Eukaryota cells organelles
- Created by: aarafa11
- Created on: 27-11-16 16:51
Nuclear Envelope
Description
- Double membrane that surrounds the mebrance
- Outer membrane = surface has ER and ribosomes
Function
- Control what material enters and exits to/from nucleus
- contains the reactions taking placing within it
Nuclear pores
Description
- 3000 pores in each nucleus
- 40 - 100 u/m in diameter
Function
- allow passage of large molecules
- either to cytoplasm or nucleus
- E.g. RNA
Nucleoplasm
Description
- Granular
- jelly-like material
- makes the nucleus bulk
CHROMOSOMES
Consists of protein- bound, linear DNA
Nucleolus
Description
- Small spherical region within nucleoplasm
Function
- Manufactors ribosomal RNA
- Assembles the ribosomes
MAY BE MORE THAN 1 IN A NUCLEUS
Nucleus
Function
- Controls the cell's activities.
- acts as the control centre of cell
- through production mRNA and tRNA = hence protein synthesis
- Contains the organism's hereditary material
- retain genetic material
- in the form of DNA and chromosomes
- Manufactures ribosomal RNA and ribosomes
Mitochondrion
Description
- Oval shape
- Double membrane
- Inner membrane is folded and form extension known as cristae
- high # in cells that have high level of metabolic activity
Function
- Aerobic stages of respiration (Krebs cycle and the oxidative phosphorylation pathway)
- production of the energy carrier molecule, ATP
- from respiratory substrates = glucose
- require a plentiful supply of ATP
Mitochondrion - Cristae
Description
- Extension of the inner membrane
- Can extend in some species - across the whole width of the mitrochondrion
Function
- Provide large SA
- for the attachment of enzyme
- other protein involved in respiration
Mitochondrion - Matrix
Description
- makes up the remainder of mitochondrion
Function
- contains protein, lipids, ribosomes and DNA
- that allows it to control the production of some their own protein
- that allows it to control the production of some their own protein
- Many enzymes involved in respiration are found in matrix
Chloroplast
Description
- Varied in shape and size
- Typically disc shape, 2-10 u/m long & 1 u/m in diameter
Function
- Contain DNA and ribosome
- quickly easily manufacture some of the protein needed for photosynthesis
ROOT CELLS DO NOT HAVE CHLOROPLAST.
Chloroplast - Envelope
Description
- double plasma membrane surrounds the organelle
Function
- Highly selective in what it allows to enter and leave the chloroplast
Chloroplast - Grana
Description
- stacks up to 100 disc like structure = THYLAKOIDS
- Within is the photosynthetic pigment = CHLOROPHYLL
- Tublar extension that joins up with the thylakoids in adjacent grana
Function
- Provide larger SA
- Attachment of chlorophyll, electron carriers & enzyme
- Carry out the first stage of photosynthesis
- These chemical are attached to the membranes in a highly ordered fashion
Chloroplast - Stroma
Description
- Fluid filled matrix
- Within are a # of other structure - starch grains
Function
- Possesses all the enzyme needed to make the sugars
- for the second stage of photosynthesis
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Description
- System of membranes enclosing a fluid-filled space
- Surface is covered with Ribosomes
Function
- Folds and processes protein
- that have been made int he ribosomes
- provide large SA
- for the synthesis of protein and glycoprotein
- provide a Pathway
- to transport of material - protein
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Description
- no ribosome
- tubular appearance
Function
- Synthesis and processes lipids & carbohydrates
Golgi Apparatus
Descritpion
- Group filled fluid membrane-bound flattened sacs - CISTERNAE
- With small rounded hollow structure - Vesicles
Protein and lipids produced by ER passed through golgi apparatus in sequence. Golgi modifies these protein (often adding non-protein components - carbohydrate). This 'labels' them, allowing them t accurately sorted and sent to correct destination.
Function
- It processes and packages new lipids and protein
- add carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoprotein
- form lysosomes
Golgi Vesicle
Description
- smalled fluid-filled sac in cytoplasm
- surrounded by a membrane and produced by the Golgi apparatus
Once sorted, modified proteins & lipids are transported in Golgi vesicles, which are regularly pinched off from the end of the Golgi cisternae. These vesicles may move to the cell surface, where they fuse with the membrane and release their content to the outside
Function
- Stores lipids and proteins made by the Golgi apparatus
- transports them out of the cell
Formation of cells
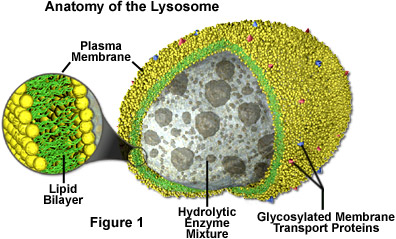
Lysosomes
Description
- Formed by the Golgi vescile contain enzyme (protease and lipase) [about 50 enzyme]
- Some contain lysozymes (enzyme hydrolyse the cell walls of certain pathogens)
- 1.0u/m in diameter
- lysosomes isolate these enzyme from the rest of the cell before releasing them - either to the outside or into a phagocyte vesicle
Function
- Hydrolyse material ingested by phagocyte cells
- Release enzyme to the outside of the cell (exocytosis) in order destroy materail around the cell
- Digest worn out organelles so that the useful chemicals they are made of can be re-used
- Completely break down cells after they have died (autolysis)
Ribosomes
Description
- small cytoplasmic granual
- occur in cytoplasm OR associated with RER
80S = found in the eukaryotic (25nm diametre)
70S = found in the prokaryotic, mitochondria & chloroplast
- each contain ribosomal RNA and protein
- vast # in cell
Function
- protein synthesis
Cell Wall
Description
- Consists # of microfibres of the polysaccharide cellulose - embedded in a matrix
- microfibres have alot of strength = overall cell wall strength
- Thin layer (middle lamella) - marks the boundary between the cemented adjacent walls
Function
- Provide mechanical strength in order to prevent the cell bursting under the pressure created by the osmotic entry of water
- Mechanical strength as a whole
- Allow water to pass along so contributes to the movement of water through the plant
PLANTS = CELLULOSE
ALGAE = CELLULOSE OR GLYCOPROTEIN
FUNGI = CHITIN (nitrogen polysaccharides)
Vacule
Description
- Fluid filled sac bounded by a single membrane (TONOPLAST)
- Contains solution of mineral salt, sugars, amino acid, waster and sometimes pigment (anthocyanins)
Function
- Make cells turgid
- Sugars and amino acid may act as temporary food store
- Pigments may colour petal to attract pollinating insects.

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Is a myofibril an organelle »
- Do I need to know how to draw structures for carbohydrates? (AQA A Level Bio) »
- 25 mark essay question »
- Paper 3 AQA a Level biology »
- Any good youtube channels for Bio + Chem a levels? »
- HELLO »
- Access to Science course »
- Alevel biology understanding »
- 25 marker essay biology »
- Biology OCR past paper question help. »
Comments
No comments have yet been made