SOCIOLOGY TOPIC 5
0.0 / 5
- Created by: hayley ashton
- Created on: 08-04-13 21:11
2 stats of official statistics & gender patterns?
1. 4 out of 5 convicted offenders in England & Wales are male 2. By the age of 40, 9% of females had criminal conviction against 32% of males
1 of 51
1 stat of official statistics show among offenders?
Higher proportion of female than male offenders are convicted of property offences. Higher no of males than female offenders convicted of violence or sex offences
2 of 51
1 more stat of official statistics show among offenders
Males more likely to be repeat offenders, have longer criminal careers & commit more serious crimes. EG Men 15 times more likely to be convicted of homicide
3 of 51
3 questions these stats raise?
1.Do women really commit fewer crimes or are figures invalid picture? 2.How can we explain why those women commit? 3.Why do males commit more crimes than females?
4 of 51
2 arguments saying women are less likely to offend/be prosecuted?
1.Female crimes like shoplifting less likely to be reported. Property crime less noticed than sexual/violent crimes by men 2.Even when women are detected or reported, less likely to be prosecuted
5 of 51
Chivalry thesis?
Most criminal justice agents like police, magistrates & judges are men & are socialised into acting in chivalrous way towards women, lenient prosecuting & invalid stats
6 of 51
Evidence of chivalry thesis?
Graham & Bowlings sample of 1,721 14-25 yr olds found males were more likely to offend but difference was smaller than stats showed. 2.33 more likely to admit committing, off stats said 4 times more likely
7 of 51
Ministry of justice evidence?
Women more likely to be cautioned than prosecuted. In 2009, 49% of females were cautioned whereas only 30% males offending were
8 of 51
Evidence against Chivalry thesis?
Farrington & Morris' sentencing of 408 offences of theft in magistrates court found women weren't sentenced more leniently for comparable offences
9 of 51
Buckle & Farrington's study?
Observational study of shoplifting in a department store saw twice as many males shoplifting as females despite numbers of male & female offenders in off stats are more or less equal
10 of 51
Box's study?
Review of British & American self report studies concludes women who commit serious offences aren't treated more favourably than men. Low prosecution rate may be because their crimes are less serious/show more remorse
11 of 51
2 examples showing bias against women?
1.Double standards-courts punish girls but not boys for promiscuous sexual activity 2.Women who dont conform to accepted standards of monogamous heterosexuality & motherhood are punished harsher
12 of 51
Carlen on bias against women?
Looked at custodial sentences. When women are jailed, less for seriousness of crime but more according to courts assessment of them as wives, mothers & daughters. Girls whose parents believe them to be beyond control likely to get custodial sentences
13 of 51
Feminists on criminal justice system?
Walklate- Double standards exist, criminal justice system is patriarchal. Way system deals with ****. No of cases of male judges making sexist remarks. Not defendent on trial but victim, has to prove respectability in order to have evidence accepted
14 of 51
Functionalist sex role theory?
Parsons-Men take breadwinner role outside home while women perform expressive role in home, responsible for socialising children. Girls access to adult role model, boys reject feminine models.
15 of 51
Effect on boys on sex role theory?
Engage in 'compensatory compulsory masculinity' through aggression & anti social behaviour
16 of 51
Cohen & functionalist sex role theory?
Relative lack of adult male role model means boys more likely to turn to all male street gangs as source of masculine identity. Status earned by toughness, risk taking & delinquency
17 of 51
Walklate on sex role theory?
Criticises for biological assumptions. Parsons assumes as women have biological capacity to bear children are best suited to expressive role. Tries to explain gender differences in crime through behaviour through socialisation,ultimately based on bio
18 of 51
2 feminist approaches to explain womens lower crime rates?
1.Control theory 2.Liberation thesis
19 of 51
Patriarchal control?
Heidensohn- Women commit fewer crimes because patriarchal society imposes greater control over them & reduces opportunities to offend. Operates at home, public spaces & work
20 of 51
Control at home?
Womens domestic role restricts their time & movements, reducing opportunities to offend. Women who try to reject domestic role find partners try to impose it through domestic violence
21 of 51
Dobash & Dobash?
Show many violent attacks result from mens dissatisfaction with wives' performance of domestic duties. Excise control through financial power by denying women funds for leisure. Daughters less likely to be allowed out late, Develop bedroom culture.
22 of 51
Control in public?
Women controlled by threat/fear of male violence against them EG sexual violence. EG Islington crime survey found 54% of women avoided going out after dark for fear of being victim, only 14% men
23 of 51
Heidensohn on control in public?
Sensationalist media reporting of **** adds to womens fear. Controlled by fear of being defined as not respectable. Dress, make up, demeanour etc can gain reputation. May avoid going to pub alone - sites of criminal behaviour -for fear of being loose
24 of 51
Control at work?
Controlled by male supervisors & managers. Subordinate position reduces opportunities to engage in major criminal activity at work. EG Glass ceiling prevents women from rising to senior positions with great opportunity to commit fraud
25 of 51
General overview of Heidensohn?
Patriarchal restrictions on womens lives mean they have fewer opportunities for crime. Also recognises patriarchy can push women into crime EG Women more likely to be poor & may turn to theft or prostitution for decent living standards
26 of 51
Class & gender roles?
Carlen - Unstructured interviews of 39 15-46 yr old w/c women convicted of range of crimes like theft, fraud, violence, drugs etc. 20 in prison or youth custody. Some m/c offenders, most convicted serious criminals were w/c
27 of 51
Hirschi's control theory?
Used by Carlen to explain female crime. Argues humans act rationally & are controlled by being offered a 'deal', people will turn to crime if they dont believe the rewards will be forthcoming
28 of 51
2 types of rewards/deals?
1.Class deal-women who work will be offered material rewards, with decent standard of living & leisure opportunities 2.Gender deal-patriarchal ideology promises women material & emotional rewards from family life by conforming to domestic gender role
29 of 51
Class deal?
Women had failed to find legit way of earning decent living & felt powerless/oppressed/victims of justice. 32 had always been poor. Some gained qualifications in jail but didnt help to gain work. Many had problems/humiliation claiming benefits
30 of 51
Gender deal?
Most women either not had opportunity to make deal or saw few rewards. Some were abused physically/sexually by dads or partners. Over 1/2 had ben in care, brealing bonds with family & friends. Those leaving/escaping care got homeless/unemployed/poor
31 of 51
Overview of Carlen?
For these women, poverty & being brought up in care/oppressive family life were 2 main causes of criminality. Being criminalised & jailed made class deal even less available to them & made crime even more attractive
32 of 51
Evaluation of Heidensohn & Carlen?
Heidensohn shows many patriarchal controls that prevent women from deviating. Carlen shows how failure of patriarchal society to deliver promised 'deals' to some women removes controls preventing offending
33 of 51
Criticisms of Heidensohn & Carlen?
Both see womens behaviour as determined by external forces like patriarchal controls or class & gender deals. Underplays importance of free will & choice in offending. Carlens sample small & unrepresentative consisting largely of w/c
34 of 51
Liberation thesis?
Adler-As women become liberated, crimes more frequent & serious as mens. Changes in structure of society caused changes in womens offending behaviour. Patriarchal controls/discrimination lessened, opportunities in education/work more equal =more oppo
35 of 51
3 bits of evidence to support increase in white collar crimes?
1.Overall rate of female offending gone up from 1in7 to 1in6 2.Adler-Pattern of female crime shifted, rising levels in armed robbery 3.Growth of 'girl gangs' - denscombes study
36 of 51
2 Criticisms of liberation thesis?
1.Female crime began rising long before liberation movement 2.Most female criminals are w/c, group least influenced by liberation
37 of 51
2 more criticisms of liberation thesis?
1.Chesney-Lind found evidence of women branching to male offences like drugs but usually due to link with prostitution, unliberated 2.Little evidence that illegitimate opportunity structure of crime has opened up to women
38 of 51
Cain on why men commit crime?
'Men as males have not been the subject of the criminological gaze.' Until recently criminologists havent asked what it is about being male that leads men to offend
39 of 51
Messerschmidt on masculinity & crime?
Argues masculinity is social construct or 'accomplishment' & men have to constantly work at constructing. Because of this they have more resources. Hegemonic masculinity is dominant masculinity, prestigious
40 of 51
Messerschmidt on subordinated masculinity?
Include gay men, no desire to accomplish hegemonic masculinity, as well as l/c & ethnic minority men, lacking resources
41 of 51
White middle class youths & crime?
Have to subordinate in order to achieve m/c status, leading to accommodating masculinity in school. Outside, masculinity takes oppositional form through drinking & vandalism
42 of 51
White working class youths & crime?
Less chance of educational success. So masculinity is oppositional in & out of school. Constructed around sexist attitudes, being tough & opposing teacher authority = lads by Willis
43 of 51
Black lower working class youths & crimes?
Few expectations of reasonable job & may use gang membership & violence to express masculinity, or serious property crime to achieve material success
44 of 51
3 criticisms of Messerschmidt?
1.Is masculinity an explanation of male crime, or just a description of male offenders? 2.Doesnt explain why not all men use crime to accomplish masculinity 3.Over works concept of masculinity to explain virtually all male crimes, from joy riding
45 of 51
Winlow - Postmodernity, masculinity & crime?
Study of bouncers in Sunderland, deindustrialised & unemployed. Working here provided young men with money & opportunity for illegal ventures in drugs etc, aswell as masculinity through use of violence
46 of 51
Winlows link to Cloward & Ohlin?
Draws on distinction between conflict/criminal subcultures. Modern society always been violent conflict subculture in Sunderland, 'hard men' earned status through violence. Absence of professional criminal subculture meant little opportunity to commi
47 of 51
Body capital?
Postmodern conditions, organised professional criminal subcultures emerged as result of new illegit business opportunities in night economy. To maintain rep & employment, men must use their body capital. Men must use their body capital. EG Bouncers
48 of 51
Overview of Winlow?
Important as shows expression of masculinity changes with move from modern industrial to postmodern deindustrial society. Opens up new criminal opportunities for men who use violence to express masculinity by growth of organised criminal culture
49 of 51
Dobash & Dobash with interviews?
Investigated domestic violence with unstructured interviews. Enabled trust to establish rapport, resulting in more detailed & valid data. Suggested domestic violence was more widespread than indicated by police stats
50 of 51
Drawbacks of Dobash & Dobash's study?
Many victims may not wish to talk to strangers about abuse & may be difficult to obtain a representative sample to study. May also be difficult to find safe setting for interview
51 of 51
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Higher proportion of female than male offenders are convicted of property offences. Higher no of males than female offenders convicted of violence or sex offences
Back
1 stat of official statistics show among offenders?
Card 3
Front
Males more likely to be repeat offenders, have longer criminal careers & commit more serious crimes. EG Men 15 times more likely to be convicted of homicide
Back

Card 4
Front
1.Do women really commit fewer crimes or are figures invalid picture? 2.How can we explain why those women commit? 3.Why do males commit more crimes than females?
Back
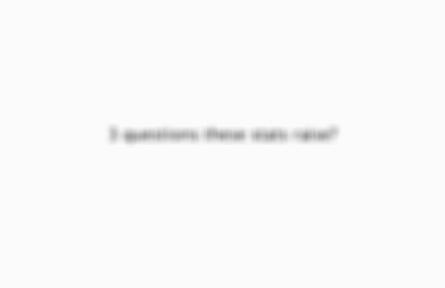
Card 5
Front
1.Female crimes like shoplifting less likely to be reported. Property crime less noticed than sexual/violent crimes by men 2.Even when women are detected or reported, less likely to be prosecuted
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- AQA Sociology A LEVEL »
- How do you revise A level Sociology? »
- Tips on improving Sociology A level grade and English Lit for aqa »
- Revision Struggles?! Join the 2023 TSR All Day Revision Thread! »
- How can I achieve A-A* in a-levels!!!!! »
- Advice about continuing an A- level subject in year 13 »
- 6 weeks till my A-levels!! - my GYG blog :)) »
- How to study sociology in one year and resit 2 a levels »
- Sociology Help Thread »
- A-level Sociology Study Group 2022-2023 »
Similar Sociology resources:
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made