Psychological Explanations of Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
0.0 / 5
- Created by: Emilyio
- Created on: 14-04-16 14:15
(A01) Cultural Ideals - Gregory et al 2000
The National Diet and Nutrition Survey of Young People found that 16% of a 15-18 year old girls in the UK were currently on a diet
1 of 28
(A01)Media Influences - Jones & Buckingham 2005
The media doesn't influence everyone in the same way, for example - those with low self esteem are more likely to compare themselves to idealised images portrayed in the media
2 of 28
(A01)Ethnicity - Grabe & Hyde 2006
Meta-Analysis of 96 studies. They found a difference between African-American and Caucasian and Hispanic females. African-Americans reported significantly less body dissatisfaction than the other two groups.
3 of 28
(A01)Ethnicity -Pollack 1995
In many non-Western cultures, like Fiji and the Caribbean, there are more positive attitudes towards large body sizes of which are associated with attractiveness, fertility and nurturance.
4 of 28
(A01)Peer Influences - Eisenberg et al 2005
US study found that dieting amongst friends significantly related to unhealthy weight controls, such as the use of diet pills or purging.
5 of 28
(A01)Peer Influences - Jones & Crawford 2006
found that overweight girls and underweight boys were most likely to be teased by their peers, suggesting that through teasing, peers serve to endforce gender-biased ideals
6 of 28
(A01)Peer Influences - Hilde Bruch 1973
claimed that AN origins are in early childhood. She distinguished between effective parents who respond approprately to their childs needs (feeding them when hungry) and ineffective parents who fail to reach their child's internal needs.
7 of 28
(A01)What did Bruch 1973 find?
She found that children of ineffective parents may grow up confused about their internal needs, becoming over reliant on their parents. Adolescence are often unable to feel in control of their bodies so they take excessive control by abnormal habits.
8 of 28
(A01)Perfectionism - Stober et al 2006
retrospectively evaluated personality traits in teenage boys and girls recieving treatment for AN. They found high levels of perfectionism in 73% of girls and 50% in boys.
9 of 28
(A01)Impulsiveness - Butler & Montgomery 2005
found that, when compared to a normal control group, AN patients responded rapidly (but inaccurately) to performance tasks, indicating impulsiveness.
10 of 28
(A02) Cultural Ideals - Hoek et al 1998
Examined records of 44,192 people admitted into hospital between 1987 -1989 in Curacao (non-Westernised Caribbean island). They found 6 cases of AN, a rate of which is claimed to be within the vrates if AN in Western countries.
11 of 28
(A02)Media Influences - Becker et al 1002
Adlescent Fijian girls following the introduction of the television in 1995. These girls showed s desire to lose weight and become more like Western TV characters.
12 of 28
(A02)Media Influences - Yamamiya et al 2005
This research showed that instructional intervention prior to media exposure idealised female images prevents the adverse effects of exposure.
13 of 28
(A02)Ethnicity - Cachelin & Regan 2006
tey found no difference in prevalence of disordered eating between African-American and Caucasian participants
14 of 28
(A02)Ethnicity - Roberts et al 2006
The stereotypical view that white populations have higher incidence of AN than black populations appear only to be true in older adolescents.
15 of 28
(A02)Peer influences - Shroff & Thompson 2006
found no correlation among friends on measures of disordered eating in an adolescent sample. Going against Jones & Crawford, it may be that gender differences only appear in older adolescents.
16 of 28
(A02)Peer influences - Lunde et al 2006
A study of 10 year olds found a +. correlation between body mass index (BMI) and teasing o both boys and girls. Supporting Jones and Carwford.
17 of 28
(A02) Bruch's Psychodynamic explanation - Steiner et al 1991
support bruch. Oservations of adolescents with AN have a tendency to define their children's physical needs rather than allowing their children to define their own.
18 of 28
(A02) Bruch's Psychodynamic explanation - Bruch 1973
She found that parents claimed to 'anticipate' their childrens needs rather than ever letting them 'feel' hungry.
19 of 28
(A02) Bruch's Psychodynamic explanation - Button & Warre 2001
Support Bruch's claim that people with AN rely excessively on the opinions of others, worry about how others view them and feel a lack of control over their lives.
20 of 28
What scale is used to measure personality, particularly perfectionism?
Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale
21 of 28
(A02) Perfectionism - Halmi et al 2000
322 women with a history of AN across Europe and US. Those who had a history of AN scored higher on the MP scale when compared to healthy women. The extent of perfectionism was directly linked with the severity.
22 of 28
(A02) Halmi et al 2000, extended
This stud also included those who had relatives who suffered from AN, and enlisted them into the study. It showed that perfectionism seemed to run into families, indicating that there's a possible genetic vulnerability to suffering from AN.
23 of 28
(A02) Perfectionism - Nilsson et al 1999
Longitudinal study shows importance of perfectionism in the DURATION of AN. Those with short illness duration had lower levels of perfectionism and those with high levels were more at risk of long illness duration
24 of 28
(A03) Methodological issues - bias sample
There is frequent reliance upon clinical populations, which represents a bias view on the relationship with personality and disordered eating.
25 of 28
(A03) Methodological issues - personality or...?
There may be confusion between personality traits and certain short-lived states that are caused by starvation
26 of 28
(A03)What ethical issues may be in place?
privacy, informed consent, confidentiality and the failure to protect against any potential harm.
27 of 28
(A03) Real-World Application
The fashion industry in France have signed a charter of good will. It's to stop eating disorders and promoting a certain body image among young women. The charter includes a pledge by fashion industries to use diverse body types, not just thin.
28 of 28
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
The media doesn't influence everyone in the same way, for example - those with low self esteem are more likely to compare themselves to idealised images portrayed in the media
Back
(A01)Media Influences - Jones & Buckingham 2005
Card 3
Front
Meta-Analysis of 96 studies. They found a difference between African-American and Caucasian and Hispanic females. African-Americans reported significantly less body dissatisfaction than the other two groups.
Back

Card 4
Front
In many non-Western cultures, like Fiji and the Caribbean, there are more positive attitudes towards large body sizes of which are associated with attractiveness, fertility and nurturance.
Back
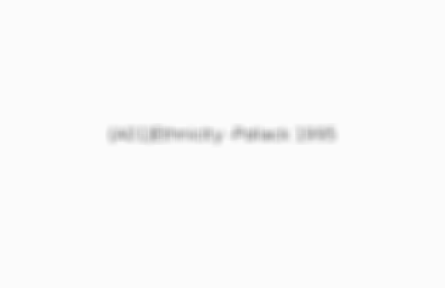
Card 5
Front
US study found that dieting amongst friends significantly related to unhealthy weight controls, such as the use of diet pills or purging.
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- TW: I don't want to feel full »
- Why do I have an eating disorder when I don't have all of the symptoms? »
- TW: Eating disorder thoughts getting worse »
- Has anyone ever not wanted to engage in anorexia treatment because of how their »
- Are doctors always right? »
- If you are sick, why wouldn't you want to get better? »
- Edexcel A-level Psychology Paper 2 (9PS0 02) - 25th May 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- Why do people find it concerning if someone's BMI is not in the healthy range? »
- How am I gaining weight »
- What kind of effects would it have if an underweight person has fizzy drink every day »
Similar Psychology resources:
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
1.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
5.0 / 5 based on 3 ratings
Comments
No comments have yet been made