Chemistry
0.0 / 5
- Created by: Tierneyadair
- Created on: 19-04-17 15:12
Accurate
A measurement is considered accurate if it is judged to be close to the true value.
1 of 50
Acid
A sour substance which can attack metal, clothing or skin. The chemical opposite of an alkali. When dissolved in water, its solution has a pH number less than 7. Acids are proton (H+ ion) donors.
2 of 50
Alkali
A soluble base with a pH greater than 7. Makes OH- ions in water.
3 of 50
Alkali Metal
Elements in group 1 of the periodic table e.g. Lithium
4 of 50
Alloy
A mixture of metals (and sometimes non metals). E.g. brass = copper and zinc.
5 of 50
Aluminium
A low density corrosion-resistant metal used in many alloys, including those used in the aircraft industry.
6 of 50
Anomalous Results
Results that do not match the pattern seen in other data collected or are well outside the range of other repeat readings. They should be retested and if necessary discarded.
7 of 50
Atmosphere
The relatively thin layer of gases that surround planet Earth.
8 of 50
Atom
The smallest part of an element that can still be recognised as that element.
9 of 50
Atomic Number
The number of protons (which equals the number of electrons) in an atom. It is sometimes called proton number.
10 of 50
Biofuel
Fuel made from animal or plant products.
11 of 50
Calcium Carbonate
The main compound found in limestone. It is a white solid whose formula is CaCO3.
12 of 50
Carbon Monoxide
A toxic gas whose formula is CO.
13 of 50
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but remains chemically unchanged itself at the end of the reaction.
14 of 50
Chromatography
The process whereby small amounts of dissolved substances are separated by running a solvent along a material such as absorbent paper.
15 of 50
Compound
A substance made when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. E.g. water is made from hydrogen and oxygen (H2O).
16 of 50
Core
The centre of the Earth.
17 of 50
Covalent Bond(ing)
The attraction between 2 atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons.
18 of 50
Crust
The outer solid layer of the Earth
19 of 50
Data
Information, either qualitative of quantitative, that have been collected.
20 of 50
Distillation
Separation of a liquid from a mixture by evaporation followed by condensation
21 of 50
Electrolysis
The breakdown of a substance containing ions by electricity.
22 of 50
Electrolyte
A liquid, containing free moving ions, that is broken down by electricity in the process of electrolysis.
23 of 50
Electron
A tiny particle with a negative charge. Electrons orbit the nucleus in atoms or ions.
24 of 50
Element
A substance made up of only 1 type of atom. An element cannot be broken down chemically into any simpler substances.
25 of 50
Emulsifier
A substance which helps keep immiscible liquids (e.g. oil and water) mixed so they do not separate out into layers.
26 of 50
Ethene
An alkene with the formula C2H4.
27 of 50
Evidence
Data which has been shown to be valid.
28 of 50
Fair Test
A fair test is one in which only the independent variable that has been allowed to affect the dependent variable.
29 of 50
Flammable
Easily ignited and capable of burning readily.
30 of 50
Fractional Distillation
Separation of many substances in a mixture by heating, using the fact that they have different boiling points.
31 of 50
Gas
A state of matter with no definite shape or volume.
32 of 50
Global Warming
An increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere (especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes).
33 of 50
Hazard
A source of danger.
34 of 50
Hydrated
Crystalline and containing water molecules.
35 of 50
Hydration
The process of combining with water.
36 of 50
Hydrocarbon
An organic compound containing only carbon and hydrogen.
37 of 50
Hypothesis
A proposal intended to explain certain facts or observations.
38 of 50
Ion
A particle that is electrically charged (positive or negative).
39 of 50
Ionic Bond(ing)
The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
40 of 50
Limewater
A solution of calcium hydroxide, used to test for carbon dioxide.
41 of 50
Liquid
A substance in the fluid state of matter having no fixed shape but a fixed volume.
42 of 50
Mass Number
The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus.
43 of 50
Mixture
(chemistry) a substance consisting of two or more substances mixed together (not in fixed proportions and not with chemical bonding).
44 of 50
Mole
The amount of substance in the relative atomic or formula mass of a substance in grams
45 of 50
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
46 of 50
Mortar
a building material made by mixing lime, plaster, or cement with sand and water
47 of 50
Neutral
pH 7.
48 of 50
Nucleus
the positively charged dense centre of an atom.
49 of 50
Periodic Table
A table that shows the elements, their atomic number, symbol, and average atomic mass; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together.
50 of 50
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Acid
Back
A sour substance which can attack metal, clothing or skin. The chemical opposite of an alkali. When dissolved in water, its solution has a pH number less than 7. Acids are proton (H+ ion) donors.
Card 3
Front
Alkali
Back
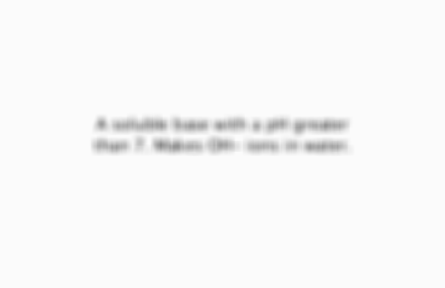
Card 4
Front
Alkali Metal
Back

Card 5
Front
Alloy
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Notes for edexcel international as level »
- A level chemistry »
- my question is about a level »
- IGCSE separate sciences and double award resources »
- Pharmacy at Reading (MPharm) »
- a level biology and chemustry »
- should i give up? »
- How can I get 7s/8s/9s in GCSEs with my Jan Mocks »
- Mastering SEO: A Guide to Selecting and Optimizing Keywords and Phrases »
- A-level chemistry revision, taking notes and exam practise help and paper 3 »
Similar Chemistry resources:
2.5 / 5 based on 3 ratings
3.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 3 ratings
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
4.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
1.0 / 5 based on 3 ratings
2.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Comments
No comments have yet been made