Biology
- Created by: 31AllenK2
- Created on: 03-06-19 15:56
Animal & Plant Cells
Animal & Plant
- Nucleus, job is it contains DNA
- Cytoplasm, job where most chemical reaction takes place
- Cell membrane, job controls substances passing in and out
- Mitochondria, job where aerobic respiration
Plant Only
- Vacuole, job contains cell sap
- Cell wall, job Provides strength
- Chloroplast, job Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Specialised Cells
Red blood cell- job is to carry oxygen around the body. Has no nuclues, mitochondria in order to carry more oxygen(hemoglobin). Has a biconcave disc shape so it can fit through the capilliares
White Blood cell-job to destroy bacteria. they can change shape so they can chase or ingolb. Has a nucleus.
Egg cell- job sexual reproduction. Lots of cytoplasm.
Sperm Cell- Job sexual reproduction. tail to help it move.
Sensory Neurone- Job Receptors to brain and spinal cord long fibres to carry impulses.
Motor Neurone- Job Carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscualr glands long fibres.
Root hair- job absorption, Extension of cell increases surface area.
Xylem- Job to carry Water no cytoplasm or organelles
Phloem- job Dissolved Sugar Compansion cell with organelles.
Guard cell- job allow C02 to enter for photosynthesis can open up and close.
Cells, Tissues and Organs
Tissues is a group of cells that work together to do a specific job
Organ is a group of tissues that work together to do a specific job
Organ System is a group of organs that work together to do a specific job.
Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport
Diffusion is when molecules go from a high concentration to a low concentration until the molecules are equally spread out.
Factors affecting, Temperature: more kinectic energy rate increases, Surface Area: bigger the SA faster the rate. link to villi & Alevoli
Osmosis is the movement of water. from a high concentration to a low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. Too much salt cell shrivels up. Too much water cell explodes. Equal amount the cell is Isotonic, no net gain so when 2 molecules move there is no gain.
Active Transport is the movement of molecoules from a low concentration to a high it needs ATP which is made by respiration in the mitochondria and needs oxygen to work.
Heart PT 1

Heart PT2
Right Ventricle muscle wall is smaller than the left as it doesn't need to pump the blood as far as the left side does. As the left side needs to pump blood to your feet where as the right side only to your lungs which are closer.
Cardio-vascular Disease (CVD)
Cornoary arteries- job is to supply oxygen to the hearts muscle
Risk Factors
- Smoking-Less Oxygen into blood
- High fat diet- High cholesterol build up
- Lack of exercise- Overweight
- High stress life- High blood pressure
- Inherited Genes- parents have had CVD you will mostly like
Atheroma is a build up of fat which narrows/blocks the coronary arteries. Links to a stroke as it could break off and get into the Aorta it could travel to the brain and block the capillaires stopping oxygenated blood getting through.
Cardio-vascular Disease (CVD) PT2
Treating CVD
Statins= + reduces chlorestrial. - Side effetcs
Angioplastry= +Ballon wire mesh opens coronary artery, - sometimes temporary
Change lifestyle/Diet= + stop smoking, exercise, cutout fat in diet, - will power people don't have to do it.
Testing a Leaf for starch
1. Liquid? Boiling water
Why? Cell Wall breaks down
2.Liquid? Alchol
Why? Removes the chlorophyll
3. Liquid? Water
Why? Removes the alchol
4.Liquid? Iodine
Why? Test for starch
De-starching a plant
How? Dark for 24hrs
Why? Turns all the starch into glusoce.
Transpiration
Rate of water up take from roots to leave
1.Plants Absorb water via Osmosis through the root hair cell has small hairs to increases the SA
2. Water is caarried up the stem into the xylem tissue one way upwards to the leaf.
3.Goes up the stem into the leaves for photosynthesis then used in respiration after it is finished it leaves via the stomatoa or it is used to create pressure inisde the cells e.g vacuole (Turgid full of water)
4. Phloem tissue goes 2 ways and is water with dissolved glucose.
Factors Affecting Transpiration Rate
Light, More=speeds up photosynthesis
Temperature, rate up as photosynthesis is controlled by enzymes
Wind Speed, Increase rate increase as the wind evaporates the water
Humidity, Decreases the rate no concentration graident
Leaf structure
1. Cuticle- Waterproof layer surface of the leaf
2.Upper Epidermis- Transparent layer of cells surface of the leaf
3. Palisade Layer- Cells are tall closely packed to absorb maximum light, contain many chloroplasts
4. Spongy Layer- Capture light and makes food, have air spaces between to allow easy gas exchange.
5. Lower epidermis- Bottom Layer of the leaf Contains guard cells and stomata
6.Stomata- Tiny holes allow gas exchange
7.Guard cells- Cells open & close to control gas exchange & water loss
8.Xylem- Transport Water up the plant
9. Phloem- Transport of Sugars around the plant.
Leaf structure pt2

Mineral Absorption
Plant Deficiencies
Nitrates-Needed for stem growth Lack- Short plant
Phospates-Needed for root growth Lack- Small roots
Potassium- Needed to make chlorophyll Lack- Yellow leaves
Fertiliser are used to help improve plant growth as they conatin Nitrate, Phospoates and Potassium
Food Chain
The Plant is the producer
1st Animal is the primary consumer is a herbivore
2nd Animal is the secondary consumer is a Omnivore
3rd Animal is a Tertitary Consumer is a carnivore
The arrows in a food chain show energy the source of energy in a food chainis the sun
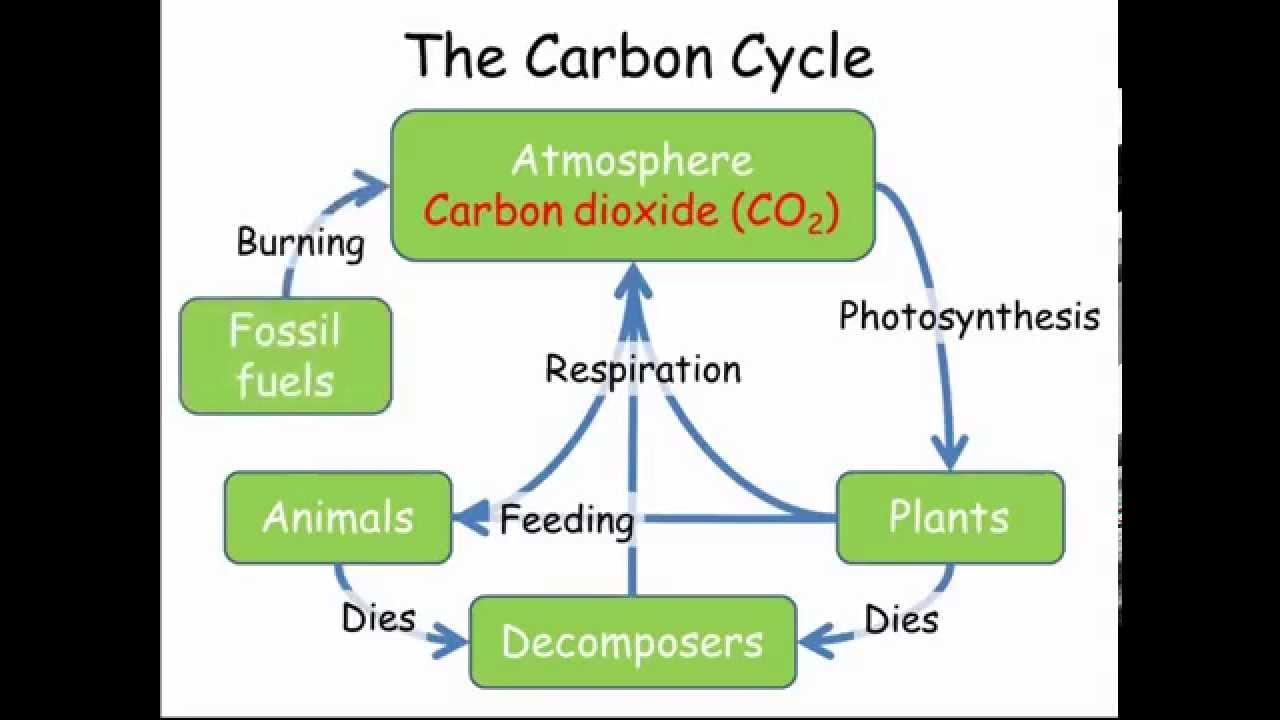
Carbon Cycle
Human Impact on Environment
- Combustion
- Car pollution
- Hunting
- Not recycling
- Deforestation
Goverment Agencies
Monitor Environment -Air/Water pollution
Protect the Environment- Conservation of animals,/ plants
Improve Environment- Farming & Building
Intensive Farming
Fertilisers- Makes plants grow faster, increas yeld. Problems- Algae grow on top block light kill fish
Pesticides- Kill bugs, Increase Yeld. Problems Concentration Increases Toxic as it goes up the food chain.
Antibiotics- Prevent Diseases, Increase yeld. Problems- Pass on into use, resistant as it has been used too much.
Battery farming-Increase yeld, increase number they sell more money. Problems- Can't grow as big as in the open. animal currelty, Inhuman, Diseaeses Spread faster.
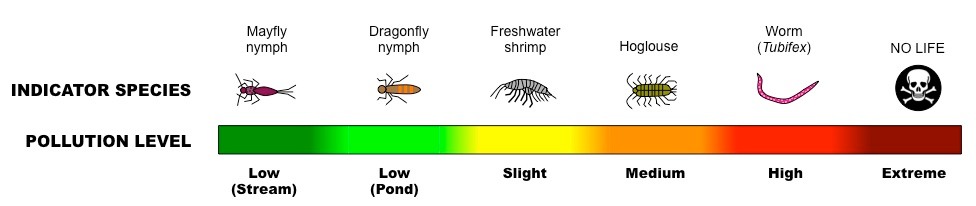
Indicator Species

Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen-fixation
Legume plants such as peas, beans and clover contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert nitrogen gas from air into a form that plants can use to make proteins. Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria are also found in the soil. When they die the nitrogen they have fixed into their biomass is converted into ammonium.
Feeding
Animals consume plant protein, digest it using specific enzymes and absorb the free amino acids.
Production of nitrogenous waste products
Animals cannot store excess protein in their bodies. They break it down and turn it into waste products and excrete them from their bodies.
Decomposition
decomposers(some free-living bacteria and fungi) break down animal and plant proteins (from dead organisms) and nitrogenous waste products to release energy. As a result of decomposition nitrogen is released into the soil in the form of ammonium.
Nitrification
A group of free-living soil bacteria called nitrifying bacteriaconvert ammonium into nitrates in order to obtain energy.
Denitrification
This is when bacteria in the soil convert the nitrate back into nitrogen gas which then gets released back into the atmosphere.
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Is a myofibril an organelle »
- Viruses »
- Biochemistry Personal Statement Example »
- Biology paper 1 2023 »
- Biology question molecules »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 3 [21st June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Unofficial Mark scheme: AQA GCSE Biology Paper 1 Triple Higher Tier 16th May 2023 »
- What life science degree should I do? »
- Why r bicarbonate ions removed from red blood cells »
- Grade Growth Chronicles | From C's to A's (23-24) »
Comments
No comments have yet been made