Nature of Law Cases (case examples)
0.0 / 5
- Created by: debbie.t
- Created on: 17-04-16 00:14
R v M'Naughten (1843)
Killed the private secretary based on his delusions that the Tories were trying to persecute him and drove him to do this.
1 of 27
R v Windle (1952) - wrong
Though the defendant was suffering from a mental illness, his statement 'I suppose I'll hang for this' shows his awareness that his act was lawfully wrong
2 of 27
R v Clarke (1972) - defect of reason
Defendant placed items in her bag of which she'd forgotten (medical evidence showed she was a diabetic and suffered from depression), there was no cognitive fault identified therefore no defect of reason.
3 of 27
Professor Norrie in Crime, Reason and History - defect of reason
'Partial delusion obliquely...related to crime could inform its commission just as much as more total delusion about the nature and quality of the act'.
4 of 27
Bratty v A-G for Northern Ireland (1962) - disease of the mind
HELD : any mental disorder which manifested in a violent act, and was prone to recur, was a disease of the mind.
5 of 27
R v Burgess (1991) - disease of the mind
Sleepwalking, prompted by internal causes, classified a disease of the mind.
6 of 27
R v Hennessy (1989) - disease of the mind
The disease of the mind was classified by the internal factor of having an inherent physical defect causing low blood sugar levels/unawareness and not the lack of insulin injected in him
7 of 27
R v Stapleton (1952) - problems
The mere fact that the defendant had acknowledged his conduct was contrary to the law was inconclusive (he could have believed it would be approved by the reasonable man).
8 of 27
Professor Norrie in Crime, Reason and History - problems
'The conception of mental disease and its effects on conduct went much further that the law allowed'
9 of 27
Royal Commission on Capital Punishment - problems
The M'Naghten test has been described as 'entirely obselete and misleading on the conception of the nature of insanity'.
10 of 27
Statistic : 11.6% inmates are found not guilty by insanity between 1991-2001
But 1/5 of innmates serving time suffer from 4/5 of the major mental illnesses. This shows how restrictive the defence is
11 of 27
S2(1) of the Homicide Act 1957
Defendant must prove that they were 'suffering of the mind' which 'substantially impaired his mental responsibility for the killing'
12 of 27
Jeremy Dein and Jo Sidhu
Good Law survives the test of time if, and only if, it can demonstrate its continued relevance
13 of 27
R v Dudley and Stephens (1884)
Tom Dudley, Edwin Stephens, Edward Brookes and Richard Park set off for Australia on the 5th of May. They lost their yacht to the storm on the 20th July. Killed Richard Parker on the 24th/25th July and were rescued on the 29th July
14 of 27
Lord Coleridge - 'unnecessary and profitless act'
6 months imprisonment rather than the death penalty, there was the desirability for mercy, but didn't want to entertain the defence of necessity or vindicate their actions through acquitting the crime
15 of 27
Lord Coleridge - 'absolute divorce of law from morality would be fatal'
Lord Hale - 'hunger doesn't justify larceny' = a watershed of crimes
16 of 27
Re A Case (2001) - real necessity
Conjoined twins separated, in mary and jodies best interest and it was legal
17 of 27
Problems of the Dudley case - Lord Coleridge - we should be self sacrificial even though it is our duty to preserve our life (Natural Law)
Fails to distinguish between justification and excuse, sets superhuman standards, superficially dismiss authority
18 of 27
Legal reasoning and Practical ethics is peculiar
Utilitarianism, Human rights etc, runaway train , kill 1 or 5 ?
19 of 27
R v Morgan (1989)
Train driver passed a SPAD and killed 5 and injured 87 people, was charged with two accounts of negligent manslaughter on 2nd september 1990
20 of 27
Manslaughter by gross negligence (5 elements)
Andrew v DPP (1937) - 1. duty of care owed, 2.Doesn't behave like the reasonable man 3.Enough to be risk of death 4.Death is resulted 5.Negligence is so gross it is criminal
21 of 27
Donoghue v Stevenson (1932)
The case of negligence - decomposing snail
22 of 27
R v Adomako (1994)
Anaesthetist failed to realise that the patients tube wasn't connected during a surgery, and they died from cardiac arrest (gross negligence)
23 of 27
30 October 1990
Defendants appeal was successful and he only spent 1 out of his 4 months in prison on special considerations :no alcohol involved, he was injured himself, and history of previous SPAD's at the same junction, admission to responsibility, good record
24 of 27
R v Morgan (2007)
Lack of evidence made Morgan plead guilty. The engineer Mr bell introduced significant measures to stop the SPAD's in that junction
25 of 27
LJ Latham - Test for defendant
It tests whether there was an obvious or serious risk of death or injury and if it was caused by lack of thought to consequences or just merely taking risks
26 of 27
Health & Safety at Work Act 1974
Inquiry , Network Rail and Thames Trains who were found guilty under this act. It is now difficult to defend against this act, as defendants need to show that the risk is trivial to be acquitted of their charge
27 of 27
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Though the defendant was suffering from a mental illness, his statement 'I suppose I'll hang for this' shows his awareness that his act was lawfully wrong
Back
R v Windle (1952) - wrong
Card 3
Front
Defendant placed items in her bag of which she'd forgotten (medical evidence showed she was a diabetic and suffered from depression), there was no cognitive fault identified therefore no defect of reason.
Back
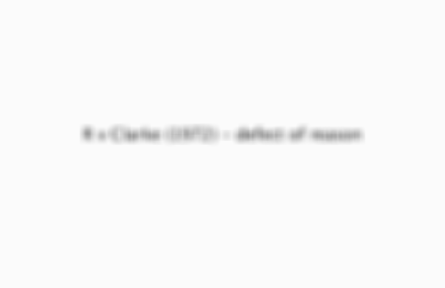
Card 4
Front
'Partial delusion obliquely...related to crime could inform its commission just as much as more total delusion about the nature and quality of the act'.
Back

Card 5
Front
HELD : any mental disorder which manifested in a violent act, and was prone to recur, was a disease of the mind.
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- What is the most boring law module? »
- Paralegal Work Experience »
- OCR A Level Law Paper 3 »
- What Gcse grades are likely to be acceptable for oxford »
- FM2, Elastics and springs question »
- Five SAS soldiers arrested for alleged war crimes in Syria »
- Eduqas A-level Religious Studies 1 (A120UA0-1-A120UF0-1) & 2 (A120U20-1) [Exam Chat] »
- Need help to find references »
- BA (Hons) - Law (Jurisprudence) at Oxford only allows choice of 2 optional papers? »
- [deleted] »
Similar Law resources:
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Comments
No comments have yet been made