Biology
- Created by: Maria is the best
- Created on: 11-12-17 16:20
Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ systems
The smallest structural and foundation of an organism-->Cell
Is made up of a similar group of cells-->Tissue
A group of similar tissues working together-->Organ
A group of organs working together-->Organ system
A group of organ systems working together-->Organism
muscular tissue-contract to bring about movement
glandular tissue-can produce substances such as enzymes and hormones
epithelial tissue-covers some parts of the body
Structure of the digestive system
Mouth-the teeth cut and crush food helps chew food-this is mechanical digestion-makes it smaller-enzymes are released as a biological catalyst and helps us chew faster and swallow our food. Special glands under the tongue produce saliva and helps break down and lubricate food so it's able to go down gullet smoothly
Oseophagus-food moved down through digestive system by a process called peristalis-contraction of two sets of muscles in walls of the gut, one set runs along gut while other circles it-wave like contractions creating squeezing action-moving down gut
Stomach-organ-digests food and can store food--muscular tissue churns food and other contects of the stomach--glandular tissue produces digestive juices, including acids and enzymes--Epithelial tissue covers outer and inner surfaces of stomach. Stomach contains hydrohloric acid (HCl) and has a pH of 1.5-3.5
Panreas & Liver-pancreas produces' enzymes & insulin to help break down/store food-liver produces bile(alkaline substance stored in gall bladder secreted into small intestine where it breaks down-emulsifies-fats) that aids digestion. After stomach food travels to small intestine - enzymes in small intestine work best in alkaline conditions-food acidic after being in stomach
Structure of the digestive system (cont.)
Small intestine-food is digested and nutrients are absorbed-small intestine is long as it needs a large surface area to absorb food and nutrients-absorption across happens quickly if surface=thin and surface area=large-inner wall of small intestine adapts so substances pass across quickly and efficiently:has thin wall-one cell thick-many tiny villi-gives big surface area. If small intestine had thick cell wall & small surface area-lots of digested food might pass out of body before there's a chance for it to be absorbed by. Villi (one=villus) stick out->big surface area and also contain blood capillaries to carry away absorbed food molecules
Large intestine-absorbs water & undigested food-makes faeces-if not enough water is absorped=diarrhoea-too much water absorption=constipation
Rectum & Anus-rectum stores faeces until comes out of anus--anus regulates discharge of waste & indigestable substances out of body-can hold faeces from going out of body till individual finds appropriate place for defacation
Enzymes, substrates, lock and key model
Enzymes are:
- biological catalysts
- not living-cannot die
- protein molecules
- specific-each enzyme can only break down one molecule
Substrate=key Enzyme=lock
Substrate goes into enzyme like a key goes into a lock and fits perfectly
Optimum temp. for enzyme is temp at which activity is greatest-usually 37 degrees
Enzyme reactions=slow at low temp because substrate molecules moving to slow-temp gives energy to enzyme
Structure of blood cells
The blood carries oxygen(haemoglobin-found in red blood cells), glucose and white blood cells. One function of blood is to transport dissolved substances around the body, protect the body and regulate the temperature.
Blood contains:
- Red blood cells->job is to transport oxygen around the body-have large surface area for absorbing area and oxygen carried in haemoglobin-when oxygen binds to haemoglobin we call it oxy-haemoglobin
- White blood cells->different types but same function=is to defend against micro-organisms that cause disease-do this by: engulfing unwelcome micro-organisms(phago cytosis)and digest them, producing antibodies to fight them, produce antitoxins to neutralise any toxins produced by micro-organisms-are larger than red blood cells
- Platelets->small fragments of cells-have no nucleus-helps blood to clot together at a wound and stops you from losing too much blood-also stops micro-organisms for getting in at wound-lack of platelets can cause excessive bleeding and bruising
Structure of blood cells (cont.)
Plasma
- Pale straw coloured liquid that carries everything in blood
Carries:
- Red and white blood cells and platelets
- Minerals and nutrients like glucose, water and amino acids-these are soluble products of digestion-are absorbed from small intestine and taken to cells of body
- Carbon dioxide from organs to lungs
- Urea(urine)from liver to the kidneys
- Hormones
- Proteins
- Antibodies and antitoxins produced by white blood cells
Structure of heart
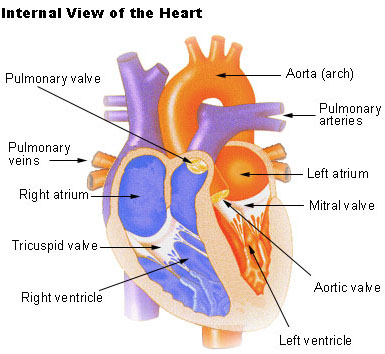
Cardivascular system
Cardiovascular disease is a term used to describe diseases of the heart or blood vessels-example=coronary heart disease.
Coronary heart disease=when arteries that supply blood to heart muscle(coronary arteries)get blocked by layers of fatty material building up-causes arteries to become narrow so blood flow=restricted and lack of oxygen to heart muscle-can result in heart attack
Treatment of coronary heart disease-Stents
Stents
- Arteries get blocked/weakened-narrowed due to CHD-can cause heart attacks-stent placed in artery to keep artery open so blood can flow through
Advantages
- success rate=high
- lower risk of heart attack for long time
Disadvantages
- complication=bleeding, irregular heartbeats and infection
- arteries sometimes reclose
- drugs needed to stop blood clotting
Treatment of coronary heart disease-Artificial val
Artificial Valves
- valves in heart control direction of blood-disease can cause valves to degenerate-stop opening/closing properly-makes person tired and restless
Two types of replacment:
- Mechanical valve-made from man-made material e.g.metal, cloth/ceramic
- Biological valve-made from human/animal(made mostly of pigs)
Advantages
- success rate=high-prolong life & new valve last up to 20 years
Disadvantages
- may need blood thinners-to stop clotting
- always risk of serious complication with surgery
Treatment of coronary heart disease-Artificial val
Artificial Valves
- valves in heart control direction of blood-disease can cause valves to degenerate-stop opening/closing properly-makes person tired and restless
Two types of replacment:
- Mechanical valve-made from man-made material e.g.metal, cloth/ceramic
- Biological valve-made from human/animal(made mostly of pigs)
Advantages
- success rate=high-prolong life & new valve last up to 20 years
Disadvantages
- may need blood thinners-to stop clotting
- always risk of serious complication with surgery
Treatment of coronary heart disease (cont.)
Bypass surgery
- blocked parts of arteries removed
- replaced with bits of vein from other parts of body
- used when arteries are badly blocked-stents can't be used
- general anasthetic needed
- very expensive
Artificial blood products
- made from stem cells
- when donated blood not available & problem with safety of donated blood
Treatment of coronary heart disease-Blood transfus
Blood transfusions
Advantages
- increased shelf life(how long blood is stored before blood transfusion)
- doesn't need to be refridgerated
- more efficient at carrying oxygen
- no need to match blood group
Disadvantages
- effect only short lasting
- products are expensive
Plant tissues
Epidermal tissue - this covers the whole plant and has a waxy cuticle so water can't get out - only exit is through stomata - has upper epidermis and lower- lower epidermis=transparent to light can pass through into palisade layer
Palisade mesophyll tissue - part of leaf where most photosynthesis happens and contains a lot of chlorophyll for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll tissue - is also in leaf and contains big air spaces to allow gases to diffuse in and out of cells
Xylem and Phloem tissue - transport water, mineral ions and food around plant
Meristem tissue - found in roots and shoots of plant and can differentiate into different plant cells (are similar to stem cells)
Xylem and Phloem tissue
Phloem
- carries dissolved food from leaves to rest of plant
- transprot system in multidirectional (both ways)
- end plates between cells
- living cells
Xylem
- form continuous vascular bundles (strands of vessels) from roots to stem and leaves
- carries water and minerals from roots to stem and leaves
- transport is unidirectional (one way)
- no end plate between cells
- strengthened with lignin
- dead cells
Stomata + Guard cells
Stomata
- are pores on the underside of the leaf
- opens so carbon dioxide can diffuse through leaf + closes so oxygen can't escaping->what stomata is specialised for
- stops water escaping
- has little holes
- water evaporates out of plant thorugh stomata
Guard Cell - controls stomata (opens and closes)
Specialised plant cells (examples)
Root hair cell
- specialised for absorbing water and mineral ions
- grow into long 'hairs' that stick into soil-gives plant big surface area
- has thin cell wall
- active transport allows root hair cell to absorb mineral ions
Xylem
- specialised for transporting water in plant-process=transpiration
- xylem cells=hollow in centre
- hard lignin in cell wall->helps with fast slowing water
Phloem
- specialised for transporting food (dissolved substances) around body-process=translocation
- made up of elongated cells with pores-holes in end of cell wall so sugars can pass through
Transpiration
Transpiration=movement of water from roots to out of leaves
Transpiration happens fastest if really high concentration in one place & low concentration in other(Diffusion)
Factors that affect rate of transpiration:
- Wind - blows excess water away - moves water molecules away from stomata - wind has low concentration of water molecules outside of leaf & high concentration of water inside leaf
- Humidity - high humidity=a lot of water molecules in air and plant=slow transpiration-low humidity=not much water molecules in air and a lot of water molecules in plant=fast transpiration
- Temperature - when it's warm particles have more energy to evaporate & diffuse
- Light Intensity - photosynthesis happens when there's light(sun)-can't happen in dark, when stomata is closed little water can escape-when light stomata is open-water can escape
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Is a myofibril an organelle »
- Viruses »
- Biochemistry Personal Statement Example »
- Biology paper 1 2023 »
- Biology question molecules »
- What life science degree should I do? »
- Unofficial Mark scheme: AQA GCSE Biology Paper 1 Triple Higher Tier 16th May 2023 »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 3 [21st June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Why r bicarbonate ions removed from red blood cells »
- AQA A-level biology essay topics »
Comments
No comments have yet been made