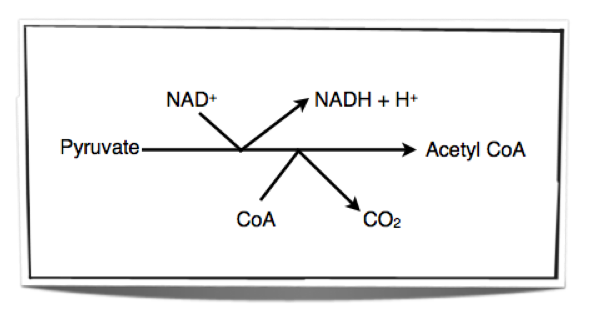
- Pyruvate produced from glycolysis are actively transported into the MATRIX of the mitochondia:
- Pyruvate oxidised by removing hydrogen- taken up by NAD to form NADH (reduced NAD)
- Pyruvate loses a carbon atom and CARBON DIOXIDE is formed.
- Acetyl group combines with COENZYME A to form ACETYLCOEZYME A.
2pyruvate+ 2NAD+ 2CoA→2acetyl CoA+ 2NADH+ 2CO2
Comments
No comments have yet been made