Biology B2
B2 revision material
- Biology
- Cells, tissues and organsDNA and inheritanceEnzymes and digestionEvolution, extinction and natural selectionPhotosynthesis and transpirationRespiration and exercise
- GCSE
- All boards
- Created by: katie
- Created on: 17-11-14 20:31
Diffusion
An area with higher concentration of particles move to lower concentration of particles.
Particles move down a concentration gradient. This is called net movement.
Diffusion allows oxygen in a blood vessel to move into the cells.
Cell Structure
Nucleus: controls cell activities
Cytoplasm: where chemical reactions occur
Cell Membrane: controls what goes in and out of cells
Ribosomes: makes protein from amino acids
Mitochondria: produces energy from respiration
Chloroplast: contains chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight.
Vacuole: contains sugars and salts
Cell wall: provides strength
Specialised Cells
Sperm Cell:
Mitochondria: provides energy from respiration for it to swim
Tail: so it can swim to the egg
Root Hair Cell:
Hair-like Structure: increased surface area so it can absorb more water
Red Blood Cell:
No Nucleus: more space to carry oxygen
Shape: larger surface area so it can carry more oxygen
Animal Organs
CELLS ----> TISSUES ----> ORGANS ----> ORGAN SYSTEMS
Muscle Tissue- contracts which allow movement
Gladular Tissue- produces enzymes and hormones
Epithelial Tissue- covers some parts of the body
These are all found in the stomach. The muscular tissue churns up food in the stomach and mixes enzymes together. The gladular tissue produces digestive juices such as acids and enzymes. The epithelial tissue is to cover the inner and outer surfaces of the stomach.
Salivary Gland: produces saliva which contains enzymes to break down food
Liver: produces bile which emulsifes fats
Large Intestine: absorbs water and produce faeces
Small Intestine: digests and absorbs soluble food
Stomach: mixes acids with proteins to digest food
Pancreas: gland which produces enzymes and hormones
Plant Organs
Leaves: main organ for photosynthesis
Stem: transport minerals and water
Roots: absorb water/nutrients and provide anchorage
Inside the leaf-
Epidermal: tissues on covering both sides of the leaf
Mesophyll (palisade and spongy): for photosynthesis
Xylem and Phloem: transport
Photosynthesis
CARBON DIOXIDE + WATER ---lightenergy---> GLUCOSE + OXYGEN
Chlorophyll absorbs light energy. Carbon dioxide is found in the air. Water is found in the soil through roots.
Oxygen is a waste product and released into the air by the leaves.
Glucose can be converted into starch to make it into long chains to store it in the leaf.
Glucose can be used for respiration to provide energy.
Glucose can be used to make cellulose which is part of the cell wall.
Glucose can produce fats and oils.
Glucose can make proteins with nitrogen from the soil.
Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
Increasing the factors give a higher rate of photosynthesis.
more photosyntheis = more growth
Distribution of Living Things
What could affect distribution?
- Temperature
- Amount of light
- Pollution
- Availability of water
- Availability of nutrients
- Availability of oxygen and carbon dioxide
- New competition
Random Sampling:
Quadrat- must be done randomly and a series of reading must be taken to make result reliable.
Transect- place a quadrat along an evenly marked rope.
Proteins and Enzymes
Proteins are a long chain of amino acids. They can produce:
- Structual tissue
- Hormones
- Antibodies
- Biological catalysts
ENZYMES ARE BIOLOGICAL CATALYSTS. - they speed up reactions in the body.
Enzymes have a job of breaking down a molecule or joining molecules together to make a new molecule.
Temperature and Ph of Enzymes
Enzymes only work on specific substrate molecules.
As you increase the temperature, enzymes move around quickly making it more likely for it to bump into the right substrate. It will then reach the optimum temperature and as the temperature increases from then on the shape of the enzyme will get destroyed. It has been denatured and can not be changed back.
The best Ph for most enzymes is neutral. However stomach enzymes work best in acidic conditions and small intestine enzymes work best in alkaline conditions
Enzymes in Digestion
Amylase breaks down starch to turn it into sugars.
Protease breaks down protein to turn it into amino acids.
Lipase breaks down lipids to turn it into fatty acids and glycerol.
Mouth- converts starch into sugar
Stomach- converts protein into amino acids
Small Intestine and Pancreas- converts all (pancreas releases enzymes)
Liver- produces bile (alkali) so anything acidic coming out of the stomach can be made alkaline.
Enzymes in the Industry
Bacteria you want is put into a fermenter so you can grow the bacteria to produce enzymes.
Biological Detergent:
- Protease- digests the proteins
- Lipase- breaks down the fat or oil
- The enzymes are effectives at a low temperature. Above 35 degrees the enzymes will denature.
Baby Food:
- Protease- make shorter chains than protein so it will be pre-digested as it will be hard for babies to digest. Protein is good for growth.
- Carbohydrase- Starch can be made into sugar syrup to provide energy and is easier to digest.
Advantages:
- Reactions at a low temperature and low pressure so less energy is used. This makes it cheap and good for the enviroment.
- Can be reused.
Disadvantages:
- Costs alot to produce an enzyme.
- Denature at a low temperature.
Aerobic Respiration
Respiration provides energy. Aerobic respiration is with oxygen and occurs in the mitochondrias.
Glucose + Oxygen ----> carbon dioxide + water (+energy)
Why is energy essentail?
- Living things need to build molecules into larger ones.
- Animals need to contract muscles for movement.
- Mammals and birds need to produce the temperature of 37 degrees.
- Plants need to build sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids to build protein for growth.
Your heart rate increases during exercise to pump blood around the body which supplies glucose and oxygen to the muscles. During exercise we need more glucose and oxygen for aerobic respiration to provide energy.
In the muscles during exercise the glycogen gets broken down into glucose so the glucose can produce energy by respiration. Rememeber glycogen is glucose joined up.
Anaerobic Respiration
When there is unsufficient oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes place.
Glucose ------> Lactic Acid + Little Energy
We need oxygen to produce energy. During anaerobic respiration there is an incomplete breakdown of glucose due to little oxygen, this produces lactic acid.
When you get a build up of lactic acid it causes muscles to become tired and stop contracting efficiently. To remove lactic acid, blood needs to flow through the muscle.
Oxygen oxidises the lactic acid to remove it, this is why we still continue to take heavy breaths after exercise. This is called the oxygen debt.
The lactic acid will then convert into carbon dioxide and water which are waste products.
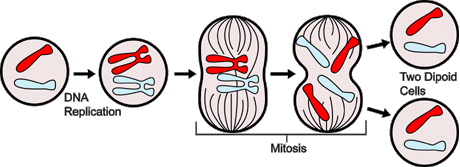
Mitosis
Mitosis is when normal body cells reproduce.
Mitosis happens for; growth, replacement cells and asexual reproduction.
Every cell made will have to have the same number and type of chromosomes in the nucleus which is 46.
Meiosis
Meiosis happens in the ovaries and testes.
It has two divisions and will produce four cells each with a single set of chromosomes (23).
Stem Cells
Stem cells are unspecialised and can be whatever cell we want.
Instead of throwing these cells away from IVF we can take them and make them into cells which can help people. For example people with parkinsons disease or for a heart transplant.
Social Side:
- Save lives
- Cure diseases
- Saves costs
Ethical Side:
- Killing humans?
- No right to interfere
- Religious views
Genetic Variation
Genes- Small section of DNA that controls your features
Your chromosomes will match up to your mother's and father's becasue you were given half of your mothers and half of your fathers.
Dominant Gene- a gene that will show
Recessive Gene- a gene which will show if a dominant gene isn't there.
Inheritance of Gender
There are X and Y chromosomes.
XY = Male
** = Female
A male can only pass on an X or a Y and a female can only pass on and X or an X. Therefore there is a 50% chance that it will be a girl or a boy.
DNA Structure
DNA is found in the chromosomes in coils to make it compact. If you stretch DNA out and zoom in you will see that it is double helix.
You will also see that DNA has bases. Each base must compliment the base at the other side. Three bases together are called triplets which code for an amino acid which make protein.
A base can be A,C, G or T.
DNA Fingerprinting
Producing a DNA fingerprint:
- A sample of DNA is mixed with enzymes. Enzymes cut up the DNA into strands.
- The strands of DNA are put into gel.
- Electric current is put across the gel to encourage the strips of DNA to move.
Used for:
- Paternity or maternity tests
- Criminal identification
- Forensics
Polydactyly
Polydactyly is a dominant genetic disorder where someone is born with an extra digit.
Allele: one version of the gene. e.g tongue rolling is the gene, whether you can or cannot are the alleles.
If a child has inherited a dominant allele then they will be affected by Polydactyly.
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis is a recessive genetic disorder. It is a disease which affects cell membranes. It causes thick mucus so it affect the panceas (digestion) and the lungs (breathing). A child can only get Cystic Fibrosis if they inherit two recessive alleles. However they still will be carriers of the disease if they inherit one dominant allele and one recessive allele. This means that they could still pass it on to their children even though they haven't got it themselves.
- Genotype- combination of alleles for a characteristic
- Phenotype- the feature expressed
- Heterozygous- two different alleles
- Homozygous- two of the same alleles
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance in pea plants.
However people at the time didn't believe him because:
- He wasn't a scientist (he was a monk)
- His work wasn't published widely
- Genes were not discovered
- Religion
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel discovered inheritance in pea plants.
However people at the time didn't believe him because:
- He wasn't a scientist (he was a monk)
- His work wasn't published widely
- Genes were not discovered
- Religion
Embryo Screening
Embryo screening is checking alleles in cells to see if they have certain diseases.
They take an egg cell from the mother and a sperm cell from the father and check to see if they have the alleles of a disease. If not they implant them in the mother with healthy alleles so they baby is disease free. (IVF)
Fossils
Fossils are remains of organisms from many years ago.
We can find hard parts (teeth and fossils) because they do not decay easily. Also we can find traces (footprints and burrows). We can find absence in the right conditions (if there is no oxygen or warmth etc for decay).
Geological activity can destroy fossils.
Fossils can show:
- how new species are formed
- how some species have become extinct
- how new organisms arise
However there is a lack of enough valid and reliable evidence to be certain.
Extinction
Extinction can be caused by:
- New disease
- New predators
- Catastrophe
- New competitor
- Enviromental change
- Cyclical nature of speciation
Speciation
Speciation can be caused by:
Isolation- species seperated by a barrier e.g mountains, sea, river etc
Genetic Variation- caused by a range of alleles
Natural Selection- advantageous characteristics that suit the enviroment are passed on
Speciation is when a species become so different they cannot interbreed.
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Is a myofibril an organelle »
- Viruses »
- Biochemistry Personal Statement Example »
- Biology paper 1 2023 »
- Biology question molecules »
- Unofficial Mark scheme: AQA GCSE Biology Paper 1 Triple Higher Tier 16th May 2023 »
- What life science degree should I do? »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 3 [21st June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Why r bicarbonate ions removed from red blood cells »
- Grade Growth Chronicles | From C's to A's (23-24) »
Comments
No comments have yet been made