Exchange surfaces
- Created by: 5siult8gp;
- Created on: 01-04-17 20:03
Why we need a specialised exchange surface:
size (SA:V) : If they have large size it will take longer for oxygen to diffuse to the center of the cell. they have a smaller surface area to volume ratio so gas exchange is slower.
Metabolic activity: If the organism is more active there is a greater demand for oxygen and produce alot of carbon dioxide
SA: V
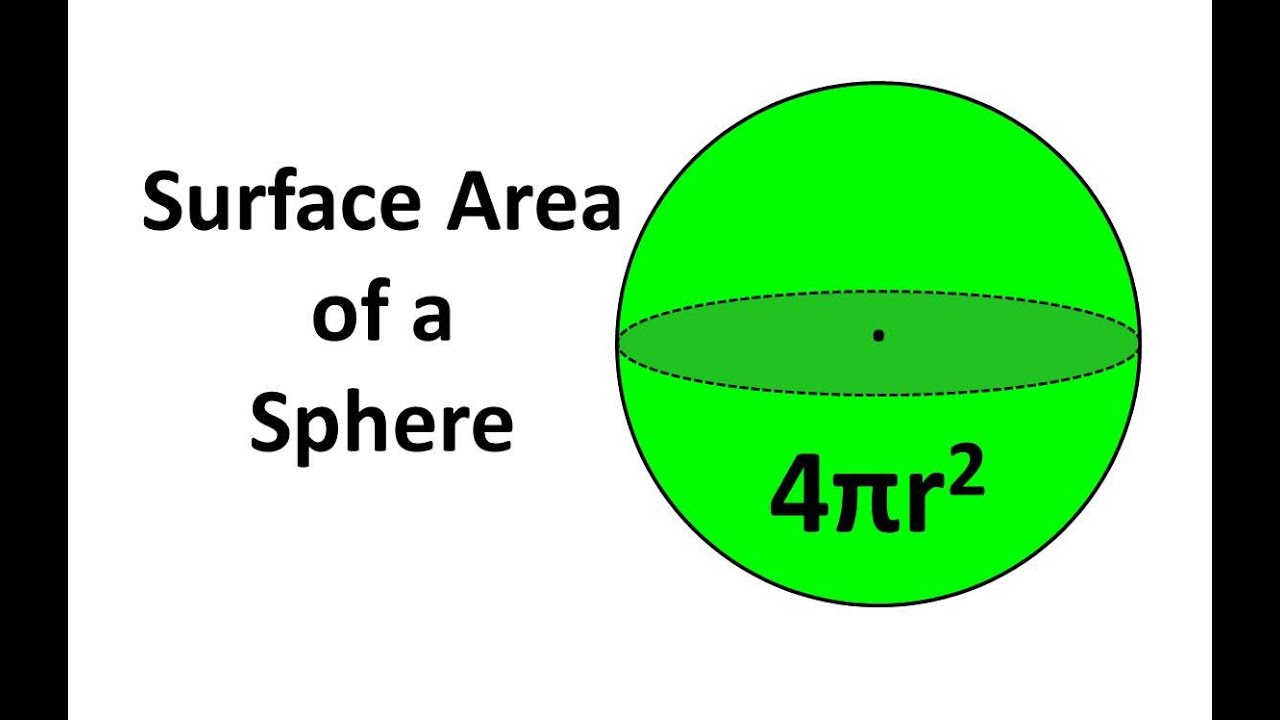

Radius: 1
SA: 12.6
V: 4.2
SA:V = 3:1
Features of efficent gas exhange:
Increased surface area
Thin layers- The distance that the substance have to diffuse is short, making the process (gas exchange) fast and efficent
Good blood supply- the steeper the concentration gradient, the faster the diffusion rate. Having a good blood supply ensures substances are constantly dilivered to and removed from the gas exchange.
Ventilation to maintain diffusion gradient-
The mammalian gaseous exchange:
Nasal caivity
Large surface area, Good blood supply which warms the air to body temperature
Has a hairy lining that contains mucus which traps dust and microorganisms and stops them from entering the lungs.
Moist surfaces, which increases the humidity of the air reducing evaporation
Trachea
Carries clean air from the nosal cavity to the lungs.
Wide tube- contains incomplete rings of strong flexible cartilage, which…
Comments
No comments have yet been made