Adaption and Selection
4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
- Created by: Florence Boyd
- Created on: 26-04-13 10:04
What is adaptation?
The process of natural selection where organisms adjust to suit the changing environment in which they live.
1 of 26
Diversity in organisms arises from changes to its DNA. In what two ways does this occur?
1. Changing the quantity or structure of the DNA of an organism - mutation. 2. Recombining the excising DNA of two individuals - occurs during sexual reproduction.
2 of 26
What is the genetic information in bacteria?
As in other organisms, DNA.
3 of 26
What way do bacteria combine the DNA of two individuals?
Conjunction, not strictly sexual reproduction.
4 of 26
How do mutations in DNA result in different characteristics?
DNA bases added/ deleted/ replaced. Could lead to different amino acid - different amino acid sequence - different polypeptide = different protein. If protein is enzyme -disrupt metabolic pathway- production of proteins Proteins effect characteristic
5 of 26
What happens when conjunction occurs?
One bacterial cell transfers DNA to another bacterial cell.
6 of 26
Describe the stages of conjunction.
One cell produces projection that meets other cell and forms conjunction tube. Donor cell replicates a plasmid which is broken to make it linear before entering recipient cell through conjunction tube. Liner strand forms a circle in recipient cell.
7 of 26
What is the result of conjunction?
The cell acquires new characteristics from donor cell.
8 of 26
In conjunction, DNA from one species can be passed to another species. What is this called?
Horizontal gene transmission.
9 of 26
What is it called where genes are passed down from one generation of a species to the next generation of a the same species?
Vertical gene transmission.
10 of 26
What are antibiotics?
Substances produced by living organisms that can destroy or inhibit the growth of microorganisms.
11 of 26
How do antibiotics kill bacteria?
They inhibit the proper formation of cell walls.
12 of 26
In bacterial cells, water constantly enters by osmosis. This would normally cause the cell to burst - what would this process be called?
Osmotic lysis
13 of 26
How is osmotic lysis prevented in bacterial cells?
The wall that surrounds all bacterial cells is made of a tough material that doesn't stretch easily. As water enters the cell by osmosis, the contents expand and push against cell wall. Cell wall resists expansion and halts further entry of water.
14 of 26
How do certain antibiotics kill bacteria by preventing them from forming cell walls?
They inhibit the synthesis and assembly of important peptide cross-linkages in bacterial cell walls - weakens the walls, making them unable to withstand pressure so are unable to prevent water entering - osmotic lysis occurs, killing the bacterium.
15 of 26
What restriction is there to the antibiotic that uses the process of preventing the formation of cell walls? Name an antibiotic that works in this way.
They are only effective when bacteria are growing as it inhibits the formation of cell walls. Penicillin works this way.
16 of 26
A strain of bacteria developed resistance to penicillin through a random mutation. What did this mutation cause and how does it make the bacteria resistant?
The mutation resulted in certain bacteria being able to make a new protein which was an enzyme which broke down the antibiotic penicillin before it could kill the bacteria. The enzyme was named penicillinase.
17 of 26
Is it the presence of antibiotics that causes bacteria to mutate?
No, mutations occur randomly and are very rare.
18 of 26
How is antibiotic resistance passed from species to species?
By transfer of the DNA for resistance during conjunction.
19 of 26
Explain why antibiotic resistance is more likely to del elope as more antibiotics are used.
When antibiotics are used, they only kill the non-resistant bacteria. This reduces competition and makes it easier for the resistant bacteria to survive and so pass on the resistance to subsequent generations and to other species.
20 of 26
Why might a patient stop taking antibiotics prematurely?
Because the vast majority of the bacteria have been killed so the patients' symptoms may have subsided, making them think that they are better so they stop taking the antibiotic.
21 of 26
What is the danger of stopping a course of antibiotics prematurely?
The most resistant strains of bacteria are the ones that remain, these multiply and spread to others. There is therefore a selection pressure that leads to the development of strains of bacteria that do not respond to antibiotic.
22 of 26
How can strains of antibiotic resistant bacteria leads to multiple-antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria? How are they treated?
The strains interchange genes for resistance with other strains, by conjunction. A 'cocktail' of three or four antibiotics is used to ensure that at least one will be effective.
23 of 26
Why would patients with Tuberculosis be more likely to stop taking antibiotics prematurely than patients with some other disease?
The course of treatment is very long - 6 to 9 months.
24 of 26
MRSA is especially prevalent in hospital. What does this mean for the transmission and severity of the disease in hospital?
People in hospital tend to be older, sicker and weaker than the general population - more vulnerable to the infection. Many people live in close proximity and are examined by doctors and nurses - just touched other patients - perfect for transmission
25 of 26
Why are multiple-drug-resistant strains more likely to arise in hospital?
Many antibiotics are used in hospital - any mutant antibiotic-resistant strain of the bacterium has an advantage over non-mutant strains. With many different antibiotics being used, strains can more easily develop multiple resistant strains.
26 of 26
Other cards in this set
Card 2
Front
Diversity in organisms arises from changes to its DNA. In what two ways does this occur?
Back
1. Changing the quantity or structure of the DNA of an organism - mutation. 2. Recombining the excising DNA of two individuals - occurs during sexual reproduction.
Card 3
Front
What is the genetic information in bacteria?
Back
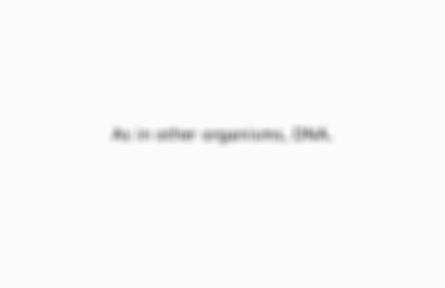
Card 4
Front
What way do bacteria combine the DNA of two individuals?
Back

Card 5
Front
How do mutations in DNA result in different characteristics?
Back

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Advanced Higher Biology Project Ideas »
- TSR Goes Green: Careers in the Environmental Sector »
- Biological sciences choosing universities »
- Competition of Organisms »
- What is UCL’s Earth Science BSC like? »
- EPQ help tribes / indigenous »
- A-level Biology Study Group 2023-2024 »
- Good Grades And Experience Are Worthless (Nature Jobs, Science, Humanities) »
- Geography NEA »
- Enviromental Science or Conservation and Ecology »
Similar Biology resources:
0.0 / 5
5.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
0.0 / 5
1.5 / 5 based on 2 ratings
Comments
No comments have yet been made