B1 Cell Biology
- Created by: _livipaws_
- Created on: 12-05-18 15:41
1.1 What's in Cells?
1.1.1 Types of Cells:
All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells are the basic unit of living organisms. They provide structure and carry out certain functions. There are two different types of cell:
Eukaryotic Cells:
- Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists (single-celled organisms that don't fit other categories.)
- They are 10-100 micrometres in size.
- A eukaryote is an organism made up of eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Cells:
- They are 0.1-5.0 micrometres in size.
- A prokaryote is an organism made up of prokaryotic cells.
- Bacteria are prokaryotes.
Key Features of prokaryotic cells:
Lack of Nucleus:
- Prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus (where DNA is stored).
- Instead, their genetic material is stored in a single DNA loop in the cytoplasm (watery jelly that fills the cell).
Plasmids:
- Prokaryotic cells may have one or more small rings of DNA, which are called plasmids.
- These plasmids can replicate (have copies made) and move between cells so their genetic information can be shared.
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts:
- Prokaryotic cells do not contain mitochondria (where respiration takes place) or chloroplasts (where photosynthesis takes place).
1.1.2 Animal, Plant & Bacterial Cells:
Animal Cells:
Sub-cellular structures are things found in a cell. An animal cell contains the following sub-cellular structures:
Cell Membrane:
- The cell membrane separates the interior (inside) of the cell from the environment outside.
- It is selectively permeable (it can control substances moving in and out of the cell)
Nucleus:
- The nucleus is the control centre of the cell.
- It contains chromosomes (which contain the cell's genetic material)
Ribosomes:
- Ribosomes are responsible for synthesising (making) proteins.
Mitochondria:
- Mitochondria are the 'powerhouses' of the cell.
- Aerobic respiration (the process which uses sugar and oxygen to release energy) releases energy in the mitochondria.
Cytoplasm:
- Cytoplasm is a jelly-like fluid that fills the cell.
- It is where most of the cell's chemical reactions take place.
Permanent Vacuole:
- A permanent vacuole is a fluid-filled sac that stores water.
- It is enclosed in a membrane(a wall that substances can pass through).
- It can make up as much as 90% of a plant cell's volume.
Chloroplasts:
- Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which is needed for the process of photosynthesis.
Cell Wall:
- The cell wall surrounds the cell and is made of cellulose.
- The cell wall increases the structural strength of the cell.
Differentiation in Plants and Animal.
Cell differentiation can happen at different stages of development in plants and animals.
Plants:
- Many plant cells can differentiate throughout their lives.
- This means that plants are always able to create new tissue.
Animals:
- Most animal cells differentiate early on in their development.
- In mature animals, cells mostly divide (one cell splits to create two cells) to replace cells and repair tissues that are already present.
- New tissues are rarely created by cell differentiation.
Plant Cuttings Example:
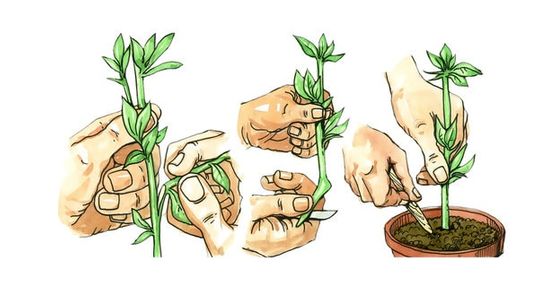
- If you cut a small section off a plant stem and plant it, come cells in the plant stem are able to differentiate to create new root tissues.
- This allows a whole new…
Comments
No comments have yet been made