CATALASE CATALYSES HYDROGEN PEROXIDE INTO WATER AND OXYGEN.
THE VOLUME OF OXYGEN RELEASED OVER A PERIOD OF TIME AT VARYING TEMPERATURES.
How the experiment is carried out:
- Boiling tubes set up containing same volume of H2O2.
- Rest of the apparatus set up as shown in diagram.
- Each boiling tube put in a water bath at different temperatures (10-50 degrees celsius at 10 degree intervals) along with other a seperate boiling tube containing the catalase. Allow to heat up to desired temperature.
- Use a pipette to add the same volume and concentration and catalase to each boiling tube and quickly add the bung and delivery tube.
- Use a stopwatch to record the volume of oxygen produced in a minute.
- Repeat the experiment at each temperature and form a mean volume of oxygen produced at each temperature.
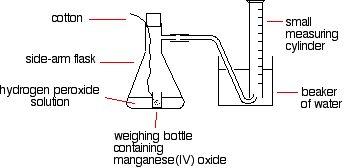 (Ignore reference to mang-oxide)
(Ignore reference to mang-oxide)
Comments
No comments have yet been made