Inheritance, variation and evolution
0.0 / 5
- Created by: vickieboadi
- Created on: 13-02-19 19:18
who is the father of genetics
Gregor Mendel
1 of 51
what is a phenotype
the physical appearance of the genes
2 of 51
what does a gene do
controls a characteristic
3 of 51
what is an allele
different forms of a gene
4 of 51
what is a genotype
the alleles for a gene
5 of 51
what does recessive mean
allele must be on both chromosomes
6 of 51
what does dominant mean
characteristics expressed even if present on one chromosome
7 of 51
how do you work out the probability of each phenotype that the offspring could inherit
using a punnet square
8 of 51
what does homozygous
two identical alleles for a characteristics
9 of 51
what does heterozygous
two different alleles for a characteristics
10 of 51
what is a clone
an organism or cell, or group of organisms or cells, produced asexually from one ancestor or stock, to which they are genetically identical
11 of 51
what are sections of DNA called
gene
12 of 51
what are protiens made out of
amino acids
13 of 51
what is a genome
it is the entire genetic make up of an organisms
14 of 51
when was the Human Genome project and what did it discover
in 2003 and it discovered that we have around 21000 genes in our body
15 of 51
what did the Human Genome Project help us to understand
it helps us to study migration patterns in humans, understand the cause for communicable diseases and searching for genes linked to inherited diseases
16 of 51
what is an inherited disorder
a genetic disorder passed on from parents
17 of 51
what type of allele cause Polydactyly
a dominant allele
18 of 51
how is the condition Polydactyly characterized
with extra finger and toes
19 of 51
what are the symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
mucus remains thick and sticky, less air can get into the lungs, breathing difficulties, trap germs and infections, patient cannot break down food does not put on weight easily
20 of 51
how is Cystic Fibrosis caused
it is caused by a mutation in protein cell membrane which controls the viscosity of mucus
21 of 51
what type of allele is Cystic Fibrosis
a recessive allele
22 of 51
what do you call a person who has inherited the recessive allele for a disease, but is not affected
they are a carrier
23 of 51
what id a mutation
a change in the base sequence; occur all the time, often in non-coding parts of the DNA
24 of 51
what are the three ways to screen for a genetic disorder
DNA analysis of IVF embryo, DNA analysis of cells from the placenta, DNA analysis of cells found in amniotic fluid
25 of 51
advantages of screening
money saved by not treating individuals with a disorder who have been aborted or the parents can financially prepare to care for the child, laws are in place to prevent screening for all 'undesirable' conditions, prevent poor quality of life
26 of 51
disadvantages of screening
screening is expensive, screening for 'designer traits' - problematic and prejudice, embryos have a right to life and cannot give consent
27 of 51
what is species
a group of organisms with similar characteristics that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
28 of 51
genotype only characteristics
gender and dimples
29 of 51
environmental only characteristics
accent and tan
30 of 51
what is natural selection
occurs when a mixed population of a species is faced with an environmental change, some versions of genes are advantageous and ensure the survival a reproduction of that individual so those genes are passed onto future generations and kept in the pop
31 of 51
what is selective breeding
is when humans artificially select the animals or plants they want to breed together so that the genes for a desired characteristic can remain in a population
32 of 51
what is genetic engineering
is a process which involves modifying the genome of an organism by introducing a gene from another organism to give a desired characteristcs
33 of 51
what is an advantage of GM crops
increased yield and no problems so far
34 of 51
what is a disadvantage for GM crops
transplanted genes get into other species which affects food chains
35 of 51
what is an advantage of GM animals
medicines can be mass produced and nutrients can be produced e.g. golden rice
36 of 51
advantage of genetically modified bacteria
as diabetes is on the rise more drug has to be made to meet the growing demands
37 of 51
disadvantage of GM bacteria
only works if the bacteria are capable of making human protein
38 of 51
who is the father of genetics
Gregor Mendel - fascinated with pea plants growing in a garden
39 of 51
3 conclusions by Gregor Mendel
characteristics are determines by hereditary units, these units are passed on unchanged from both parents, units can be dominant or recessive and if both are inherited together, the dominant unit is expressed
40 of 51
what is a clone
a individual produced asexually and is gentically identical to the parent
41 of 51
how to make clones
take cuttings from the plant or tissue cloning
42 of 51
how to make clone from cuttings
take cuttings from the plant - then put it into hormone rooting powder (auxin) - then it will grow into a mature - one plant from one cutting
43 of 51
how to make clones from tissue cultures
few cells scraped off tissue - put into a growth medium with auxin and nutrients - cells and tissue divide by mitosis and differentiate -they are put into composte and many clones are made - sterile conditons
44 of 51
how to make clones from embryo cloning
used by livestock breeders - animal given fertility hormones - fertilize eggs from the womb with sperm - then you wash out the embryo from womb - embryos split into individual cells - these then split by mitosis- then implanted into another cow
45 of 51
how to form clones from adult cell cloning
you take the prize animal - take any cell from their body - take out the nucleus from the cell and bin the cell - then you take and egg cell from a female animal - then you implant the nucleus with use of electricity - egg cell will start to divide
46 of 51
disadvantages of adult cell cloning
expensive and low success rate
47 of 51
disadvantage of cloning
no variation and if a new disease came no one has resistance
48 of 51
what does evolution mean
the change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time
49 of 51
what is speciation
the formation of new species
50 of 51
fiches practice exam questions
variation in the beak - being isolated on the islands changed the food that was available on each island - best adapted beak - -survival - reproduced passed on beak shape - many generations later if different birds cant produce fertile offspring .
51 of 51
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
what is a phenotype
Back
the physical appearance of the genes
Card 3
Front
what does a gene do
Back

Card 4
Front
what is an allele
Back
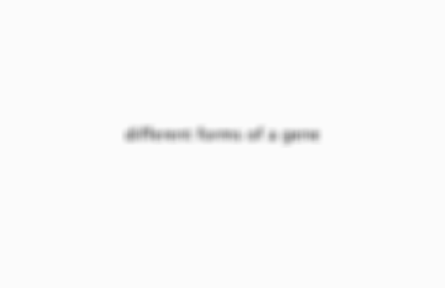
Card 5
Front
what is a genotype
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Biology Paper 2 AQA Triple Higher 2023 »
- 25 mark essay question »
- THIS IS FOR SCIENCE GCSE OKAY ( AQA), can practicals from paper 1 come up in paper 2 »
- Eduqas A-Level Biology Component 2 [16th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Computer Science NEA Project Idea »
- My GCSE journey!! 🦞 »
- OCR BIOLOGY PAPER 3 Predictions? »
- Does inheritance affect my student loan? »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 2 [16th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Student Finance and inheritance »
Similar Biology resources:
0.0 / 5
4.0 / 5 based on 3 ratings
3.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
3.5 / 5 based on 15 ratings
5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
2.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made