected the sector by increasing demand for treatments, makeup and equipment, which means that those treatments that celebrities are using will influence people to want to have the same. There is also a need to keep up with friends and peers.
Products - makeup ranges for different skin tones, the vast range of hair and makeup products.
Services - hair (relaxing, straightening, shaving in different patterns, extensions, wefts), beauty (semi-permanent makeup, tanning, lash and brow extensions, cosmetic enhancements, nail enhacements).
Equipment - heated styling, shaving and hair removal.
Technological Advancements
Products - anti-ageing skin care, mineral based makeup, light reflecting hair colourants, high definition makeup (designed for tv and films), organic, low sensitivity, products for delicate skin and gel nail products.
Equipment - air brushing for makeup and tanning, photographic editing for magazines by the use of computers and generated imagery such as photoshop.
Media - the use of internet and social media for professional training, demonstrating skills and displaying looks (Instagram, Pinterest, YouTube, Facebook).
Changes to the Economy
Effects of recession on hair and beauty businesses - if there is a recession there will be unemployment, salons will need less staff and people will have less disposable income to spend on treatments and products.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) - the best way to measure a country's economy. GDP is the total value of everything produced by all the poeple and companies in the country, Each quarter of the year, the GDP is measured and if it falls twice in a row then the country will go into recession.
Product pricing - if there is a change in the economy it will affect the price of products and treatments. Some salons will enter into price wars to compete for clients. Luxury products ranges may suffer, as people willl not be able to afford them.
Effect of products on hair and skin
Shampoo/Detergents - wetting, suspending, emulsifying: keeps oil and water (immiscible) from seperating. Hydrophilic head breaks waters's surface tension, whereas hydrophobic tail bonds with oil or fat molecules.
Hair Conditioners - moisturising, closing hair scales and re-structuring bonds in the hair's cortex.
Skin sun protection creams - absorption and reflection of UV rays.
Skin cleansers - surfactants and emollients lower surface tension, remove dirt and sebum.
Exfolliators - beata and alpha hydroxides (BHA, AHA) soften and remove dead skin cells, encourage regeneration, brighten the skin tone. Bead exfoliators remove dead skin cell and cause irritation.
Cuticle Remover - reduction of keratn to remove dead skin cells to celar the nail.
The Importance of using Design
An increasing number of businesses are using design to deliberately make themselves different from the competition. Design imagery acts as a mechanism for businesses growth and innovation. Customer trustis placed on familliar brands through advertising, so achieving the right image is key to business progression.
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Looks are subjective? »
- Can I study both beauty and business with just gcse »
- Do any girls have short hair these days? »
- Would you date a girl who wears wigs? »
- I don’t feel beautiful »
- Are these comments made to me racist? »
- Hot Girls *PICS* »
- I'm literally disgusting and nobody would date me »
- no one ever looks at me »
- Do guys think redheads are hot »
Comments
No comments have yet been made