Blood Vessels, Blood Pressure & Cardiac Output
0.0 / 5
- Created by: ntygs19
- Created on: 11-03-20 16:30
What are the 5 types of blood vessels?
1. Arteries. 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins
1 of 41
Where do arteries carry blood?
AWAY from the heart to the body tissue.
2 of 41
What are the 3 layers of arterial walls? In what ordeR?
1. Endothelium (inner) 2. Smooth Muscle (middle) 3. Outer Layer
3 of 41
The structure of the middle layer of smooth muscle gives arteries their 2 main properties. What are they?
1. Elasticity 2. Contractivity
4 of 41
Elasticity and Contractivity allow for the diameter of the blood vessel lumen to change. What is a decrease in diameter called?What is an increase in diameter called?
1. Vasoconstriction 2. Vasodilation
5 of 41
What are Arterioles? Where do they carry blood?
Small arteries that deliver blood to capillaries.
6 of 41
What is a main function of arterioles?
Regulating blood flow through vasoconstriction and Vasodilation
7 of 41
What are capillaries? What type of vessels do they connect?
Microscopic blood vessels connecting arterioles and venules.
8 of 41
Why are they called 'EXCHANGE VESSELS'?
Because they permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and the body's cells.
9 of 41
What regulates blood flow through capillaries? Pre_ S_
Precapillary sphincters
10 of 41
Filtration and Reabsorption is facilitated by capillaries. What drives it?
Pressure
11 of 41
How does filtration occur?
Fluid with nutrients is pushed from capillaries into interstitial fluids
12 of 41
What type of pressure drives filtration?
Capillary blood pressure
13 of 41
How does reabsorption occur?
Fluid with wastes is pulled into capillaries from interstitial fluid
14 of 41
What type of pressure drives reabsorption?
Blood Colloid Osmotic Pressure
15 of 41
What is the term for the ability of tissue to automatically adjust its blood flow in order to match its metabolic demands?
Autoregulation
16 of 41
What is metabolic demand?
How much oxygen and nutrients the cells are using and needing.
17 of 41
If metabolic demand is HIGH, the capillary blood pressure will be (higher or lower?) than blood colloid osmotic pressure? Will more filtration or reabsorption occur?
If metabolic demand is high, the capillary blood pressure will be HIGHER than blood colloid osmotic pressure, meaning FILTRATION will occur (nutrient-filled fluid will filtrate from capillary to tissue cells)
18 of 41
If metabolic demand is LOW, the capillary blood pressure will be (higher or lower?) than blood colloid osmotic pressure? Will more filtration or reabsorption occur?
If metabolic demand is HIGH, the capillary blood pressure will be LOWER than blood colloid osmotic pressure, meaning REABSORPTION occurs as the tissue cells have more wastes to expel, and the low pressure in capillaries will pull the wastes out.
19 of 41
What are venules? What iare they structurally similar to?
similar in structure to arterioles - walls thinner near capillary and thicker towards the heart.
20 of 41
What type of oxygen does it transport? Where does it transport it?
DEOXYGENATED blood containing wastes towards the heart and lungs for reoxygenation
21 of 41
Whattype of oxygen do veins transport? Where to? What are they structurally similar to?
Tranports DEOXYGENATED blood to the heart and lungs. Structurally similar to Arteries.
22 of 41
What prevents backflow of blood in veins?
Venous valves
23 of 41
Venous Return is the movement of blood from the _ to the _ to the _ to the Atria of the Heart
Venous Return is the movement of blood from the CAPILLARIES to the VENULES to the VEINS to the Atria of the Heart
24 of 41
What is blood pressure?
The pressure exerted by circulating blood against the arterial wall
25 of 41
Arterial BP = __ x _ _
Arterial BP = CO (Cardaic Output) x PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE
26 of 41
What is Cardiac Output?
Volume of blood ejected per minute from the left ventricle into Aorta
27 of 41
Cardiac Output = _ _ x _ _
Cardiac Output = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
28 of 41
What is stroke volume?
The amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle with each contraction
29 of 41
What is Heart Rate?
Number of contractions per minute
30 of 41
What type of feedback system is BP regulation?
Negative feedback system
31 of 41
What are the sensory receptors involved in regulation of BP?
Baroreceptors
32 of 41
Where are baroreceptors located? 2 places
Carotid Sinus and Arch of Aorta
33 of 41
What do baroreceptors register? 2 things B_ P_ and C_ O_
Blood pressure and cardiac output
34 of 41
BP regulation is a negative feedback system. Baroreceptors send sensory information via G_ nerves to what part the __ Centre.
Via Glossopharyngeal Nerves to the CV Centre.
35 of 41
Where is the CV centre located?
Medulla Oblongata in the Brain Stem
36 of 41
If the CV centre registers BP or CO to be too high or too low, it send signals to the Spinal Cord which sends signals where?
Cardiac Accelerator nerves
37 of 41
What do the cardiac accelerator nerves trigger?
SA and AV nodes, and Ventricular Myocardium
38 of 41
What do SA and AV nodes, and Ventricular Myocardium do?
Increase or decrease blood pressure or flow.
39 of 41
Several interconnected feedback systems control blood pressure and flow by adjusting what 4 factors?
Heart rate, stroke volume, peripheral resistance and blood volume
40 of 41
CV Centre helps regulate heart rate and stroke volume, and controls the negative feedback system. It receieves input from what 3 main types of sensory receptor?
1. PROPRIOceptors, 2. BAROreceptors 3. CHEMOreceptors
41 of 41
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Where do arteries carry blood?
Back
AWAY from the heart to the body tissue.
Card 3
Front
What are the 3 layers of arterial walls? In what ordeR?
Back

Card 4
Front
The structure of the middle layer of smooth muscle gives arteries their 2 main properties. What are they?
Back

Card 5
Front
Elasticity and Contractivity allow for the diameter of the blood vessel lumen to change. What is a decrease in diameter called?What is an increase in diameter called?
Back
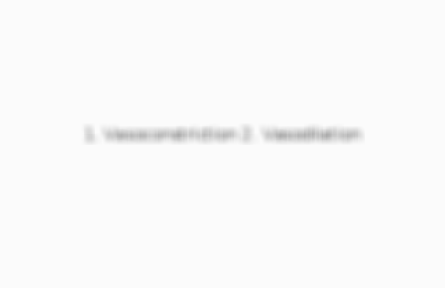
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Ocr biology as - i need to know everything on the heart »
- Calculating cardiac output from table »
- About cardiac physiology »
- A&P revision recommendations »
- dissertation topic »
- biology blood vessel a level »
- systolic pressure »
- Btec applied science unit 5 January 2024 »
- Pharmacy students at uni »
- Higher Biology 2023 »
Similar Nursing resources:
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
Comments
No comments have yet been made