B4.4 Biogenetics
- Created by: lottiehatherell
- Created on: 05-09-18 16:47
Subcellular structure of a plant cell:
cytopasm- where the reactions happen
ribosomes- ribosomes make protein. protein is needed for many cell functions such as repairing damage or directing chemical processes.
cell membrane- controls what goes in and out
cell wall- supports the cell
chloroplasts- where photosynthesis happens
mitochondria- where respiration happens
vacuole- stores cell sap - keeps the cell ridgid
nucleus- controls the cell - stores genetic information
Equations:
Parts of a plant:
stem = carrys nutrients and water from the roots + holds the plant up
roots = absorbs water and nutrients
leaves = photosynthesis
flower = attracts insects for reproduction and pollenation
Tissues in the cross section of a leaf:
lower epidermis- covers the lower surface and protects them
upper epidermis- covers the surface and protects them
palisade mesophyll- contains lots of chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis
spongy mesophyll- contains some chloroplasts, but also has big air spaces and a large surface area to make diffusion of gases easier
xylem and phloem- transport tissues, xylem carries water and dissolved mineral ions from roots up to the leaves, phloem carries dissolved food from leaves around the plants.
stomata-takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen guard cells open and close .
Hierachy of organisms:
cells --> tissues ---> organ ---> organ system --> organism
THE 5 USES OF GLUCOSE
1. converted into insoluble starch for storage
2.used to produce amino acids for protein synthesis
3. used to produce fats and oils for storage
4. used to produce cellulose to strengthen the cell wall
5. used for respiration for the plant
ADAPTIONS OF LEAVES
1. large surface area- more sunlight absorbed for photosynthesis
2. thin- chloroplasts are more accessible to the sun
3. veins (xylem and phloem)- a transport system to move food and water
4. lots of chloroplasts- lots of photosynthesis
5.air spaces within the leaf- to allow easy gas exchange
CHLOROPLAST
Cells in algae and plants are full of sub-cellular structures called chloroplasts, they contain a green substance called chlorophyll which makes the leaf green.
During photosynthesis the energy is transferred from the environment to the chloroplasts by light.
Photosynthesis:
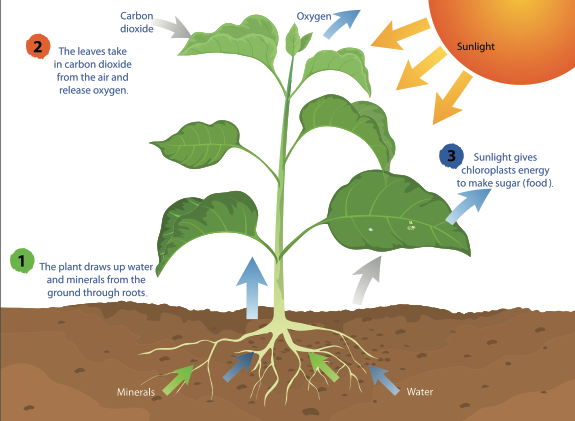
word equation: carbon dioxide + water --> glucose + oxygen
symbol equation: 6Co2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS:

USES OF OXYGEN
- oxygen is mainly released into the air which we then use for respiration
- each year plants produce approximately 368000000000 tonnes of oxygen.
Required Practical : Investigating the effect of a factor on the RATE of photosynthesis using an aquatic organism such as pondweed.
rate- how much reactant is used or how much product we get in a certain period of time
Conclusion- we found that the further away the light was from the pondweed,…
Comments
No comments have yet been made