Cell Ultrastructure
- Created by: Jacqui2
- Created on: 15-05-17 12:20
Cell Surface Membrane
- Also known as the plasma membrane
- It consists of phospholipids and proteins (FLUID-MOSAIC<protein smay move>)
- A phospholipid bilayer with proteins distributed throughout
- Structure:
- Bilayer of phosophilips
- Hydrophilic ends out. Hydrophobic ends in
- Glycoprotein/Glycolipid
- Proteins- hydrophobic regions in contact with the lipid layer
- Carbohydrate is found on the outer face only
- Cholestrol may be found (animal) among the hydrocarbn chains - acts as lubricant and temp buffer
- Function:
- Membranes fuse together during exocytosis and endocytosis due to fluidity from lipids
- Prevent passage of water souble substances while allowing passage of fat soluble molecules (water may pass as its so small)
- Some carrier proteins move molecule actively across the membrane a the conc gradient
- Some also move molecules by faciliated diffusuin
Cell Surface Membrane

Controlling the passage of materials in and out of cells
Hydophilic molecules (glucose, nucleic acids, amino acids and proteins) are not soluble in lipids and so do not readily pass through the phospholipid bilayer. They pass through by faciliated diffusuion. Passive movement. down a conc gradient, by carrier proteins. They have hydrophillic channels which solutes can pass. Alternatively they may be small globular proteins that move in the membrane shuttling their load back and forth
Mitochoindria
- Sausage shaped and are involved in the production of ATP by aerobic respiration, therefore are found in very active cells e.g sperm and companion cells
- The mitochondrion is the organelle of respiration/synthesis of ATP
- They possess a double membrane, where the inner membrane is in folds known as cristae.
- The matrix contains eenzymes, ribosomes and circular DNA.

Animal & Plant Cell


Ribosomes
- Make proteins
- Non-membranous
- May occur in groups called polysomes
- Made up of rRNA and proetin and move along mRNA to bring about protein synthesis
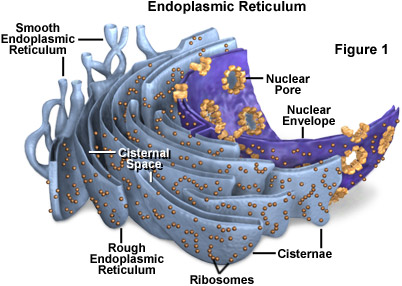
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Formed by the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope
- Know as Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) when ribosomes acting as the site of protein synthesis
- SER lacks protein synthesis and is concerned with lipid synthesis
- Overall role is to collect and transport synthesised products
- Small vesicles bud off to form the forming face of the golgi apparatus
Nucleus
- DNA is spread throughout the nucleus in the form of chromatin
- Heterochromatin - dark
- Euchromatin - light
- Nuclei also have one or more nucleoli
- Are not distinct organelles - not bound by a membrane
- Nucleoli contain DNA which can code for rRNA to make ribosomes
- Double membrane with pores
- Outer membrane is evaginated to form the ER
Golgi Apparatus/Lysosomes/Vesicles
Golgi
- Stacks of membrane bound sacs - cisternae
- At the forming face new cisternae are constantly being formed by the fusion of vesicles
- At the maturing face, cisternae breaks off into vesicles
Proteins are processed and packaged as they travel throughout the golgi. Carbohydrates can be added to them to form glycoproteins. These along with vesicles can be packaged into vesicles for secretion from the cell (exocytosis)
Lysosomes
- Are produced by the golgi bodies
- Vesicles containing powerful hydrolytic enzymes known as lysozymes
- Used in the digestion of denatured organelles
- On occassion the lysosomes may release their enzymes, thereby digesting the whole cell (autolysis)
Vesicles
- Membrane bound sacs, responsible for endocytosis and exocytosis
- Formed by budding of golgi, ER and invagitation of the cell surface membrane
- Contain modified protein for transport
Vesicles
Endocytosis - transport of material into the cytoplasm
- Phagocytosis - particles entering the cell are solid
- Pinocytosis - particles entering the cell are liquid
Chloroplasts (Plant Cells)
- Bound by a double membrane - chloroplast envelope
- The inner membrane is folded into a series of structures know as the lamella
- The stroma is a colourless matrix containing:
- Each grana is made up of between 100-200 flattened sacs called thylakoids
- Thylakoids contain phtotsynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll
- Intergranal Thylakoids interconnect adjacent grana
- Starch grains act as a temporary store for photosynthesis products
- Small amount of DNA and oil droplets are also present
- Each grana is made up of between 100-200 flattened sacs called thylakoids

Microtubules/Cell Wall
Microtubules
- Involved in movement of cell components within the cytoplasm
- Spindle fibres that form from the centrioles during nuclear division are microtubules
Cell Wall
- Surround the cell membrane
Plants
- Constructed of cellulose
- Calcium Pectate binds adjacent walls - middle lamella
- Ting strands of cytoplasm called plasmodesmata pass through holes in the walls
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Biology immunity question »
- Biology 4.1 Immunity (T cells and B cells) »
- Biology - cell differentiation »
- GCSE Biology »
- Biology question water potential »
- GCSE Biology »
- biology gcse help »
- biology question »
- Cell in circuit is reversed »
- Does the exam board have to stay within the specification? »


Comments
No comments have yet been made