Introduction to Bacteria
- Created by: Ro-Po 17
- Created on: 21-07-18 12:43
Introduction to Bacteria
L.Os
- Describe the basic structure of bacteria
- Describe basic functions of different structures
- Describe and apply basic concepts of taxonomy
Bacteria are small, rate at which nutrients and waste enter and leave the cell = inversly proportional to cell size
Therefore:
- Higher growth rates
- Faster evolution
- Adapt and exploit new environments
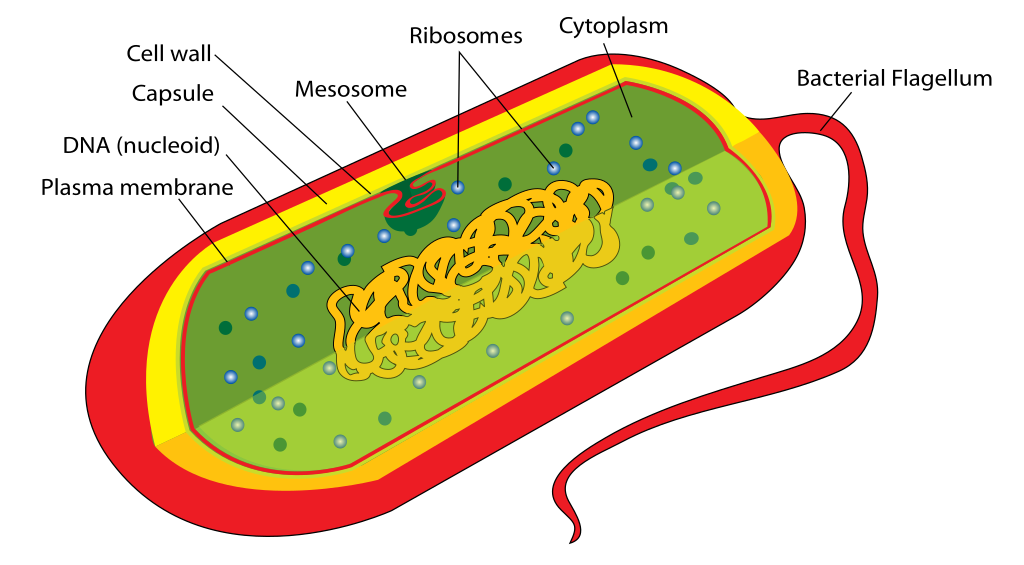
Basic Structure of Prokaryotic cell
- Cell wall = petidoglycan
+ flagella, pili etc. Provide ridgidity - Cell/Plasma membrane = phospholipid bilayer
Regulates passage in/out bacteria via pore and channels - Cytoplasm
DNA, RNA, Enzymes, Regulatory proteins, Protein synthesis machinery - Nuclear region
No true nucleus
Cell Wall
DIvides bacteria into 2 main groups
- Gram -- = doesn't tuen purple in crystal violet. then use safranin/carbol fuchsin = Pink stained
- Gram + = turn purple in crystal violet
CW = largely Peptidoglycan
- Polysaccharide backbone + NAG and NAM with cross-linked peptides (short-chain Animo Acids)
- These AAs provide rigid structure
- Enzymes involved in forming crosslinks = targets of antibiotics e.g penecillin

(Comparison in other resource)
Basically, Gram -- has an outer membrane whereas Gram+ don't.
Gram -- Outer Cell Membrane
= permeable lipid bilayer containing phospholipids and LPS (lipopolysaccharide)
Main role as protection, in…
Comments
No comments have yet been made