Biology B1, B2, B3
3.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
- Created by: ikrolivia
- Created on: 01-12-15 17:22
What is blood pressure measured in?
Millimetres of mercury (mm Hg)
1 of 136
Systolic blood pressure is...
The pressure in arteries when heart contracts
2 of 136
Diastolic blood pressure is...
pressure in arteries when heart relaxes
3 of 136
What can blood pressure be affected by?
Age and lifestyle
4 of 136
How can you reduce high blood pressure?
Regular aerobic exercises
5 of 136
Factors that lead to high blood pressure:
excess weight / excess alcohol / stress / smoking / diet
6 of 136
Why is high blood pressure dangerous?
Blood vessels weaken and eventually burst. May lead to stroke or brain damage if in brain. In kidneys it may lead to kidney damage.
7 of 136
What does low blood pressure mean?
blood does not circulate efficiently so some body parts deprived of oxygen and glucose
8 of 136
Factors which increase risk of heart disease
high bp / smoking / too much salt / high fat diet
9 of 136
When are heart attacks more likely?
Narrowed coronary arteries & thrombosis
10 of 136
What does being healthy mean?
Free from infection
11 of 136
What does being fit mean?
Relates to how much physical activity you can do and how fast you recover
12 of 136
Cardiovascular efficiency
how well heart copes with exercise and how quickly it recovers after
13 of 136
A balanced diet must contain...
carbs and fats for energy, and protein for growth and repair
14 of 136
Where are these stored?
Carbs - in liver / fats - under skin / protein - not stored
15 of 136
Protein molecules are...
Long chains of AMINO ACIDS
16 of 136
What does a protein deficiency result in?
Kwashiorkor
17 of 136
First class proteins consist of what?
Meat and fish
18 of 136
Second class proteins are what?
Plant proteins
19 of 136
What can lead to a poor diet?
poor self-image / low self-esteem / desire for perfection
20 of 136
What can a poor diet result in?
Anorexia / bulimia / obesity
21 of 136
How can you reduce the likelihood of getting cancer?
Don't drink or smoke / eat healthily / avoid sunburn
22 of 136
What's the difference between benign and malignant?
Benign = in one place // malignant = grows in other parts of body
23 of 136
Defences against pathogens
skin = barrier / blood clots = stop microorganisms entering bloodstream / respiratory system = mucus membrane to trap / stomach = hydrochloric acid
24 of 136
How do white blood cells deal with pathogens? (2 ways)
engulfing and digesting / or make antibodies to attack
25 of 136
Immunisation on page 10 revision guide!!
Just do it...
26 of 136
How can a drug be tested?
computer models - predict how it'll affect cells / animals - see how it affects living organisms (IT'S CRUEL!!) / human tissue - see how it affects human cells
27 of 136
Blind trial
Volunteers don't know whether they've been given new drug or placebo
28 of 136
Double blind trial
Neither the volunteer nor doctor knows whether been given new drug or placebo
29 of 136
What's the purpose of your nervous system?
Allows you to react to surroundings & coordinate behaviour
30 of 136
What do humans have to detect environmental changes?
Light receptors in eyes, sound/balance receptors in ears, small receptors in nose, taste receptors, touch/pressure/pain/temperature receptors in skin
31 of 136
What are neurones?
Specially adapted cells that carry a nerve impulse.
32 of 136
Name the 3 types of neurones
Sensory, Motor, Relay
33 of 136
What do neurones have?
elongated shape, insulating sheath & dendrites
34 of 136
Synapses
Electrical impulse travels down neurone until reaches synapse / transmitter substance diffuses across synapse / transmitter binds with receptor molecules on next neurone causing electrical impulse on that neurone
35 of 136
What happens with reflex actions?
They bypass your brain to give fast, automatic responses to a stimulus
36 of 136
What harm do reflex actions protect you from?
knee jerk reaction, pupil reflex controls light entering eye, automatically withdrawing your hand from hot place
37 of 136
When receiving light from near object:
ciliary muscles contract, suspensory ligaments relax, lens is short and fat to refract light a lot
38 of 136
When receiving light from far object:
!! the opposite !! to !! a near !! object !!
39 of 136
Name 3 common eye defects
long sight, short sight & red-green colour blindness
40 of 136
Binocular vision
Eyes close together, eyes have limited field view, judge distance and speed accurately, found on HUMANS and PREDATORS
41 of 136
Monocular vision
eyes on side of head, wide field view, little overlap in fields of view, found on PREY
42 of 136
State the 5 drug categories
Stimulants (caffeine) / Depressants (alcohol) / Painkillers (paracetamol) / performance-enhancing (steroids) / hallucinagens (LSD)
43 of 136
Stimulants and depressants act on what?
Synapses of nervous system. Stimulants cause more neuro-transmitters to cross synapse. Speeds up nervous impulse
44 of 136
Depressants bind with..?
Receptor molecules in membrane of next neurone, blocking transmission of impulse
45 of 136
What's an addiction?
A state of physical or psychological need for a drug
46 of 136
Withdrawal symptoms?
psychological - cravings / physical - shaking
47 of 136
What's rehabilitation?
process by which an addict learns to live without drug
48 of 136
Short-term effects of alcohol:
lack of balance, slurred speech, poor judgement, vasodilation
49 of 136
Long-term effects of drinking alcohol
liver damage as it works so hard, brain damage due to dehydration
50 of 136
Which diseases can smoking lead to?
Cancers of the mouth, throat, oesophagus & lungs / Heart disease / bronchitis / emphysema
51 of 136
What is homeostasis?
Maintenance of a constant internal environment
52 of 136
At what temperature do enzymes work best at?
37 degrees celcius
53 of 136
What is vasodilation/vasoconstriction
Widening and narrowing of blood vessels in order to increase or reduce heat loss by radiation
54 of 136
What are hormones?
Chemical messages released by glands directly into bloodstream
55 of 136
Insulin
Released by PANCREAS, controls blood sugar levels.
56 of 136
Type I diabetes
Caused by pancreas failing to produce insulin
57 of 136
Type II diabetes
Cells do not respond to insulin
58 of 136
What does insulin do?
Helps regulate one's blood sugar levels by converting excess glucose in blood by glycogen in liver.
59 of 136
What are plant hormones?
CHEMICALS THAT CONTROL growth of shoots and roots / flowering and ripening of fruits
60 of 136
Where is auxin made?
Shoot tip of plant
61 of 136
What do plant hormones include?
rooting powder / fruit ripening hormone / selective weedkillers / control of dormancy
62 of 136
What do dominant alleles do?
Control development of a characteristic, even if present only one 1 chromosome in a pair
63 of 136
If both chromosomes in a pair contain the SAME allele of a gene, it's described as...
Homozygous
64 of 136
If the chromosomes in a pair contain DIFFERENT alleles, the person is...
Heterozygous
65 of 136
Inherited diseases
Some diseases are caused by a faulty gene & so can be inherited e.g. red-green colour blindness
66 of 136
What is natural classification?
Tries to use natural relationships between organisms. Considers more evidence,
67 of 136
What is natural classification?
Tries to use natural relationships between organisms. Considers more evidence.
68 of 136
What is artificial classification?
Based on observed characteristics & is designed for a practical purpose
69 of 136
What are the 4 arthropods?
Insect / crustacean / arachnid / myriapod
70 of 136
What are 'producers'?
They're in food chains - produce biomass during photosynthesis
71 of 136
What is the trophic level?
Position or stage that an organism occupies in food chain
72 of 136
What do pyramids of numbers show?
Number of organisms at each stage in food chain
73 of 136
What do pyramids of biomass show?
Dry mass of living material at each stage in food chain
74 of 136
look at page 28 revision guide for carbon cycle!
just do it.
75 of 136
and page 29 for nitrogen cycle!!
i'm serious.
76 of 136
what does interspecific mean?
individuals of DIFFERENT species compete for SAME resource
77 of 136
What does intraspecific mean?
where organisms have exact same needs
78 of 136
What's a mutualistic relationship?
2 organisms form a relationship from which both benefit e.g. buffalo + oxpecker
79 of 136
What are adaptations?
Special features of behaviours which make an organism particularly well-suited to its environment
80 of 136
Extremophiles are...
Biochemically adapted organisms to extreme conditions
81 of 136
specialists & generalists
Specialists = suited to certain habitats // Generalists = in thermal vents. possess anti-freeze proteins
82 of 136
Predator features
built for bursts of speed, camouflaged, hunting strategy, eyes at front
83 of 136
Prey features
built for speed, use mimicry, eyes on side, live in groups
84 of 136
Penguins have a...?
Heat exchange blood flow to colder regions.
85 of 136
Adaptations to hot and dry environments
body fat stored in hump, able to tolerate changes in body temp, drinks litres of water in 1 go, hair lined nostrils trap moisture in breath
86 of 136
How does cacti cope?
long roots to reach water, waxy cuticle to reduce water loss, having spines to reduces water loss and protect water stored
87 of 136
Lamarck's theory of evolution
1) organisms change during lifetime as struggle to live 2) changes passed onto offspring
88 of 136
page 35 revision guide for natural selection evolution
dooooo ittttt now!!
89 of 136
What's ozone?
Natural gas high up in earth's atmosphere. Prevents too many UV rays getting to Earth.
90 of 136
What is a carbon footprint?
amount of greenhouse gases one is responsible for emitting
91 of 136
how is acid rain caused?
burning fossil fuels which release acid gases like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
92 of 136
Greenhouse effect
1) heat energy from sun reflected from earth's surface back out to space 2) when reaches atmosphere, some rays pass but others trapped by co2 layer. Trapped rays keep Earth warmer than it would be so allow life to exist.
93 of 136
What's a sustainable resource?
One that can be used up and replaced so isn't exhausted
94 of 136
Endangered species
...are endangered of becoming extinct unless something is done to stop it
95 of 136
How can survival of plant or animal species be threatened?
climate change / hunting / habitat destruction / pollutants
96 of 136
How can endangered species be protected?
Educating people / protecting natural habitats / making seedbanks / banning hunting / artificial ecosystems
97 of 136
Conservation programmes
protect human food supply, stabilise ecosystems, protect indigenous people, studying/identifying plants
98 of 136
Main causes of whale deaths
entangled in fishing nets / pollutants / hunting / colliding with ships
99 of 136
How can money be made from whales?
Cosmetics, food, oil, tourist attractions
100 of 136
Captivity for whales
+ can be conserved / - loss of freedom
101 of 136
Cells have what 4 things?
Cytoplasm (where ribosomes are), nucleus, cell membrane, mitochondria - respiration take place here.
102 of 136
Functions of proteins include...
Structural, enzymes, carrier molecules, hormones
103 of 136
What are enzymes?
Proteins which act as biological catalysts. They speed up chemical reactions, and are highly specific. Each one will only speed up a particular reaction.
104 of 136
What stops the lock and key mechanism from working?
Extremes of pH and high temperatures
105 of 136
What are mutations?
Changes to genes - can be spontaneous but rate can be increased by environmental factors like radiation or chemicals
106 of 136
What do mutations do?
Change base sequence of DNA. This alters shape + function of protein.
107 of 136
Aerobic respiration is...
Release of energy from glucose in PRESENCE of oxygen. Takes place in ALL CELLS.
108 of 136
What is anaerobic respiration?
ABSENCE of oxygen. Happens when muscles are working so hard that lungs & circulatory system can't deliver enough oxygen to break down all glucose through aerobic. LACTIC ACID IS PRODUCED.
109 of 136
Advantages of being multicellular
larger, cell differentiation, complex
110 of 136
Fertilisation
Occurs during sexual reproduction. 2 gametes fuse together.
111 of 136
What does becoming multicellular require?
cell communication, supplying cells with nutrients, controlling exchanges with environment
112 of 136
Diploid and haploid
Diploid = 2 sets of matching chromosomes // Haploid = 1 set of chromosomes
113 of 136
What is mitosis needed for?
the replacement of worn-out cells / repair damaged tissue / asexual reproduction
114 of 136
What is meiosis?
Cell division which occurs in testes & ovaries
115 of 136
4 components of blood
platelets (clump together), plasma (transports substances), WBC (protect against disease), RBC (carry oxygen)
116 of 136
Oxyhaemoglobin equation
haemoglobin + oxygen --> oxyhaemoglobin
117 of 136
page 50 revision guide for the heart
LOOK AT THE PAGE!!
118 of 136
artery adaptations
thick wall made of elastic muscle fibres
119 of 136
vein adaptation
have lumen and valves to stop backflow of blood
120 of 136
capillary adaptation
thin permeable walls to allow substance exchange
121 of 136
page 51 of revision guide for method of seeing plant cell parts
Just do it!!!!!!!!
122 of 136
What are stem cells?
Undifferentiated animal cells which specialise & develop into different types of cells, tissue and organs
123 of 136
Embryonic stem cells...
...can become any type of body cell
124 of 136
What is selective breeding?
animals/plants with favourable characteristics are selected and crossbred to make offspring with desired characteristics
125 of 136
Examples of selective breeding
Quantity of milk, quality of milk, beef production
126 of 136
Advantage of genetic engineering
Allows organisms with new features to be made rapidly
127 of 136
Disadvantages of genetic engineering
Inserted genes may have unexpected harmful effects
128 of 136
page 54 revision guide for more on genetic engineering
:)
129 of 136
Advantages of commercial cloning of plants
genetically identical to parents so all characteristics known / possible to mass-produce
130 of 136
Disadvantages of commercial cloning of plants
disease would affect all plants / reduction in genetic variation reduces potential for further selective breeding
131 of 136
Uses of cloning
provide stem cells for medical purposes / mass production of animals w desirable characteristics / making animals genetically engineered to provide human products
132 of 136
Ethical dilemmas about cloning humans
very unreliable / limited life span / it's wrong in religious views
133 of 136
Benefits of cloning
all same characteristics / sex and timing can be controlled / top quality!
134 of 136
Risks of cloning:
reduces genetic variation / potential for disease wiping all out / welfare concerns
135 of 136
Animal organ donors
infection concerns / ethical issues concerning welfare and rights
136 of 136
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Systolic blood pressure is...
Back
The pressure in arteries when heart contracts
Card 3
Front
Diastolic blood pressure is...
Back

Card 4
Front
What can blood pressure be affected by?
Back
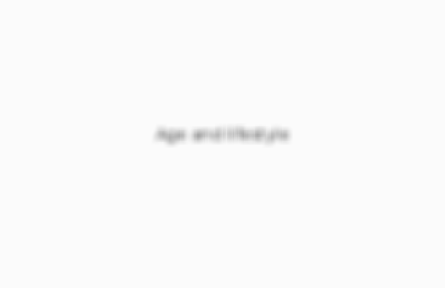
Card 5
Front
How can you reduce high blood pressure?
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- I am looking at my GCSE grades from 2017 »
- advice for revision »
- Dentistry application help 2024 »
- Edexcel GCSE HISTORY PAPER 2 (1HI0 2A-2W) - 4th JUNE [Exam Chat] »
- OCR S1 Combinations and Permutations Exam paper question. »
- Official: University of East Anglia (UEA) A100 2024 Entry »
- Physics Magnetic fields »
- Unable to do honours in bsc psychology at University of Glasgow »
- Official Dentistry 2023 Entry Applicants’ Thread »
- Official: University of East Anglia (UEA) A100 2023 Entry »
Similar Biology resources:
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
2.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
2.5 / 5 based on 3 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
1.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Comments
No comments have yet been made