To what extent and in what ways did Communism transform the GDR?
0.0 / 5
- Created by: katiegdmn1214
- Created on: 26-02-15 11:43
When was the Yalta Conference?
4-11th February 1945
1 of 84
What was decided at Yalta?
The division of Germany into four zones
2 of 84
Which countries territory was largely divided between the East and West?
Poland
3 of 84
What was the date of the Potsdam Conference?
July 17th - August 2nd 1945
4 of 84
What did Russia and the other Allies disagree on?
Boundaries and reparations
5 of 84
What were the 4 Ds?
Demilitarisation, Democratisation, Decentralisation and De-Nazification
6 of 84
What percentage of British and American reparations would Russia get, and in exchange for what?
25% of reparations in exchange for goods
7 of 84
When did the German military disband and when was it re-established?
May 1945 & 1955
8 of 84
Why did the Soviets insist Nazism had to be destroyed?
They believed Nazism resulted from Capitalism
9 of 84
How did the Soviets destroy Nazism?
Junkers were confiscated & redistributed; Confiscation of Nazi property; Relocated some equiptment and experts to Russia as reparations
10 of 84
Who was Walter Ulbricht?
Led the KPD, and later the SED
11 of 84
When did the KPD arrive in Berlin
April 1945
12 of 84
What was the Soviet Military Administration (SMAD)?
The group which supervised occupation of the Soviet Zone
13 of 84
What was 'Order No 2' and when was it issued?
It licensed the formation of political parties and was introduced on 10th June 1945
14 of 84
When were all parties brought together in a National Fron against Nazism?
July 1945
15 of 84
When did the SED form?
1946
16 of 84
Why did the SPD distrust the KPD?
Their policies and links with the army
17 of 84
When was democracy formally abandoned?
1948
18 of 84
Whose property did the SED confiscate?
Absentee factory owners, Nazis, War criminals and Junkers
19 of 84
Who did the SED belive were innocent?
Ordinary workers and peasants
20 of 84
What did the SED ensure they controlled?
Education
21 of 84
What was Marxist-Leninist?
A combination of beliefs in Marx's commitment to overthrow capitalism and Lenin's idea about the role of the party
22 of 84
What was the principle of the Marxist-Leninist 'Party of a new type'?
Democratic centralism
23 of 84
Why and when was the Bizonia formed?
To overcome economic problems in 1947
24 of 84
When was Trizonia formed?
1949
25 of 84
What was the Truman Doctrine?
US foreign policy aim to support governments fighting for 'freedom' against Communism
26 of 84
What was Marshall Aid?
The plan proposed by the US General Marshall to give financial aid to nations in Europe to help rebuild their economies and stop the spread of Communism
27 of 84
What resulted in the introduction of the Deutschmark in the West?
The growing black market
28 of 84
What was the Soviet currency?
The East German Mark
29 of 84
When was the Berlin Blockade?
24th June 1948 - 12 May 1949
30 of 84
What was the short-term cause of the Berlin Blockade?
Western currency reform
31 of 84
How was West Berlin supplied?
Food, medical supplies and fuel were brought by air
32 of 84
What did the 'Parliamentary Council' do?
Draw up the basic law for West Germany
33 of 84
When was the GDR formed?
October 1949
34 of 84
Who was the GDR president?
Wilhelm Pieck
35 of 84
Who was the GDR Prime Minister?
Otto Grotewohl
36 of 84
When was the Stasi founded?
February 1950
37 of 84
When was Lander abolished?
1952
38 of 84
What were lander replaced with?
Bezirke
39 of 84
What was the Stalinallee?
A prestige building project
40 of 84
What did the Government propose a 10% rise in in May 1953?
Productivity and working hours
41 of 84
When was the Workers' Uprising?
17th June 1953
42 of 84
When did Stalin die?
5th March 1953
43 of 84
Why did the uprising fail?
Poor organisation; No objectives; Non-intervention from the West
44 of 84
What were the consequences of the uprising?
Increase in norms were ended; More consumer goods to be produced; Ulbricht's power was strengthened; The powers of the Stasi increased
45 of 84
Why was giving land to peasants become a problem?
They were unable to farm profitably as they lacked resources and machinery
46 of 84
When was collectivisation introduced?
1952
47 of 84
What were LPGs?
Land Production Co-operatives
48 of 84
What made agriculture more efficient?
Mechinisation and the use of tractor-lending stations
49 of 84
In what year did LPGs make up 45% of the agricultural sector?
1959
50 of 84
When was food rationing on basic items stopped?
1958
51 of 84
Why were ore people leaving in 1961?
Rationing ad returned and productivity decreased further
52 of 84
What happened to many large industies?
They were nationalised
53 of 84
Where did most people work?
State-run VEBs (People's Own Factories)
54 of 84
What were the problems with the Five Year Plans?
Targets ingnored consumer demands; Emphasis on quantity over quality reduced saleability; Took too long to implement; Fixed prices did not link to supply demand
55 of 84
What did the 1951-55 Five Year Plan focus on?
Heavy industry
56 of 84
What did the 1956-58 Five Year Plan focus on?
Modernisation and the production of consumer goods
57 of 84
What did the 1951 Berlin Treaty do?
Co-ordinate trade between the East and West
58 of 84
What did joining Comecon in 1950 mean?
The economy was facilitated and integrated with the Eastern Bloc
59 of 84
What did the Seven Year Plan in 1959 aim to do?
Align economic development of the GDR with the Soviet Union, which brough in some consumer goods and improvement in living standards
60 of 84
When was the Berlin wall erected?
1961
61 of 84
What did the Berlin Wall Stabilise?
The workforce as there was less movement to the West
62 of 84
When was the Seven Year Plan abandoned?
1962
63 of 84
When was the 'New Economic System for Planning and Direction' (NOSPL) introduced?
1963
64 of 84
What did NOSPL do?
Brought more flexibility and input from workers; allowed workers to share in profits which encouraged production; emphasised quality over quantity
65 of 84
What oppertunities were there for peasants who committed themselves to the polical system?
Gained land (but were later forced to join a collective); Better machinery to work the farms; Education
66 of 84
What oppertunities were there for factory workers who committed themselves to the polical system?
Education; Oppertunity to manage factories if they were loyal to the party
67 of 84
What oppertunities were there for women who committed themselves to the polical system?
Many became doctors; Increased support with te provision of maternity and child care facilities to allow for part-time work or work at lower levels
68 of 84
What mass organisations were established by the state to give them control over all aspects of life?
Free German Trade Union League (FDGB) for workers, controlled by the SED; Democratic Women's League of Germany; League of Culture; Society for Sport and Technology; German-Soviet Friendship Society
69 of 84
What did schools become?
Polytechnic with close links to industry or sport, and provided practical work experience
70 of 84
What controlled youth organisations?
SED
71 of 84
What was the youth organisation for 6-14 year olds?
JP - Young Pioneers
72 of 84
What was the youth organisation for 14-25 year olds?
FDJ - Free German Youth
73 of 84
Were youth organisations compulsory?
No
74 of 84
Why did young people join?
Out of fear of discrimination
75 of 84
What did youth opposition support?
Western culture, based around rock and roll music
76 of 84
Was Curch-owned land seized?
No
77 of 84
Did Churches run their own internal affairs?
Yes
78 of 84
When did the Churche face severe repression?
1952-53
79 of 84
What did the 1946 Law for the Democratisation of German Schools remove?
Religious education from the curriculum
80 of 84
What was the Protestant youth group called?
Junge Gemeinde
81 of 84
Did churches receive financial support from the state?
No
82 of 84
What were blocked for Christians latter on?
Carrers, promotions and education
83 of 84
What was imposed on the young in 1954?
Jugendweihe - the Youth Dedication Service - an Atheist ceremony with a pledge to the state and Socialism
84 of 84
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
What was decided at Yalta?
Back
The division of Germany into four zones
Card 3
Front
Which countries territory was largely divided between the East and West?
Back

Card 4
Front
What was the date of the Potsdam Conference?
Back
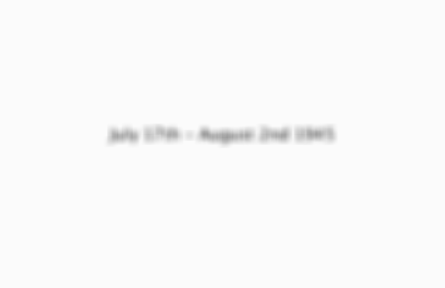
Card 5
Front
What did Russia and the other Allies disagree on?
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Edexcel IGCSE History | DEPTH STUDIES »
- OCR A-Level History Unit 2 (Y201-Y224) - 13th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- history 2023 predictions gcse questions »
- Your Perfect Country »
- OCR A Level History Non-British period study: All Exams - 22 Jun 2022 [Exam Chat] »
- AQA GCSE History Paper 1 (8145/1) - 18th May 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- Please can someone help me with some feedback on my lnat practice essay? »
- Edexcel A Level History Paper 2 (9HI0 2A-2H) - 9th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- Edexcel GCSE History Paper 3 (1HI0 30-33) - 15th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- OCR history democracy and dictatorships in germany »
Similar History resources:
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
4.5 / 5 based on 4 ratings
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made