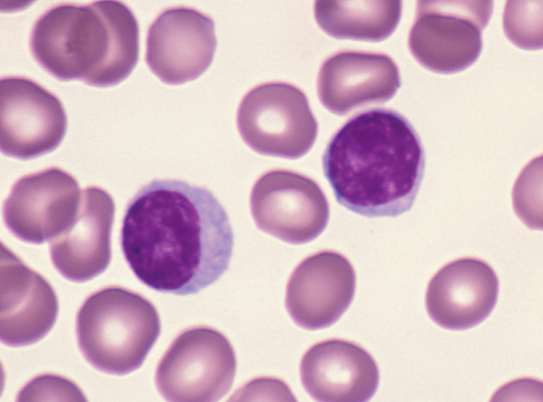
Lymphocytes have a large, darkly stained nucleus surrounded by a thin layer of clear cytoplasm. There are two kinds of lymphocytes B and T which look the same but have 2 different functions. Both are cells of the immune system. B lymphocytes produce antibodies. T lymphocytes have several functions, including cell destruction.
Comments
No comments have yet been made